Featured Courses
More
Advanced
Tools That Help You Trade Better: Moving Averages, Trend Lines, and Indicators
There are no trading rules that are applicable to any scenario. These courses will help you establish your own trading strategy, then test it and improve on it in practice

Intermediate
Technical Analysis: A Useful Tool to Understand Trends in Futures Trading
Learn to interpret candlestick patterns and identify market trends. Build a technical analysis system to make informed trading decisions.

Beginner
Guide to Gate Dual Currency Products
This course provides a comprehensive introduction to Gate Dual Currency Products, which are non-principal protected financial products with floating income and also structured financial products based on options. Compared to traditional principal-protected investment products, Dual Currency Products carry certain risks but also offer higher potential returns. If leveraging the tool effectively, investors can truly earn profits regardless of price action.
Learn by Topic
Topics
Altcoins
Bitcoin
Blockchain
DeFi
Ethereum
Metaverse
NFT
Trading
Tutorial
Futures
Quant Trading
BRC-20
GameFi
DAO
Macro Trends
Wallets
Inscription
Technology
Meme
AI
SocialFi
DePin
StableCoin
Liquid Staking
Finance
RWA
Modular Blockchains
Zero-Knowledge Proof
Restaking
Crypto Tools
Airdrop
Gate Products
Security
Project Analysis
CryptoPulse
Research
TON Ecosystem
Layer 2
Solana
Payments
Mining
Hot Topics
Sui Ecosystem
Chain Abstraction
Options
Quick Reads
Video
Daily Report
Market Forecast
Trading Bots
VIP Weekly Industry Report
ETF Leveraged Tokens
Top Stories
XRP
Pi Network
VIP Daily Industry Report
In-Depth Research
Gate Ventures
Weekly Report
Investment News
Web3 For Beginners
Base
Gate Private Wealth Management
Platform Highlights
Brand Videos
Product Tutorial Videos
TradFi
Difficulty
Beginner
Intermediate
Advanced
Latest Courses
More
Intermediate
Introduction to Programmable Oracle Networks
Blockchains are powerful but limited by their isolation from the outside world. Smart contracts can only process on-chain data, yet most real-world applications, from finance and insurance to gaming and logistics, depend on external information. Programmable oracle networks solve this problem by securely delivering and processing off-chain data for use on-chain. They extend blockchain functionality, enabling decentralized applications to interact with markets, APIs, sensors, and even other blockchains in a trust-minimized way.

Intermediate
A New Paradigm for On-Chain Identity: DIDs, Verifiable Credentials, and the Reconstruction of Web3 Trust
In the digital world, "identity" has long been viewed as a login tool, with little serious discussion about the power structures and trust mechanisms behind it. With the rise of Web3, decentralized finance (DeFi), and on-chain governance, identity has begun to evolve beyond a mere key to access systems—it now carries functions of credit, permissions, and value distribution. This course starts from this transformation, guiding you to re-examine the evolving role of identity in the digital society, and how decentralized identity serves as the critical foundation for reconstructing trust in Web3.

Intermediate
DeFi 2026: The Reshaping of the Lending Ecosystem and Its Growth Drivers
As stablecoins continue to scale and on-chain clearing and risk management mechanisms mature, DeFi lending is transitioning from a high-risk experiment into sustainable financial infrastructure. Compared with early models that relied heavily on narratives and incentives, the new generation of DeFi lending focuses more on interest rate stability, risk priceability, and capital efficiency, increasingly becoming the preferred gateway for institutional capital entering on-chain finance. From a financial-structure perspective, this course explains why DeFi lending has re-emerged as a core growth engine and the critical role it plays in the era of institutionalization.
Latest Articles
More
Intermediate
The CRS tax for the cryptocurrency industry is coming; here are three practical tips for crypto enthusiasts.
Distilling "The end of the invisible era and compliance capability as the key to success" into a central takeaway offers critical guidance for high-net-worth individuals and Web3 professionals as they prepare for the impending tax compliance threshold.
2026-01-16 11:22:34

Intermediate
I Found XMR's Hidden Sell Pressure. Then I Killed It.
The article analyzes the Wagyu v2 solution—leveraging the Hyperliquid market maker for routing to achieve low-fee, exchange-level spreads. Within 48 hours of launch, millions of dollars in trading volume propelled XMR past $600, breaking the vicious cycle of "demand being unable to set prices."
2026-01-16 11:16:33

Intermediate
What did smart money see in BlackRock and Visa's high-stakes stablecoin gamble?
This article highlights four key trends: rapid expansion of RWA, compliance advancements under the GENIUS Act, Solana’s competitive edge in payments, and the bifurcation of payment and yield pathways. Stablecoin trading volume has soared to $46 trillion (with an adjusted figure of $9 trillion), underscoring its role as the precursor to global financial infrastructure. The analysis provides readers with clear insight into the strategic all-in approach taken by industry leaders.
2026-01-16 11:12:44
Latest Research
More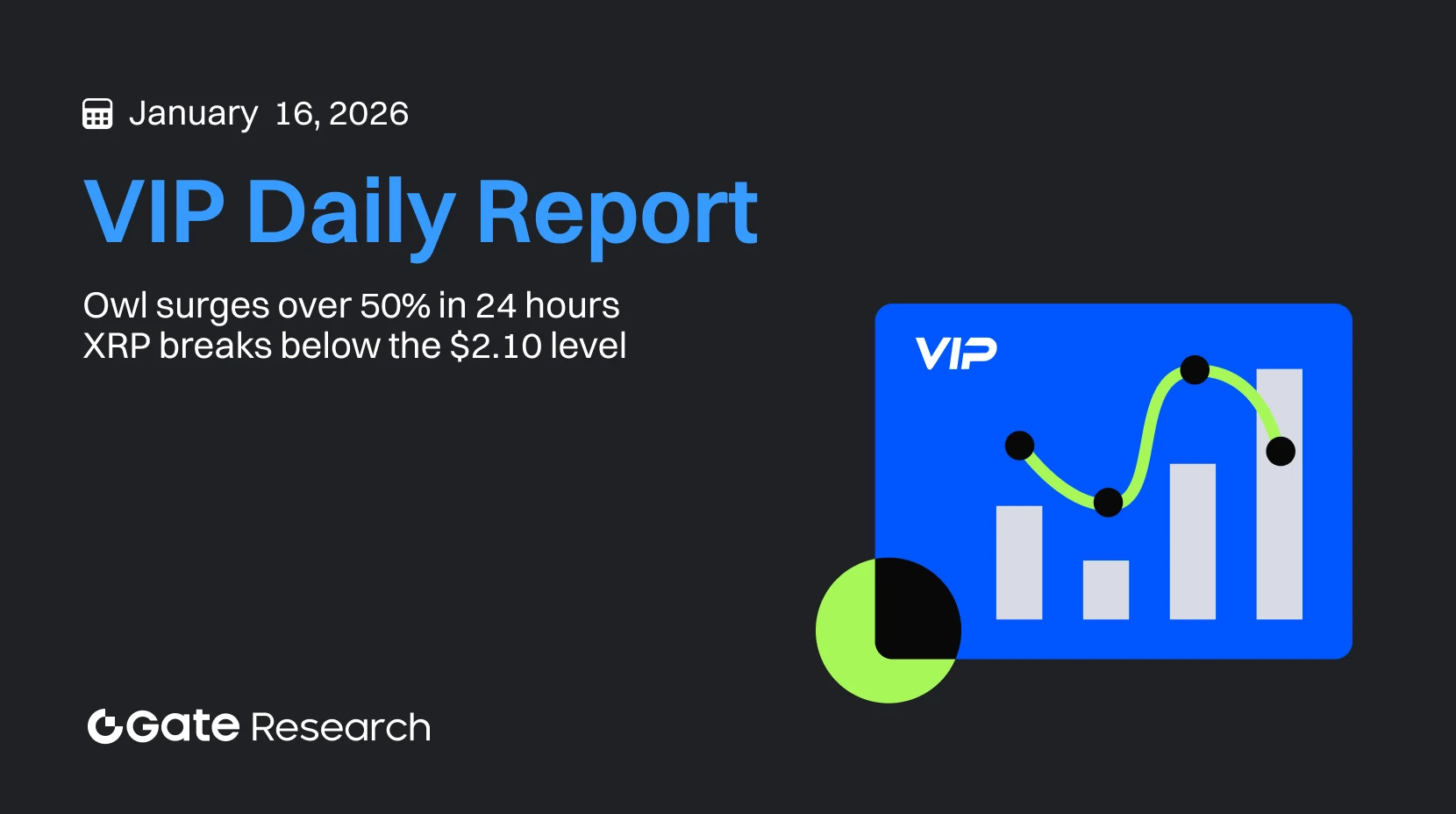
Advanced
 Gate Research: OWL Surges Over 50% In 24 Hours | XRP Breaks Below The $2.10 Level
Gate Research: OWL Surges Over 50% In 24 Hours | XRP Breaks Below The $2.10 Level
Gate Research Daily Report: On January 16, BTC entered a corrective consolidation phase after surging to around $97,900 and is now oscillating in the $95,000–$95,500 range; ETH moved into a high-level consolidation after hitting a peak near $3,403, with prices fluctuating narrowly between $3,280 and $3,320; GT shifted into range-bound consolidation after a prior rally to 10.83; and OWL led small-cap tokens with a +57.75% gain. XRP broke below the $2.10 level, with technical selling pressure dominating the short-term trend; BitMine said its $13 billion ETH holdings could generate over $400 million in annual revenue and expressed confidence that its investment in MrBeast could deliver a “10x” return; and Ripple injected $150 million into LMAX to push the RLUSD stablecoin into institutional trading infrastructure.
2026-01-16 08:32:11

Advanced
Gate Research: Ripple Injects $150M Into LMAX | BitMine’s ETH Could Earn $400M a Year
Gate Research Daily Report:On January 16, BTC entered a corrective consolidation phase after surging to around $97,900 and is now oscillating in the $95,000–$95,500 range; ETH moved into a high-level consolidation after hitting a peak near $3,403, with prices fluctuating narrowly between $3,280 and $3,320; GT shifted into range-bound consolidation after a prior rally to 10.83; and OWL led small-cap tokens with a +57.75% gain. XRP broke below the $2.10 level, with technical selling pressure dominating the short-term trend; BitMine said its $13 billion ETH holdings could generate over $400 million in annual revenue and expressed confidence that its investment in MrBeast could deliver a “10x” return; and Ripple injected $150 million into LMAX to push the RLUSD stablecoin into institutional trading infrastructure.
2026-01-16 08:07:38

Advanced
Gate 2025 Spot Listing Key Stats: Nearly 80% of Exclusive Projects Opened Up Within the First 30 Minutes, With a Median Gain of ~81%
Gate listed 447 new spot assets in 2025, and their post-listing performance showed clear market feedback across several key time points: about 54.8% of assets were up 24 hours after listing, and the average 24-hour gain among the winners was roughly 635%. In the early window, primary listings were more likely to post higher median returns (24-hour median: 12.56%, or 8.03% after trimming outliers), well above non-primary listings (24-hour median: 1.18%, or 0.86% after trimming). Gate-exclusive listings showed an even more concentrated early response: nearly 80% were up within the first 30 minutes, with a median gain of about 81%.
2026-01-16 04:53:44
Glossary
Moreapr
Annual Percentage Rate (APR) represents the yearly yield or cost as a simple interest rate, excluding the effects of compounding interest. You will commonly see the APR label on exchange savings products, DeFi lending platforms, and staking pages. Understanding APR helps you estimate returns based on the number of days held, compare different products, and determine whether compound interest or lock-up rules apply.
fomo
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) refers to the psychological phenomenon where individuals, upon witnessing others profit or seeing a sudden surge in market trends, become anxious about being left behind and rush to participate. This behavior is common in crypto trading, Initial Exchange Offerings (IEOs), NFT minting, and airdrop claims. FOMO can drive up trading volume and market volatility, while also amplifying the risk of losses. Understanding and managing FOMO is essential for beginners to avoid impulsive buying during price surges and panic selling during downturns.
nft
NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) are unique digital certificates recorded on the blockchain, designed to establish authenticity and ownership of digital items, in-game assets, membership privileges, or representations of real-world assets. NFTs can be bought, sold, and transferred, with all rules and transactions governed by smart contracts that execute automatically on-chain. They are commonly found on public blockchains such as Ethereum and across NFT marketplaces, serving use cases like collectibles, trading, and identity verification.
leverage
Leverage refers to the practice of using a small amount of personal capital as margin to amplify your available trading or investment funds. This allows you to take larger positions with limited initial capital. In the crypto market, leverage is commonly seen in perpetual contracts, leveraged tokens, and DeFi collateralized lending. It can enhance capital efficiency and improve hedging strategies, but also introduces risks such as forced liquidation, funding rates, and increased price volatility. Proper risk management and stop-loss mechanisms are essential when using leverage.


Your Gateway to Crypto World, Subscribe to Gate for a New Perspective