How Does Raydium Work? Explaining AMM and Order Book Liquidity Mechanisms
In the decentralized exchange (DEX) landscape, Raydium is one of the most influential projects in the Solana ecosystem. It not only offers AMM-based liquidity pools, but also extends liquidity to an on-chain order book, capturing the advantages of both traditional order books and AMMs. Raydium is designed to leverage Solana’s high performance and open order book ecosystem to improve trading efficiency, liquidity depth, and price discovery. This article takes a deep dive into how Raydium works and what makes it unique.
Overview of Raydium’s Core Trading Architecture
Raydium is a decentralized trading protocol built on the Solana blockchain, offering users lightning-fast swaps, liquidity provision, and yield farming. It combines the automated market maker (AMM) model with an on-chain central limit order book, allowing liquidity to flow not only within individual pools but also across a broader order book market. Raydium supports multiple pool types, including constant product pools (CPMM), concentrated liquidity pools (CLMM), and hybrid markets that interact directly with the order book.
What Is an AMM? How Raydium’s Liquidity Pools Work
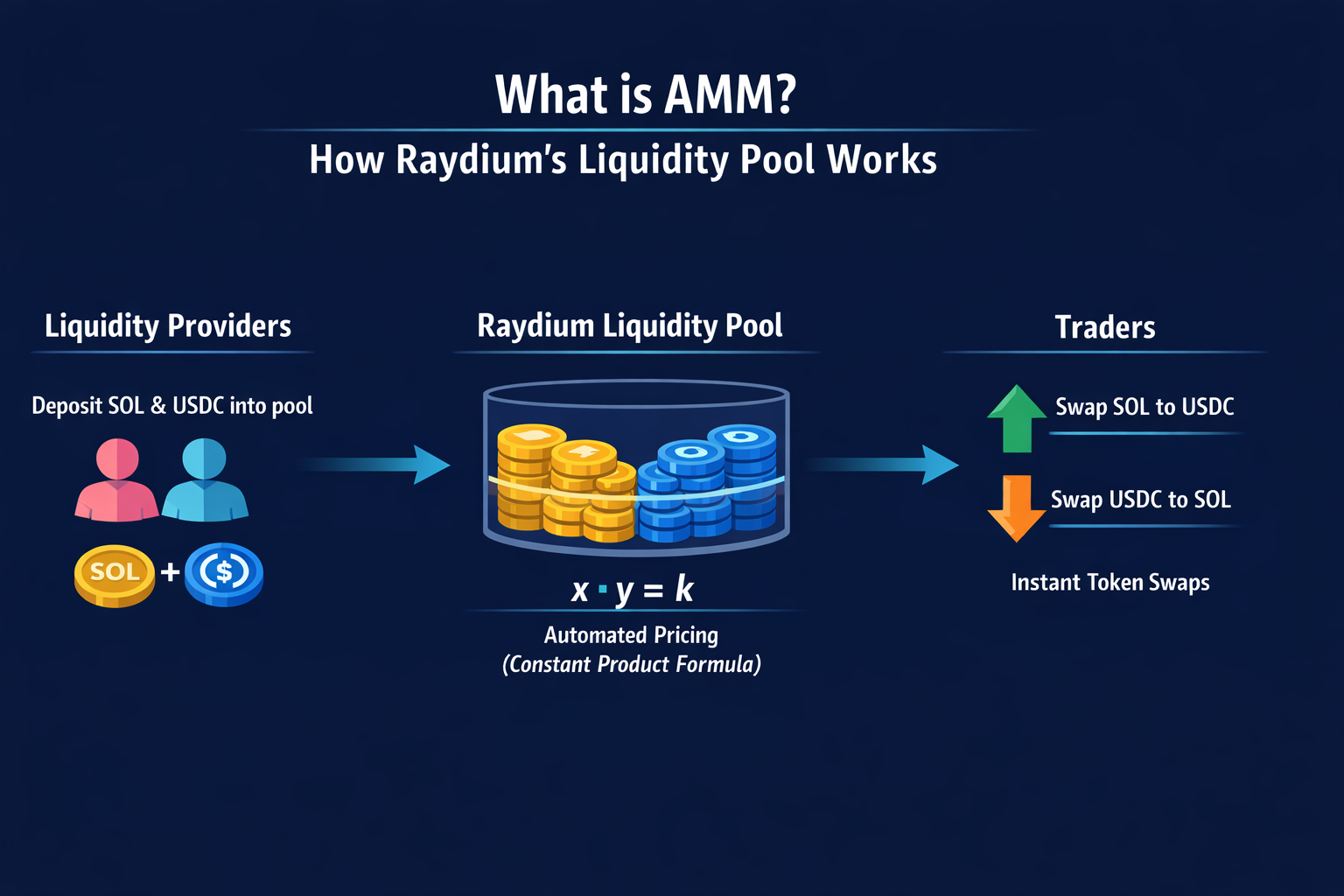
An AMM (Automated Market Maker) is an algorithmic pricing mechanism that allows users to deposit assets into liquidity pools at a set ratio, enabling others to trade without relying on traditional order matching. Prices are determined automatically through mathematical formulas, such as x * y = k, ensuring that trades can always be executed. Raydium’s liquidity pools follow this model. When users deposit a token pair, such as SOL and USDC, swaps are executed automatically through smart contracts.
Raydium offers two primary types of AMM pools:
- Constant Product Pools (CPMM), which use the classic x * y = k formula and are suitable for most trading pairs.
- Concentrated Liquidity Pools (CLMM), which allow liquidity providers to concentrate capital within specific price ranges, improving capital efficiency and fee earnings.
Liquidity providers’ asset ratios adjust automatically as trades occur, and they earn a share of the trading fees generated by the pool.
How Raydium Connects to On-Chain Order Book Liquidity on Solana
Unlike most traditional AMM projects, Raydium’s AMM can map its liquidity directly onto the on-chain order book ecosystem, currently centered around OpenBook, an open-source fork derived from Serum. This means Raydium’s liquidity does not exist solely within AMM pools. It is also exposed to the order book as limit orders, making it accessible to traders using order book-based interfaces.
At the core of this mechanism, Raydium’s AMM smart contracts allocate pool liquidity into a series of limit orders placed on the order book. This enables deep liquidity sharing between the AMM and the order book. As a result, both AMM traders and order book traders draw from the same underlying liquidity.
How User Trades Are Executed on Raydium
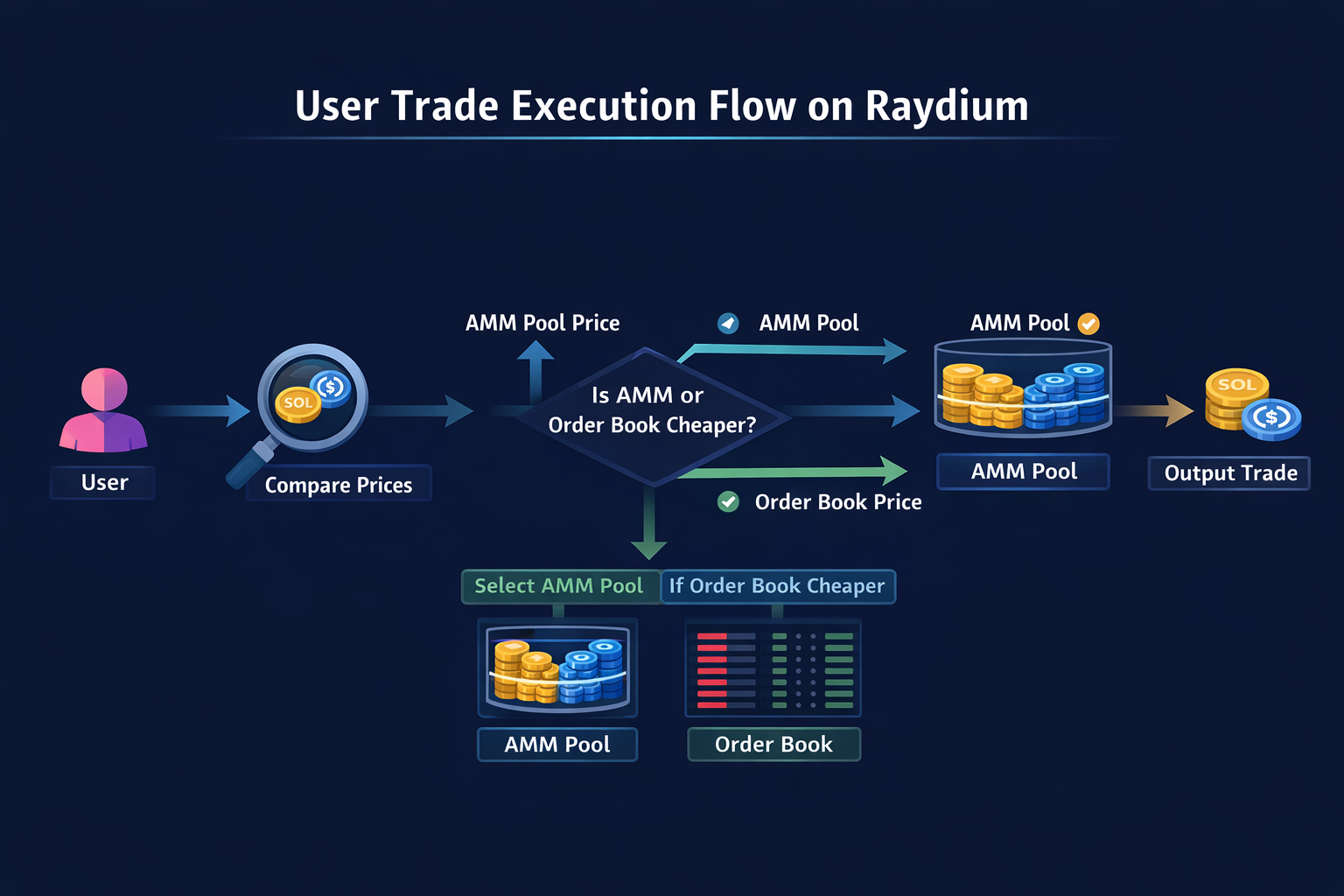
When a user executes a trade on Raydium, the system intelligently determines the optimal execution path:
- Price comparison: Raydium’s routing engine simultaneously checks prices in AMM pools and on the order book.
- Best path selection: If the AMM pool offers a better price, the trade is executed directly through the pool. If the order book offers a better price, the trade is filled via the order book.
- Trade execution: The swap is completed through the optimal route, with the appropriate fees applied.
This approach combines the permissionless execution of AMMs with the precision pricing of order books, resulting in deeper liquidity and slippage performance closer to that of centralized exchanges.
How Raydium Improves Trading Depth and Reduces Slippage
Liquidity depth and slippage are critical metrics for evaluating the trading experience on a DEX. In pure AMM models, large trades relative to pool size can cause significant price movement, leading to high slippage. By integrating an order book, Raydium allows AMM liquidity to be split into multiple limit orders distributed across different price levels. This significantly increases effective market depth and reduces the price impact of large trades.
In addition, Raydium’s routing engine aggregates liquidity across multiple pools and the order book during execution, dispersing trades across multiple liquidity sources to further minimize slippage.
How Raydium Differs from Traditional AMM DEXs
| Contrast Dimension | Raydium (Hybrid AMM + Order Book Model) | Traditional AMM DEX (Pure AMM Model) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Pricing Mechanism | AMM pricing combined with on-chain order book (CLOB) price discovery | Automatic pricing based on AMM mathematical formulas |
| Sources of Liquidity | Liquidity pools plus Solana on-chain order books, such as OpenBook | Liquidity sourced only from a single liquidity pool |
| Liquidity Visibility | Liquidity within the pool can be mapped to the order book and accessed by external trading interfaces | Liquidity exists only within the AMM pool |
| Trade Execution Method | Smart routing selects the best available price between the AMM and the order book | Trades are executed directly against the liquidity pool |
| Price Discovery Efficiency | Closer to order book markets, with prices driven by real buy and sell activity | Primarily depends on changes in asset ratios within the pool |
| Slippage for Large Trades | Trades are distributed through the order book, resulting in relatively lower slippage | Higher slippage is likely when pool depth is insufficient |
| Trading Depth Performance | Combines depth from both pools and the order book, resulting in greater overall depth | Fully dependent on the capital size of a single pool |
| Capital Utilization Efficiency | Liquidity can simultaneously support both AMM and order book trading | Capital is used only for AMM trading within the pool |
| Trading Experience | Closer to the experience of centralized exchanges (CEX) | More aligned with a native DeFi experience |
| System Complexity | More complex architecture with a high reliance on Solana’s performance | Relatively simple architecture that is easy to deploy |
Traditional AMM DEXs, such as early versions of Uniswap, rely solely on algorithmic pricing within individual liquidity pools. Liquidity can only be used within those pools. Raydium, by contrast, combines AMMs with an on-chain order book, allowing capital to serve both internal swaps and a broader flow of order book trading. This greatly improves overall efficiency and depth, especially for large trades, and delivers an experience closer to that of centralized exchanges.
Another key difference lies in order execution. Traditional AMMs price trades exclusively through formulas at the moment of execution, whereas Raydium’s smart routing dynamically selects the best available price across multiple sources in real time, maximizing user value.
How Liquidity Providers Earn Yield on Raydium
Liquidity providers (LPs) on Raydium can earn returns through several channels:
- Trading fees from AMM pools - where a fixed percentage of each trade is distributed to LPs.
- Order book maker fees - earned when Raydium’s AMM limit orders are filled on the order book.
- Incentive rewards - as some pools offer additional token rewards such as RAY or incentives provided by partner projects.
These multiple yield streams encourage more capital to enter Raydium’s pools and strengthen overall ecosystem liquidity.
Potential Future Upgrades to Raydium’s Architecture
Looking ahead, Raydium may continue to evolve in several directions:
- Deeper order book integration, as the OpenBook ecosystem matures and supports more markets and smarter order placement strategies.
- More advanced routing algorithms, improving execution efficiency across pools and order books.
- Cross-chain liquidity expansion, using bridges and interoperability tools to bring non-Solana assets into the ecosystem.
- Automated strategy tools for LPs, such as auto-rebalancing and strategy management, to reduce risk and improve returns.
Conclusion
Raydium represents an innovative DEX model that blends AMMs with on-chain order books. By injecting AMM liquidity into order book markets, it achieves deeper liquidity, lower slippage, and more efficient price discovery. Compared with traditional AMM-only DEXs, Raydium’s hybrid architecture is better suited to handling large trades and liquidity challenges, while offering diversified revenue streams for liquidity providers. As the Solana and OpenBook ecosystems continue to grow, Raydium’s design is likely to see further refinement and innovation.
Related Articles

What is Fartcoin? All You Need to Know About FARTCOIN

Gold Price Forecast for the Next Five Years: 2026–2030 Trend Outlook and Investment Implications, Could It Reach $6,000?

Crypto Future Profit Calculator: How to Calculate Your Potential Gains

2026 Silver Price Forecast: Bull Market Continuation or High-Level Pullback? In-Depth Analysis of Silver Candlestick Chart

Crypto Futures Calculator: Easily Estimate Your Profits & Risks


