The Straddle Strategy: A Guide to Consistent Income Generation
In practice, straddle strategies allow traders to capture volatility premiums when they anticipate increased price swings, or to earn steady time value when volatility is overestimated and prices consolidate. This approach offers a relatively stable and sustainable source of returns.
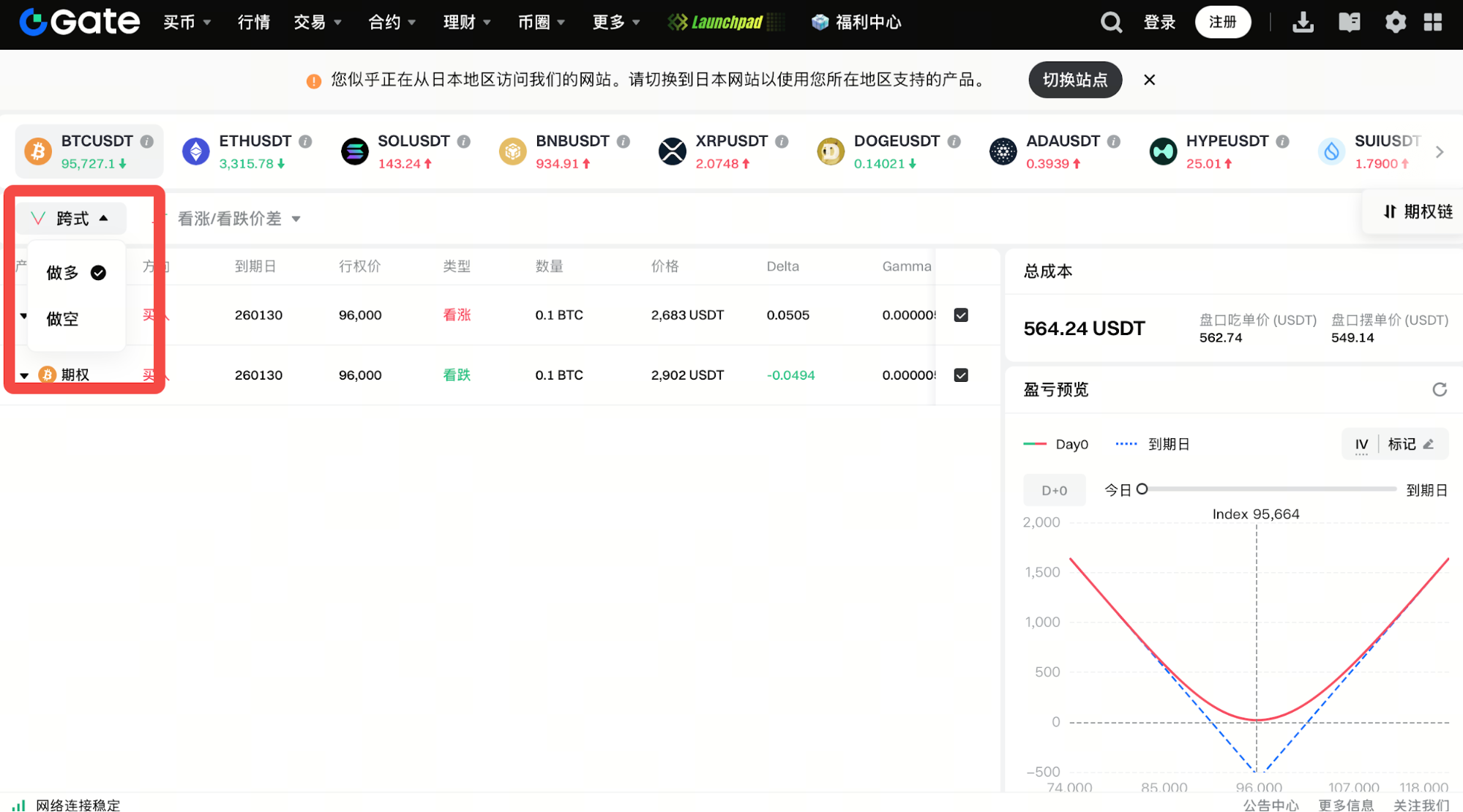
Gate Options now offers a combo strategy order feature that supports multiple options strategy combinations. Users can execute multi-leg strategies like straddles with a single click, helping them efficiently navigate range-bound markets and continuously earn premium income.
This feature also provides a comprehensive profit and loss preview for the entire strategy.
Straddle Option Strategy (Straddle)
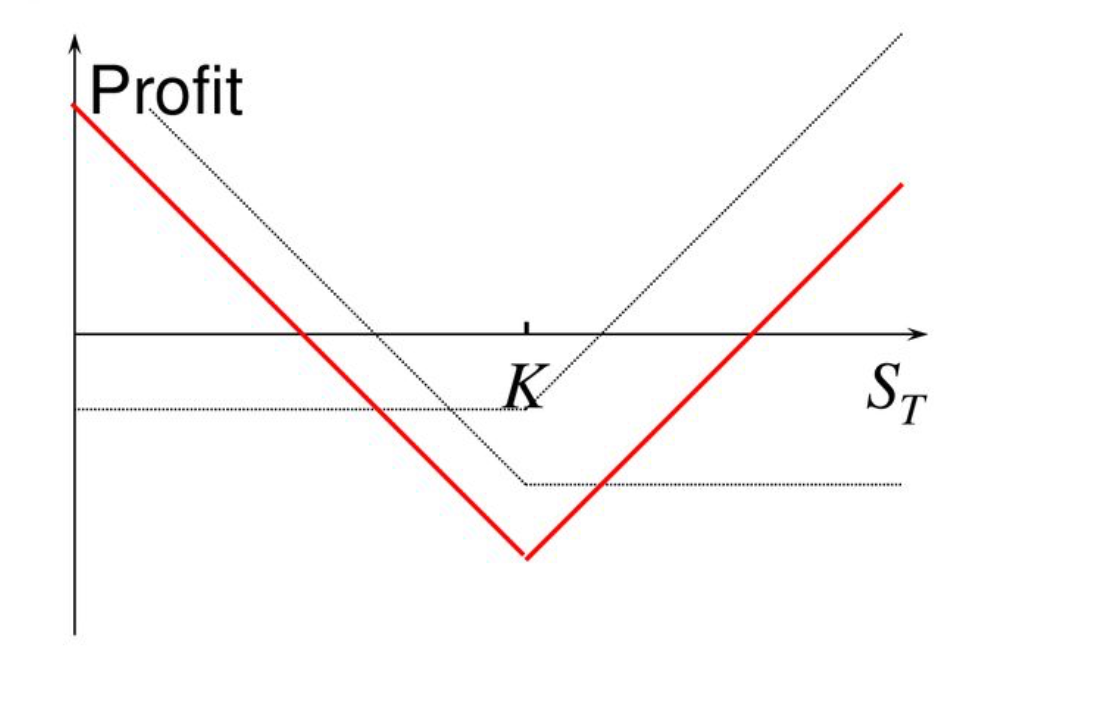
- Straddle Option Strategy (Straddle) involves buying both a call and a put option on the same underlying asset, with identical strike prices and expiration dates.
- Objective: To profit from significant moves in the underlying asset’s price, regardless of whether it rises or falls.
Strategy Features:
Bi-directional Profit: When the price moves sharply in either direction, profits from one option can offset losses from the other.
Applicable Scenarios:
- The straddle strategy is best suited for periods when substantial volatility is expected but the direction is uncertain. Typical examples include the lead-up to earnings reports, government announcements, or major events.
Strangle Combination (Strangle)
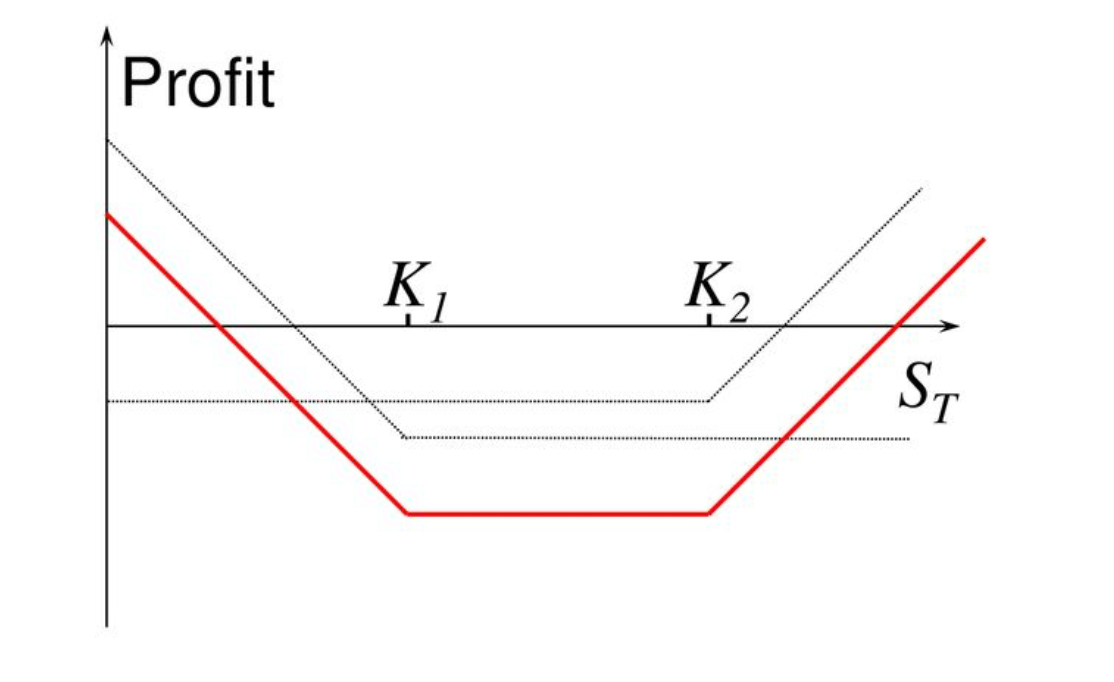
- The strangle combination (Strangle) is an options strategy used when significant volatility is expected in the underlying asset but the direction of movement is unclear. Similar to the straddle, the strangle uses different strike prices, which usually results in a lower total premium.
- The main objective is to profit from large price swings in the underlying asset, regardless of direction.
Difference from Straddle:
- Straddle: Buy a call and put option with the same strike price.
- Strangle: Buy a call and put option with different strike prices—typically set apart by a certain range—resulting in lower overall costs.
Applicable Scenarios:
- The strangle strategy is ideal when you expect significant volatility but cannot predict the direction.
- Examples include upcoming earnings releases, policy announcements, or major market events.
- The key advantage of this strategy is its lower premium cost. Compared to the straddle, it carries less risk but requires greater price movement to be profitable.
Short Strangle Strategy (Short Strangle)
Definition:
- The short strangle strategy involves selling both a call and a put option on the same underlying asset, but with different strike prices and the same expiration date.
- This approach is appropriate when the market is not expected to move significantly and the underlying asset’s price is likely to stay within a certain range.
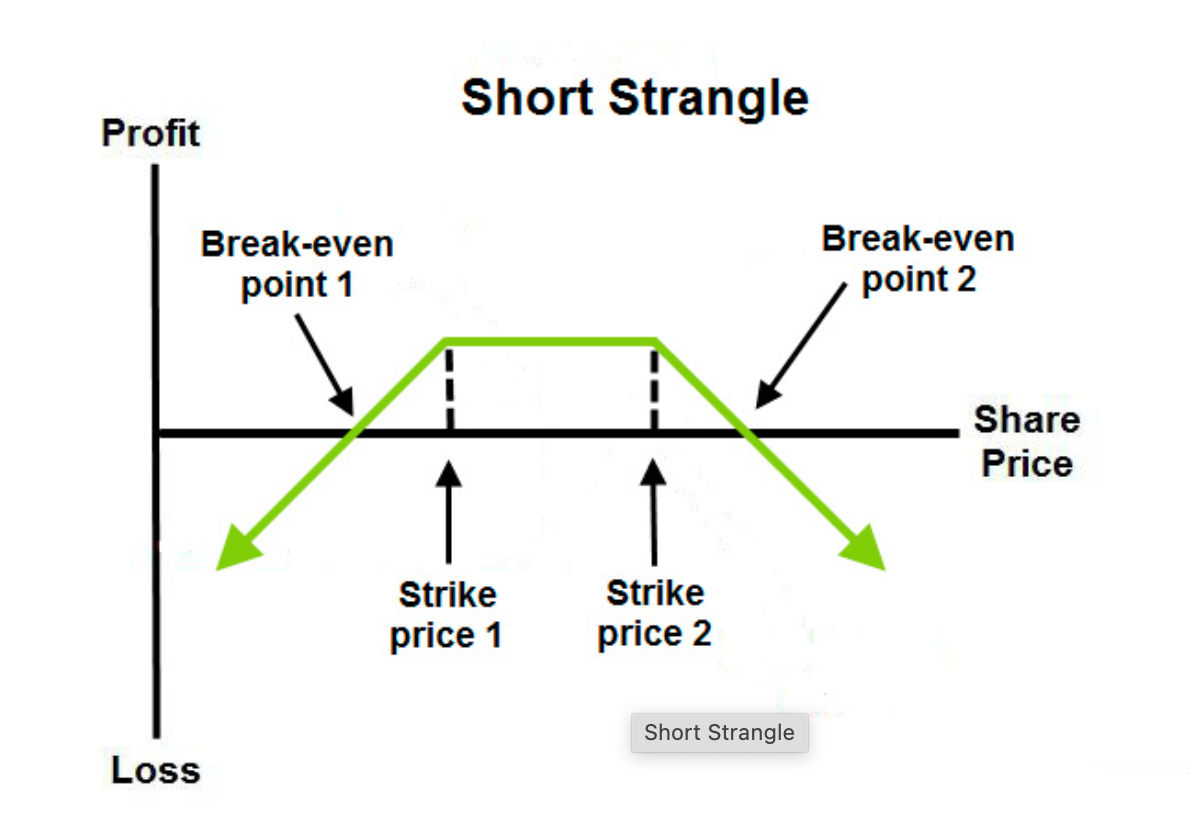
Objective:
- Earn premiums from selling both options, with the risk that large price movements could result in losses.
- If the price remains between the strike prices of the sold options, the seller retains all premium income.
Applicable Scenarios:
- The short strangle strategy is best used when the market is unlikely to experience significant volatility, such as when prices are expected to remain in a range or when upcoming events (like earnings releases or economic data) are not expected to trigger major moves.
- The greatest risk with this strategy is if the underlying asset’s price moves sharply outside the strike prices of the sold options.
Summary:
The short strangle strategy is suitable for stable market conditions, allowing traders to earn option premiums. However, sharp price movements can lead to substantial losses, so risk management is critical.
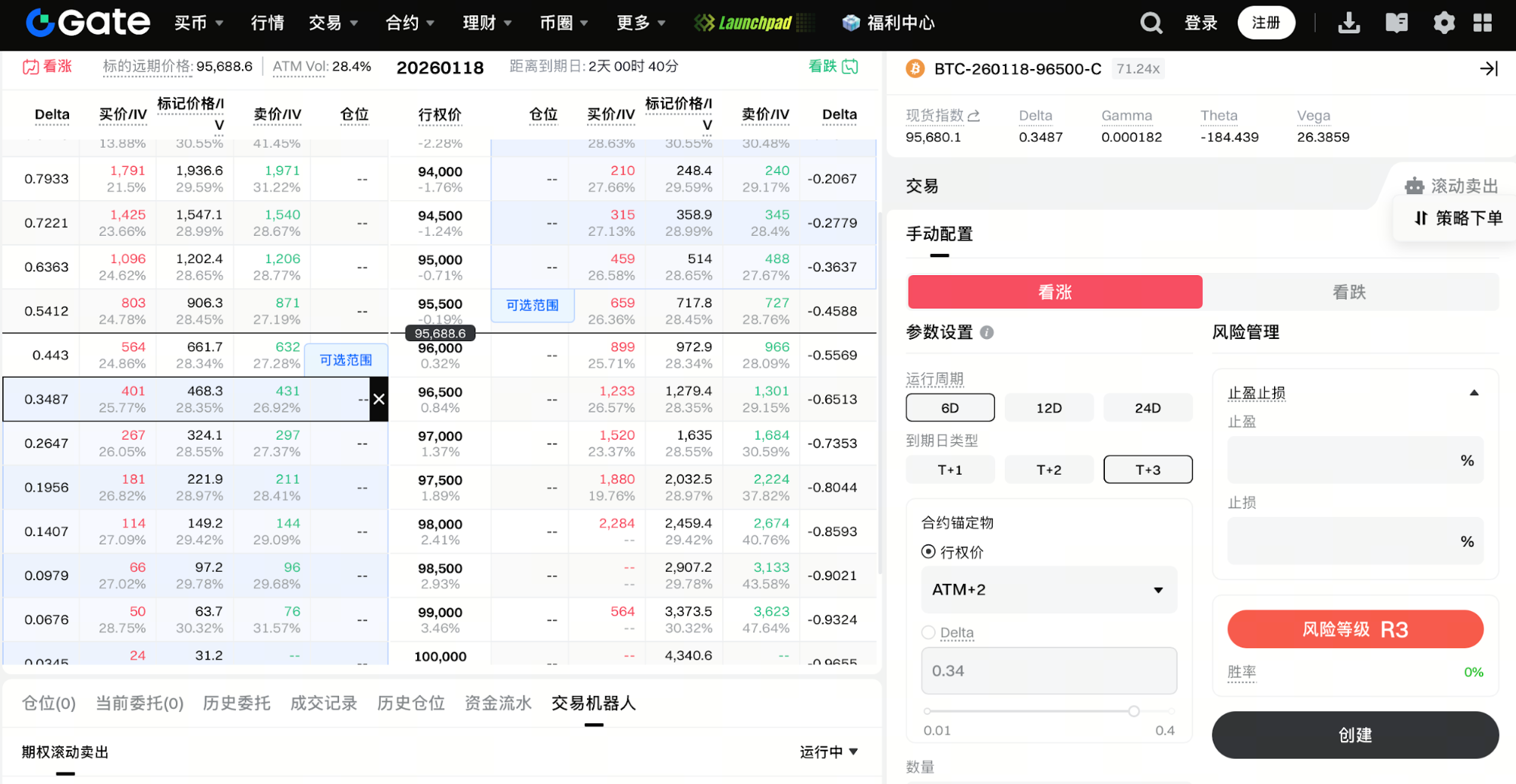
Executing the Short Strangle Strategy with the Rolling Short Options Tool
For range-bound or low-volatility markets, the short strangle is a widely used premium income strategy. Gate’s rolling short options tool helps users automate and streamline the execution of this approach, reducing manual effort and improving consistency.
With the rolling short options tool, users can set rules for strike selection (such as Delta or Strike), choose expiration cycles (T+1, T+2, T+3), specify the number of contracts to sell, and set take-profit or stop-loss conditions if desired. The system will automatically sell call and put options each cycle and seamlessly transition to the next period upon expiration, ensuring continuous execution of the short strangle strategy. The tool also offers transparent risk indicators, margin estimates, and detailed strategy explanations, empowering users to manage risk while earning consistent premium income. This is especially well-suited for traders seeking long-term participation in range-bound markets and those interested in strategy automation.
Related Articles

Boost Your Crypto Yield with the Covered Call Strategy

What is an Option?

What is Typus?
Crypto Options Trading, Explained

Building On-Chain Options and DOVs


