What Is Zama? A Comprehensive Guide to the Homomorphic Encryption–Powered Privacy Computing Platform
With the development of Web3, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing, the value of data continues to rise, but the risk of privacy leakage that comes with it has also become increasingly prominent. Whether it is public transactions on blockchains or centralized data processing in traditional cloud computing, both face the fundamental problem that “once data is used, it must be decrypted.”
Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE ) is regarded as a key technology to solve this challenge, and Zama is one of the representative platforms currently driving FHE from theory toward engineering and commercialization. This article will systematically interpret Zama’s technical foundation, product system, application scenarios, and future development direction.
What Is ZAMA?
Zama is a privacy computing platform centered on Fully Homomorphic Encryption ( FHE ), with the goal of completing computation and program execution without exposing any original data. In other words, Zama allows developers to perform operations on data that remains encrypted at all times, without exposing plaintext information at any stage.

Image source: Zama
Unlike traditional privacy solutions that rely on access control or Trusted Execution Environments ( TEE ), Zama adopts a purely cryptographic approach, and its security does not depend on hardware or centralized trust assumptions. This characteristic gives Zama unique advantages in scenarios such as blockchain, finance, identity verification, and privacy preserving machine learning.
Zama’s Mission and Development Path
Zama’s core mission is to make privacy computing a default capability, rather than an optional add on. The team believes that as long as data needs to be decrypted during computation, privacy issues cannot be fundamentally resolved.
In terms of its development path, Zama has chosen a relatively “slow but solid” route: first focusing on the engineering and performance optimization of FHE, then gradually building developer oriented toolchains and runtime environments, and finally extending into blockchain and decentralized application domains.
In recent years, as privacy compliance requirements have increased and Web3’s demand for “verifiable but opaque computation” has grown, Zama’s technical path has gradually attracted attention from mainstream capital and developer communities. Its progress in the practical application of FHE is regarded as an important industry milestone.
Analysis of Zama’s Technical Core, Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption is an encryption method that allows computations to be performed directly on encrypted data, while Fully Homomorphic Encryption ( FHE ) supports arbitrarily complex operations, including addition, multiplication, and logical operations.
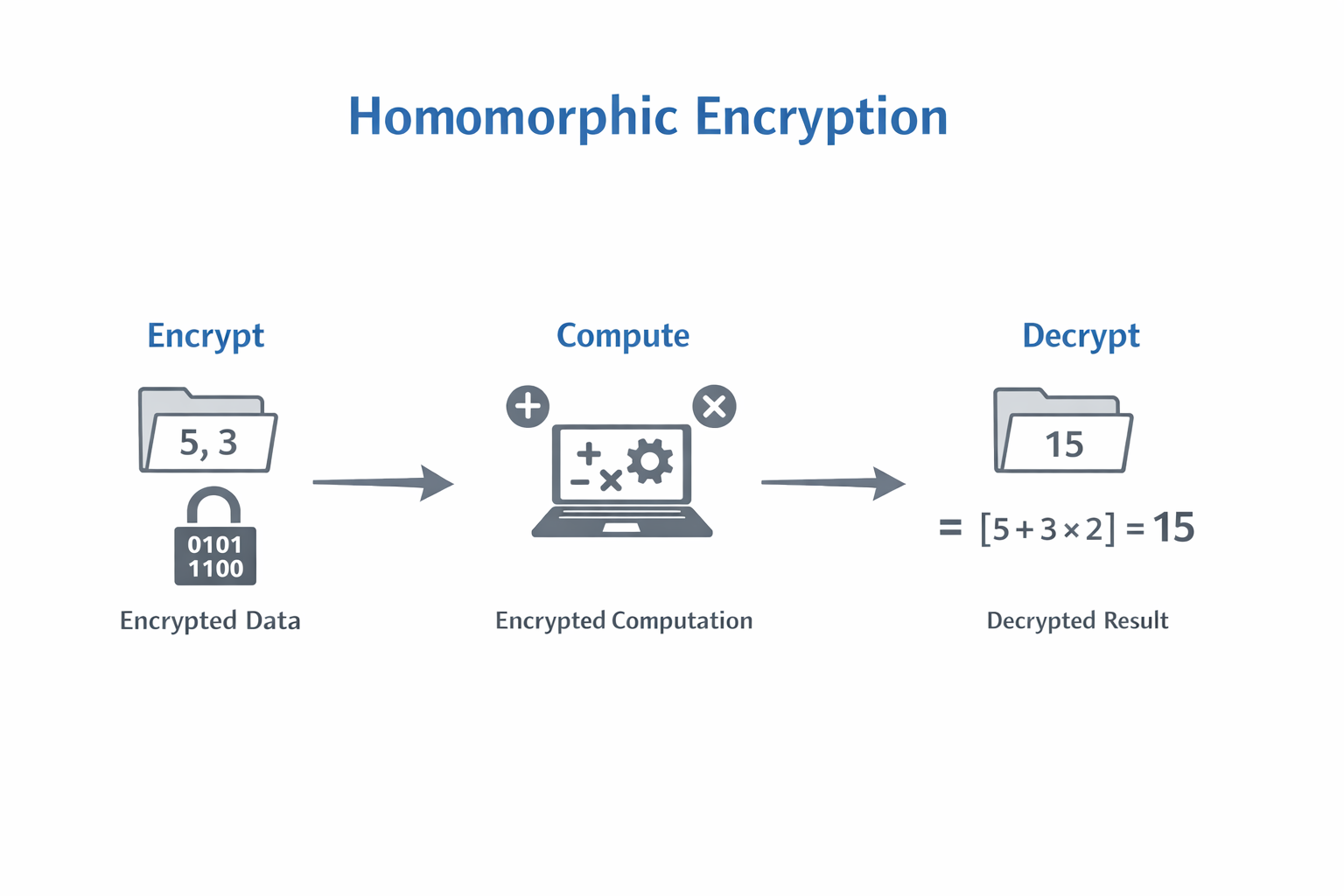
In traditional systems, the computation process is usually: encryption → decryption → calculation → re-encryption
Under the FHE model, the process becomes: encryption → encryption state calculation → encryption result output
Zama’s technical breakthrough lies in transforming FHE algorithms that originally had extremely high computational costs and existed only in academic papers into deployable and scalable engineering systems. Through compiler, runtime, and SDK layers, performance is optimized so that these systems can serve real world applications.
Zama’s Products and Development Tools ( Open Source SDKs and Runtime )
Zama does not provide only underlying cryptographic libraries, but instead builds a complete developer oriented product system:
- Concrete / Concrete ML: used to perform inference computations on encrypted data, particularly suitable for privacy preserving machine learning scenarios
- FHEVM: supports running FHE based smart contracts in blockchain environments, keeping contract state and inputs encrypted
- Developer SDKs and toolchains: help developers build privacy computing applications without needing an in depth understanding of cryptographic details
All of these tools adopt an open source strategy as a core principle, lowering the barrier to using FHE technology and facilitating security audits and community collaboration.
Zama’s Use Cases and Practical Application Examples
Zama’s technology is applicable to multiple fields with extremely high privacy requirements:
- Privacy smart contracts: hiding sensitive information such as transaction amounts and voting choices in DeFi or on chain governance
- Confidential financial computation: performing risk control models and credit assessments without exposing user data
- Privacy identity verification: proving that “certain conditions are met” without disclosing specific identity data
- Privacy preserving machine learning inference: performing model inference on encrypted data in scenarios such as healthcare and insurance
The common feature of these applications is that data is highly valuable, but the data itself should not be visible to any computation node.
How Developers Can Integrate Zama, Getting Started Steps and Integration Guide
For developers, integrating Zama typically includes the following steps:
- Selecting appropriate Zama tools ( such as Concrete ML or FHEVM )
- Using SDKs to compile business logic into FHE executable form
- Deploying the runtime or integrating it into a blockchain environment
- Tuning performance and security parameters
Zama is designed to remain as compatible as possible with existing development workflows, allowing both Web2 and Web3 developers to get started at relatively low cost.
Ecosystem and Collaboration, Enterprise Partnerships, Research Institutions, and Community Projects
Zama’s ecosystem building mainly revolves around three directions: enterprise level privacy computing applications, academic research collaboration, and developer community building.
At the research level, Zama continuously collaborates with research teams in cryptography and computer science to advance the optimization of Fully Homomorphic Encryption ( FHE ) in terms of algorithm efficiency, engineering implementation, and security parameters, accelerating the transformation of cutting edge research results into practical applications.
In terms of enterprise collaboration, Zama focuses on scenarios with high data confidentiality requirements, such as finance, data analytics, and privacy preserving machine learning. Through validation in real business environments, it explores the feasibility of FHE in performance, stability, and scalability, promoting the transition of privacy computing from proof of concept to large scale application.
At the same time, Zama promotes developer ecosystem building with open source at its core, attracting developers to participate in the exploration and optimization of homomorphic encryption applications through SDKs, sample code, and toolchains, gradually forming a technical community foundation around privacy computing.
Privacy, Security, and Compliance, How Does Zama Ensure Data Security?
Zama’s security model is based on strict cryptographic assumptions rather than trusted hardware or centralized servers. This means:
- Data never appears in plaintext form at any stage
- Even if computation nodes are attacked, original data cannot be obtained
- It helps meet the data minimization principles required by privacy regulations such as GDPR
This design gives Zama long term potential in industries with high compliance requirements.
Differences Between ZAMA and Other Privacy Computing Projects
| Dimension | ZAMA ( FHE Homomorphic Encryption ) | ZK ( Zero Knowledge Proofs ) | TEE ( Trusted Execution Environment ) | MPC ( Multi Party Secure Computation ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core concept | Direct computation on encrypted data | Proving the correctness of computation results without revealing data | Executing plaintext computation inside trusted hardware | Multiple parties jointly complete computation, no single party can obtain full data |
| Is data decrypted during computation | Not decrypted | Not decrypted ( verification only ) | Must be decrypted inside hardware | Not decrypted |
| Dependence on hardware trust | Does not depend | Does not depend | Strong dependence on hardware vendors | Does not depend |
| Main advantages | Full confidentiality of both computation process and data | High verification efficiency, suitable for blockchain scalability | Performance close to plaintext computation | High security, suitable for joint computation |
| Main limitations | High computation cost, performance still under optimization | Not suitable for complex general purpose computation | Risk of side channel attacks and hardware vulnerabilities | High communication complexity, limited number of participants |
| Typical application scenarios | Privacy smart contracts, confidential computation, privacy ML | Rollups, privacy proofs, compliance verification | Confidential cloud computing, enterprise data isolation | Joint risk control, cross institution data analysis |
| Blockchain compatibility | High ( such as FHEVM ) | Very high ( mainstream scalability solutions ) | Medium ( requires additional trust assumptions ) | Medium ( complex deployment ) |
| Security model | Pure cryptographic security | Pure cryptographic security | Hardware plus software trust model | Pure cryptographic security |
- Compared with zero knowledge proof ( ZK ) projects, Zama focuses more on “calculation process confidentiality” rather than only verifying the correctness of results
- Compared with TEE solutions, Zama does not rely on hardware trust assumptions
- Compared with multi party computation ( MPC ), FHE offers greater flexibility in the number of participants and deployment complexity
These differences give Zama a unique position in specific privacy computing scenarios.
Challenges Faced by ZAMA and Future Development Directions
Despite its broad prospects, Zama still faces some practical challenges, including computation performance, cost control, and developer education barriers. Future development directions may focus on:
- More efficient FHE compilation and acceleration
- Deeper integration with mainstream blockchain ecosystems
- More comprehensive development documentation and examples
How to View ZAMA Information and Participate in Related Trading on Gate
- Open the Gate platform and log in to your account. If you have not registered, you need to complete registration and basic security setup first.
- Enter ZAMA in the search box on the Gate trading page, then click the search result to enter the corresponding project page.
- On the project page, view ZAMA’s project overview, official descriptions, platform announcements, and related risk disclosure information.
- Scroll down the page to view ZAMA’s market data, such as price trends, trading volume, and historical performance.
- Gate has opened ZAMA spot trading. You can view supported trading pairs, trading methods, and operational rules on the page.
- Follow the page prompts to enter the corresponding trading interface. After confirming the trading rules, choose whether to participate. Specific functions are subject to the actual display on Gate.
Summary
With Fully Homomorphic Encryption ( FHE ) at its core, Zama provides a technological path that differs from traditional privacy solutions, enabling data to remain encrypted throughout computation and smart contract execution. This design fundamentally reduces the exposure risk of data during use and provides a higher level of security for privacy computing.
From the perspective of products and tools, Zama not only focuses on underlying cryptographic research, but also gradually transforms homomorphic encryption technology, which traditionally has extremely high barriers, into engineering solutions that can be practically adopted through open source SDKs, runtime environments, and developer tools. This gives it real world application value in scenarios such as blockchain privacy contracts, confidential financial computation, and privacy preserving machine learning.
At the industry level, as data compliance requirements continue to increase and Web3’s demand for privacy computing grows, the FHE path represented by Zama provides an important complement to the privacy computing ecosystem. Although challenges remain in terms of performance and cost, with algorithm optimization and ecosystem maturation, Zama is expected to play a more critical role in future privacy infrastructure.
Overall, Zama is not a single application or a short term trending project, but a long term infrastructure exploration centered on the evolution of privacy computing, and its subsequent development is worth continued attention.
FAQ
Is Zama a blockchain project?
Zama itself is a privacy computing platform focused on the engineering application of Fully Homomorphic Encryption ( FHE ) technology. Its technology can be integrated into blockchain environments to build privacy smart contracts and confidential computing applications, but Zama is not equivalent to an independent public blockchain.
What is the difference between FHE and ZK?
Fully Homomorphic Encryption ( FHE ) focuses on “how to complete computation without decrypting data,” while zero knowledge proofs ( ZK ) focus more on “how to prove that a computation result is correct.” They address different problems and are complementary within privacy computing systems.
What types of developers is Zama suitable for?
Zama is suitable for blockchain developers, backend engineers, and machine learning engineers who have privacy computing needs. Through SDKs and development tools, even those without a deep cryptography background can participate in the development of privacy computing applications.
Does homomorphic encryption affect application performance?
Compared with plaintext computation, homomorphic encryption still incurs certain overheads in computation performance and resource consumption. However, with the development of algorithm optimization, compiler improvements, and hardware acceleration, this gap is gradually narrowing, making it suitable for scenarios where privacy requirements outweigh extreme performance limits.
Related Articles

What is Fartcoin? All You Need to Know About FARTCOIN

Gold Price Forecast for the Next Five Years: 2026–2030 Trend Outlook and Investment Implications, Could It Reach $6,000?

Crypto Future Profit Calculator: How to Calculate Your Potential Gains

2026 Silver Price Forecast: Bull Market Continuation or High-Level Pullback? In-Depth Analysis of Silver Candlestick Chart

Crypto Futures Calculator: Easily Estimate Your Profits & Risks


