Ethereum price today

What Is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a programmable blockchain platform primarily designed to run smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Smart contracts are self-executing code stored on the blockchain that automatically completes transactions or operations when predefined conditions are met. DApps are decentralized applications that operate on the blockchain or interact with it. Ether (ETH) is the native currency of the network, serving as “fuel” to pay transaction fees (Gas), which helps prevent abuse and compensates validators for their resources.
To ensure network security and consensus, Ethereum utilizes the Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanism. In PoS, validators participate in block production and verification by staking ETH, and malicious actors face penalties (slashing). Unlike Proof of Work (PoW), PoS is significantly more energy-efficient. Users manage their addresses and private keys via wallets; the private key functions as a password for funds, and losing it means permanent loss of access.
Current Ethereum (ETH) Price, Market Cap, and Supply
As of 2026-01-23:
- Price: approximately $2,964.36
- Circulating supply: 120,694,468.895810 ETH
- Total supply: 120,694,468.895810 ETH
- Maximum supply: ∞ (no hard cap)
- Market cap: ~$357,781,855,815.98
- Fully diluted market cap: ~$357,781,855,815.98
- Market cap dominance: ~11.26%
- 1-hour change: +0.19%
- 24-hour change: -2.32%
- 7-day change: -10.59%
- 30-day change: -0.02%
- 24-hour trading volume: ~$433,496,624.67
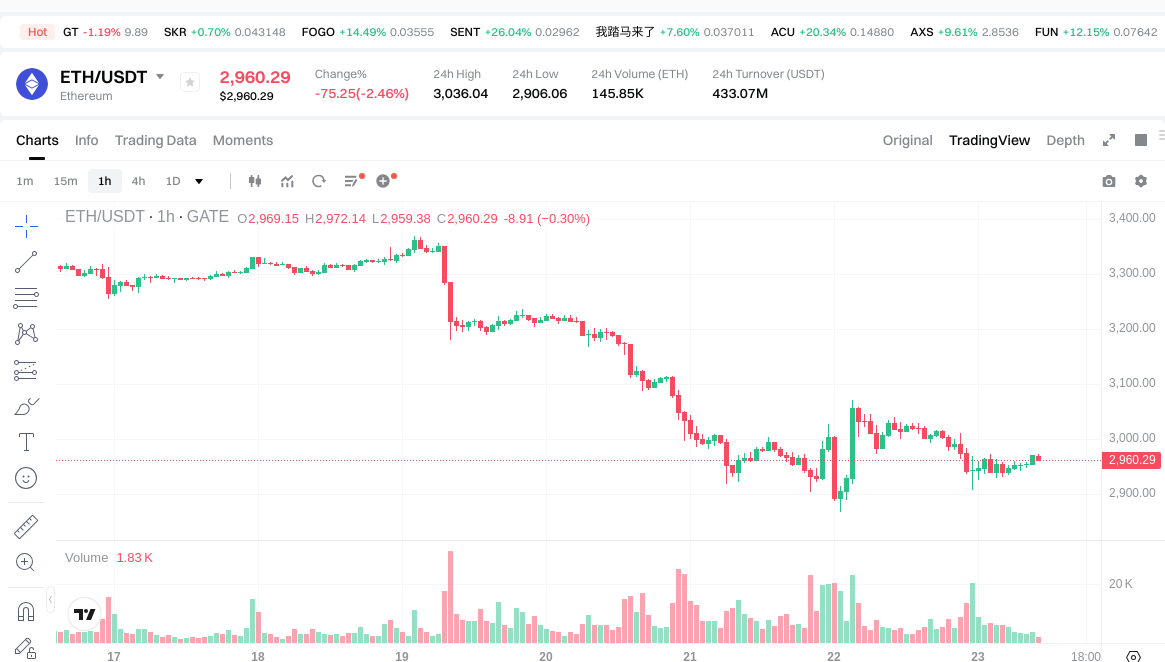
View ETH USDT price
Since the EIP-1559 upgrade, a portion of Ethereum’s transaction fees are burned, meaning that although there is no hard cap, net issuance may decrease or even turn deflationary at times. Short-term price fluctuations are driven by macro trends, regulatory developments, and on-chain activity. Before investing, monitor official updates and on-chain metrics.
Who Created Ethereum (ETH) and When?
Ethereum was proposed by Vitalik Buterin in 2013 with the release of its whitepaper and later developed collaboratively by several co-founders and contributors. Public records show development began in 2014, with the mainnet launching in 2015 under the “Frontier” phase, followed by upgrades such as “Homestead” and “Metropolis.”
Key milestones include:
- The 2021 EIP-1559 upgrade introducing fee burning
- The 2022 “Merge,” which transitioned consensus from PoW to PoS and drastically reduced energy consumption
- Further improvements with Shanghai (Shanghai/Capella) upgrades to enhance staking withdrawals and execution layer efficiency
How Does Ethereum (ETH) Work?
Ethereum’s architecture consists of two main layers: the execution layer and the consensus layer. The execution layer runs the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which processes smart contract bytecode. The consensus layer coordinates validators to produce blocks and finalize transactions using PoS.
Every transaction requires payment of Gas, which measures computational and storage costs. Users set the Gas price (the fee per unit), so total cost = Gas used × Gas price. EIP-1559 introduced base fee burning to reduce ETH supply.
Validators stake ETH to participate in block production and validation—staking involves locking assets for network rewards while exposing participants to potential penalties. Blocks achieve “finality” through multi-round voting and checkpoint mechanisms, reducing reorganization risks. To scale throughput and lower costs, Ethereum implements Rollup solutions: aggregating many transactions on Layer 2 before compressing data back to the mainnet.
What Can You Do With Ethereum (ETH)?
- Payments & Settlement: Transfer ETH or tokens between wallets; pay Gas for on-chain operations.
- DeFi Protocols: Swap, lend, earn yield, or settle stablecoins through automated, transparent smart contracts.
- NFTs & Digital Identity: Mint and trade NFTs for art, gaming assets, or membership credentials.
- DAO Governance: Vote on community proposals or funding allocations via governance tokens; processes are enforced by smart contracts.
- Asset Issuance: Organizations or communities can launch their own tokens for points systems, crowdfunding, or access management.
Wallets and Scaling Solutions in the Ethereum (ETH) Ecosystem
For wallets:
- Browser extension wallets (such as MetaMask) make interacting with DApps easy.
- Mobile wallets are ideal for daily use.
- Hardware wallets store private keys offline for enhanced security. The private key proves ownership of funds; a recovery phrase is a human-readable backup for your private key and should be stored offline.
For scaling solutions: Popular Layer 2s include Optimism, Arbitrum, and zkRollup protocols like zkSync. Rollups bundle large numbers of transactions on Layer 2 and periodically submit proofs/data to the mainnet for low fees and high throughput. When using Layer 2, consider network switching, bridge fees, and settlement times.
Key Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Ethereum (ETH)
- Smart Contract Risk: Bugs, oracle failures, or governance issues can lead to financial losses. Use well-audited and widely adopted protocols; diversify your holdings.
- Private Key & Wallet Security: Beware phishing sites, malicious signatures, or malware stealing assets. Back up recovery phrases offline; avoid screenshots/cloud storage; enable hardware wallets and multisig (if supported).
- Platform & Operational Risk: Pay attention to account security, withdrawal channels, and fees on exchanges; all platforms have operational and attack risks—withdraw to self-custody wallets for lower counterparty risk.
- Regulatory Compliance: Crypto regulations vary by region, affecting fiat gateways, tax obligations, and product legality—stay updated on local policies.
- Market & Network Congestion: Prices can be highly volatile; during periods of high activity, Gas fees surge causing higher costs and delays.
How to Buy and Securely Store Ethereum (ETH) on Gate
Step 1: Register an account at gate.com using your regular email or phone number; set a strong password different from those used elsewhere.
Step 2: Complete KYC and security setup as prompted; enable two-factor authentication (2FA) and anti-phishing codes to enhance login and withdrawal security.
Step 3: Deposit funds or recharge your account by transferring existing crypto assets or using supported payment methods when fiat purchases are available. Confirm the correct deposit network and address to avoid cross-chain errors.
Step 4: Search for ETH and place a trade—on the spot trading page, look up “ETH” and select your preferred pair (e.g., ETH/USDT). Choose market orders (execute at current price) or limit orders (set your own price). Review fees/minimum order size before submitting.
Step 5: Withdraw to a self-custody wallet—prepare an Ethereum mainnet address (usually starting with 0x), select “Ethereum” as the withdrawal network. Double-check address, withdrawal amount, and Gas fees; test with a small amount first then transfer larger sums once confirmed.
Step 6: Securely back up your wallet—write your recovery phrase on paper stored in separate locations; use software wallets for frequent transactions but hardware wallets for long-term holdings; consider multisig or vault contracts for large sums (after learning how they work).
How Is Ethereum (ETH) Different From Bitcoin?
- Purpose: Bitcoin is optimized for value storage and peer-to-peer payments; Ethereum serves as a programmable platform supporting smart contracts and application ecosystems.
- Consensus Mechanism: Bitcoin uses PoW (miners compete using computing power); Ethereum now uses PoS (validators stake ETH), which is less energy-intensive. PoW secures via hash power; PoS via staked capital.
- Supply & Monetary Policy: Bitcoin has a hard cap of 21 million coins; Ethereum has no fixed supply limit but burns transaction fees under EIP-1559—net supply may decrease over time.
- Functionality & Ecosystem: Ethereum natively supports smart contracts and token standards like ERC-20/721 for DeFi, NFTs, DAOs; Bitcoin’s ecosystem is simpler with limited contract capabilities.
- Fees & Performance: Ethereum mainnet fees can spike during congestion but Layer 2 solutions greatly reduce costs/increase speed; Bitcoin fees/confirmation times depend on network congestion/block size.
Summary of Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum is a general-purpose blockchain designed for contracts and applications—with ETH serving as network fuel powering transactions and computation. Current price, market cap, and supply metrics showcase its scale and activity; PoS consensus, EVM, and Rollup technologies form its technical foundation supporting diverse scenarios like DeFi, NFTs, and DAOs. When investing or using Ethereum, get familiar with wallets, networks, and fee structures—and prioritize contract audits, private key backups, and regulatory compliance. On Gate, begin with small test withdrawals after purchase; gradually learn mainnet/Layer 2 operations before increasing funds or usage for improved safety and experience.
FAQ
What Drives Ethereum’s Price Volatility?
Ethereum’s price fluctuates due to multiple factors including market supply/demand dynamics, technical upgrades, macroeconomic conditions, and regulatory changes. Events like the Shanghai upgrade can attract market attention; broader crypto sentiment also directly impacts ETH price. Track real-time price movements and market analysis via Gate or other major platforms.
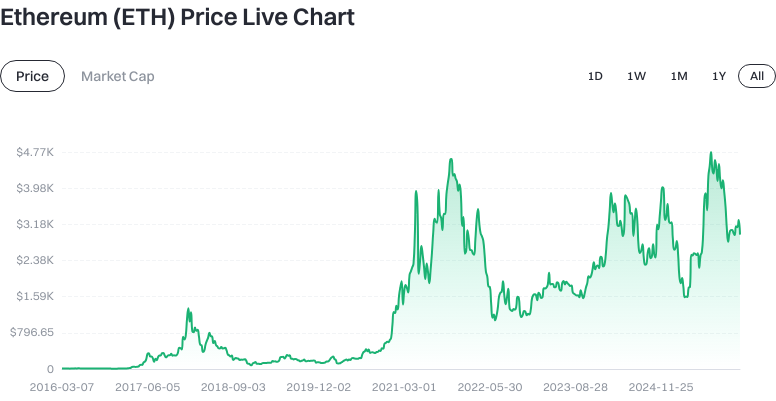
Is There a Link Between Ethereum’s Price and Bitcoin’s Price?
Ethereum tends to have a strong positive correlation with Bitcoin—when Bitcoin rises or falls, it often moves the entire crypto market including Ethereum. However, each asset may diverge based on its unique fundamentals; Ethereum’s ecosystem developments can create independent price trends.
How Can I Track Real-Time Ethereum Prices?
On Gate’s homepage you can see real-time ETH prices plus 24-hour changes and historical candlestick charts. Data sites like CoinGecko and CoinMarketCap aggregate prices across exchanges. For deeper understanding of price trends, follow mainstream media coverage and community discussions.
How Does Ethereum’s Ecosystem Affect Its Price?
A richer ecosystem increases Ethereum’s network value—typically pushing ETH prices higher. Growth in DeFi protocols, NFT popularity, enterprise adoption etc., have previously boosted prices. Over the long term, robust development and technical upgrades are fundamental factors influencing ETH value.

View ETH USDT price
Why Is Ethereum Priced in US Dollars?
Ethereum is one of the most liquid crypto assets globally; using USD as a benchmark makes international trading easier to compare. On Gate and other exchanges you can buy ETH using various fiat currencies or crypto pairs to suit local preferences.
Glossary of Key Ethereum (ETH) Terms
- Smart Contract: Self-executing code on Ethereum that enables trustless transactions/protocols without intermediaries.
- Gas: The computational fee required to execute Ethereum transactions/contracts—priced in ETH.
- EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine): The virtual environment that executes smart contract code on Ethereum—enabling programmability.
- Staking: Locking ETH to participate in network validation/rewards.
- DApp (Decentralized Application): Applications built using smart contracts on Ethereum—including DeFi,NFT, etc.
- Layer 2: Scaling solutions built atop Ethereum that reduce transaction fees/increase speed.
Further Reading & References for Ethereum (ETH)
Official Sites / Whitepaper:
Development / Documentation:
- https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum
- https://docs.soliditylang.org/
- https://ethereum.org/en/developers/learning-tools/
Authoritative Media / Research:
Related Articles

What Is Ethereum 2.0? Understanding The Merge

Reflections on Ethereum Governance Following the 3074 Saga
