What is ARPA Coin?

What Is ARPA? Definition and Key Features
ARPA is the native token of the ARPA Network, designed to power a privacy-preserving computation network. Privacy computation in this context refers to enabling joint computation and analysis across multiple parties without exposing their original data. One major cryptographic technique used is Multi-Party Computation (MPC), which allows participants to securely contribute their data for collaborative calculations. The process yields verifiable results while ensuring that the raw inputs remain confidential. The ARPA token is primarily used to pay for computation fees, incentivize and penalize compute nodes (staking involves locking tokens to gain participation rights and rewards while enforcing node accountability), and to participate in community governance proposals and voting.
ARPA (ARPA) Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply
As of 2026-01-26 (data per prompt), ARPA is priced at approximately $0.012850. The circulating supply is about 982,174,603 tokens; total supply is around 1,999,999,999.987738 tokens; maximum supply is set at 2,000,000,000 tokens. Circulating market capitalization stands at roughly $25,699,999.999842, with fully diluted market cap also at $25,699,999.999842. Market cap dominance is about 0.000830%. The 24-hour trading volume is $770,031.601421. Price changes: +0.47% over 1 hour, -10.81% over 24 hours, +6.27% over 7 days, +2.88% over 30 days.
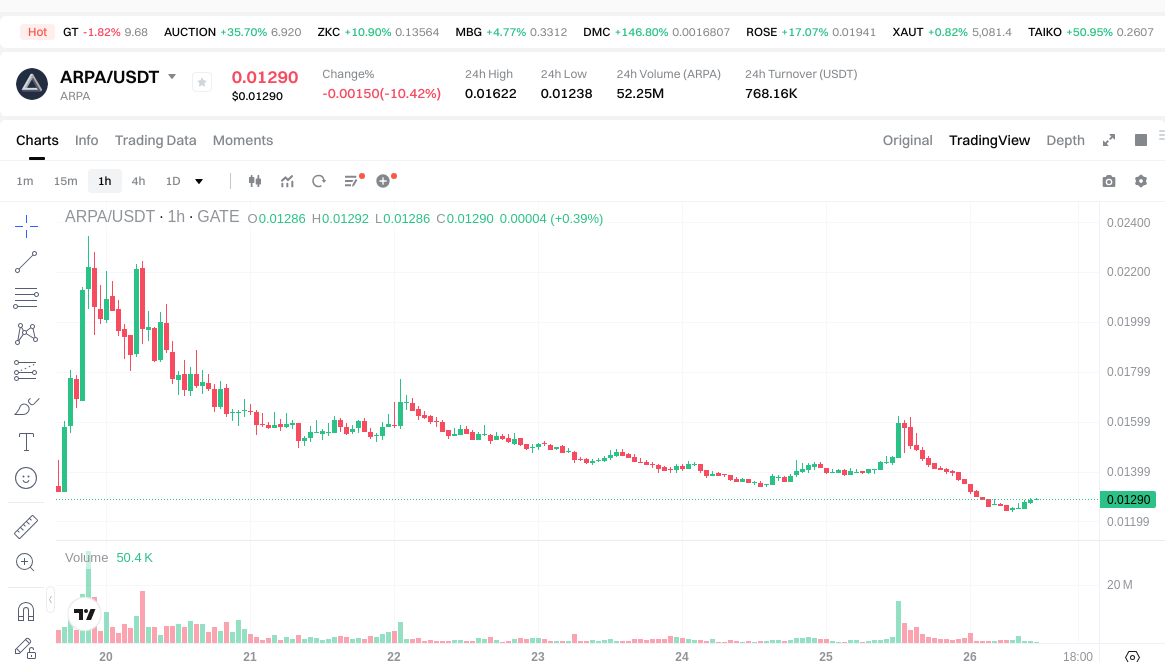
Click to view ARPA USDT price
Market capitalization is calculated by multiplying the current price by the number of tokens in circulation. Fully diluted market capitalization estimates the value by considering the maximum or total supply, offering a long-term valuation perspective.
Who Created ARPA (ARPA) and When?
ARPA Network aims to provide a privacy computation protocol layer for mainstream public blockchains, enabling enterprises and institutions to collaborate and output verifiable results without disclosing underlying data. According to available information, the ARPA token was launched on 2021-03-13. The project positions itself as a bridge between enterprises and Web3, focusing on compatibility and usability within existing blockchain ecosystems to embed privacy computation capabilities into various applications.
How Does ARPA (ARPA) Work?
ARPA leverages cryptographic technologies such as Multi-Party Computation (MPC) to allow participants to contribute their data securely for computation. There is no need to share raw data—compute nodes execute agreed-upon functions or logic upon receiving tasks, producing results with attached proofs for verification. This approach delivers the value of collaborative analytics while minimizing data leakage risks.
The network architecture typically includes modules for task publishing and matching, execution and result verification by compute nodes, and economic incentives and penalties. The token serves as payment for computation; nodes stake ARPA tokens to participate and earn rewards. Malicious behavior or protocol violations result in penalties, safeguarding network security. To integrate with mainstream public chains, ARPA provides interfaces or middleware so developers can invoke privacy computation from familiar blockchains. Key records and settlements are written on-chain for enhanced auditability.
What Are the Use Cases for ARPA (ARPA)?
- Financial Risk Management: Multiple institutions can jointly model without sharing client details, creating more robust scoring models that reduce fraud risk and improve approval rates in compliance with regulations.
- Credit Scoring & AML: Institutions can cross-analyze suspicious patterns using privacy computation without exposing underlying data.
- Marketing & Attribution: Different platforms can analyze audience overlap and conversion attribution without leaking individual user data.
- Healthcare Research: Hospitals can jointly perform statistical analysis or model training on specific metrics, expanding sample sizes while protecting patient privacy.
- Web3 Applications: Privacy computation modules can be integrated into on-chain logic for decentralized applications, offering "output-only" computations that do not reveal user inputs.
Supported Wallets and Extension Solutions in the ARPA (ARPA) Ecosystem
Users can store ARPA in non-custodial wallets—wallets where users control their private keys—such as browser extension wallets or mobile wallets. For enhanced security, hardware wallets can be used to keep private keys offline. When depositing or withdrawing tokens, always verify the official contract address and network type, and ensure sufficient gas fees are available in your wallet (gas fees are required for on-chain transactions).
For developers, the ecosystem typically offers SDKs or APIs to integrate task submission, result verification, settlement, and auditing into on-chain applications. Data providers may use extension tools like permission management and audit dashboards to record who accessed which computations and when.
Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations of ARPA (ARPA)
Technical Risks: Correct cryptographic implementation and node execution are critical; flaws or malicious nodes can compromise result reliability and economic security.
Market Risks: The token price and liquidity are volatile, with significant short-term fluctuations possible.
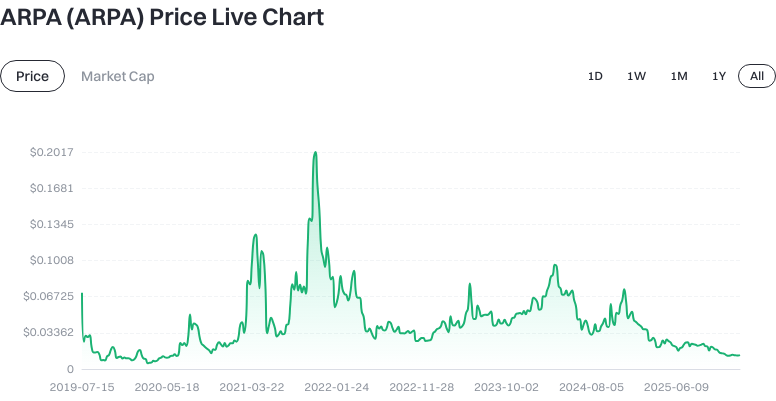
Click to view ARPA Latest Price Chart
Operational Risks: If partnerships, ecosystem growth, or developer activity lag expectations, long-term value realization may be impacted.
Compliance Risks: Privacy computation often involves data protection and cross-border compliance—different jurisdictions have varying rules on data usage. Business development must adhere to local regulations.
Security Risks: Beware of phishing sites and fake contract addresses—verify information through official channels and enable two-factor authentication along with withdrawal whitelists. Before investing or participating, start with small amounts, diversify allocations, and back up credentials securely.
How to Buy and Safely Store ARPA (ARPA) on Gate
Step 1: Register and log in to your Gate account. Visit gate.com to sign up using a strong password and access the security center after logging in.
Step 2: Complete KYC (identity verification) and security settings. KYC increases account privileges and withdrawal limits. Enable two-factor authentication and withdrawal whitelist for enhanced security.
Step 3: Deposit funds. You can deposit stablecoins like USDT or use fiat onramps. After funding your account, transfer assets from your funding account to your spot account to ensure balance availability.
Step 4: Place a spot market order. Search for “ARPA/USDT” and choose between limit orders (set your own buy price) or market orders (execute at current market price). After ordering, check status under "Orders/Positions."
Step 5: Withdraw and securely store your tokens. For long-term holding, transfer ARPA to a non-custodial wallet—backup your seed phrase and private key securely offline; never store them online or in plain text. Always verify network and address when withdrawing; test with a small amount before transferring large sums. For short-term trading, tokens may remain on the exchange but always enable security settings and monitor risk alerts regularly.
Risk Reminder: For any operation, consider splitting orders, setting price alerts, and having contingency plans. In case of extreme volatility, prioritize position control and risk exposure management.
ARPA (ARPA) vs Oasis Network (ROSE): Comparison
Technical Approach: ARPA focuses on providing MPC-based privacy computation as a protocol layer for mainstream blockchains—essentially a plug-and-play privacy network; Oasis Network is an independent Layer 1 blockchain emphasizing confidential computing and privacy-focused smart contracts, with native execution of applications.
Token Utility: ARPA is mainly used for computation settlement, node staking, and governance incentives; ROSE powers network gas fees, staking, and governance.
Ecosystem Positioning: ARPA aims to deliver privacy computation services across chains and applications with high compatibility; Oasis focuses on developing native dApps and data tokenization within its own blockchain ecosystem.
Both serve privacy and compliance needs but differ in implementation paths and developer experience—their suitability depends on the specific application scenario.
Summary of ARPA (ARPA)
ARPA is a privacy computation network centered on Multi-Party Computation (MPC), using its token for computation payments, node staking, and governance. It enables collaborative computing across entities with verifiable outcomes while preserving data confidentiality. As of January 26, 2026, ARPA sits in the mid-cap range with notable short-term volatility—participants should closely monitor price and liquidity dynamics.
Key application areas include financial risk management, credit scoring, marketing attribution, and healthcare research; developers can embed privacy computation into existing on-chain apps via APIs or middleware. It’s recommended to monitor project partnerships, technical roadmap stability, regulatory developments—and follow best practices such as phased participation, contract address verification, robust account security settings, and self-custody backups to balance potential returns with risk management.
FAQ
What Is the Main Use Case for ARPA?
ARPA is the native token of the Arpa Chain network. It is primarily used for paying network transaction fees, participating in governance votes, and staking for mining rewards. Token holders can stake ARPA to earn network incentives and vote on protocol upgrades or parameter changes.
Where Can I Buy ARPA?
ARPA is listed on several major exchanges including Gate. On Gate you can trade ARPA directly with fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies in both spot and margin markets. For optimal trading experience, choose exchanges with high security standards and good liquidity.
Is ARPA Suitable for Long-Term Holding?
Whether ARPA suits long-term holding depends on project outlooks, market risks, and individual investment goals. Arpa Chain focuses on privacy computing and data security—a sector with promising potential—but cryptocurrency volatility is high. Study the project’s whitepaper and tech progress thoroughly before investing; develop a sound risk management strategy.
What Are the Main Risks of Holding ARPA?
Primary risks include market volatility leading to price drops, project development lagging expectations, or uncertainties in crypto regulation. Diversify your investments; never allocate more than you can afford to lose; keep up with project news and market trends regularly.
How Can I Safely Store My ARPA?
You can store ARPA in hardware wallets (such as Ledger), non-custodial wallets (like MetaMask), or exchange wallets. Hardware wallets offer top-tier security but are less convenient; non-custodial wallets require careful management of private keys; exchange wallets are user-friendly but depend on platform security. For large holdings use hardware wallets; for smaller amounts or daily trading use non-custodial wallets.
Glossary of Key Terms Related to ARPA (ARPA)
- Privacy Computing: A set of methods enabling computations and verifications on data without exposing the underlying information using cryptographic techniques.
- Multi-Party Computation (MPC): Cryptographic protocols that allow multiple parties to jointly compute a function while keeping their individual inputs private.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: Cryptographic methods that enable one party to prove a statement’s truth without revealing any information beyond the validity of the statement itself.
- On-Chain Data Privacy: Security mechanisms within blockchain networks that prevent public access to transaction details or user information.
- Verifiable Computing: Technologies ensuring that computational results are correct and independently auditable by third parties.
- Decentralized Privacy Infrastructure: A distributed network of nodes offering privacy services without relying on centralized authorities.
References & Further Reading on ARPA (ARPA)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Developer Resources / Documentation:
-
Authoritative Media / Research:
Related Articles

The Future of Cross-Chain Bridges: Full-Chain Interoperability Becomes Inevitable, Liquidity Bridges Will Decline

Solana Need L2s And Appchains?
