What is AVAX?

What Is Avalanche?
Avalanche is a public blockchain platform designed for decentralized applications (DApps) and custom blockchains, with AVAX as its native token. Its defining features include the Avalanche consensus mechanism, which enables near-instant transaction finality (meaning that once a transaction is confirmed, it cannot be reversed), and full compatibility with Ethereum’s development toolkit. This allows developers and users to interact with Avalanche using familiar wallets and programming languages.
Additionally, Avalanche introduces Subnets, which let teams launch independent blockchain networks tailored to specific requirements. The AVAX token is used to pay network fees, serves as the staking asset for validators, and allows holders to participate in on-chain governance.
Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of Avalanche (AVAX)
As of the provided data (2026-01-26), the key metrics for AVAX are:
- Latest price: $11.65; 1h change: -0.43%; 24h: -2.90%; 7 days: -7.30%; 30 days: -5.50%
- Circulating supply: 431,267,278.848590 AVAX; Total supply: 462,936,347.627825 AVAX; Max supply: 720,000,000 AVAX
- Market capitalization: approximately $5.393 billion; Fully diluted market cap: about $5.393 billion; Market dominance: 0.17%; 24-hour trading volume: around $1.5692 million
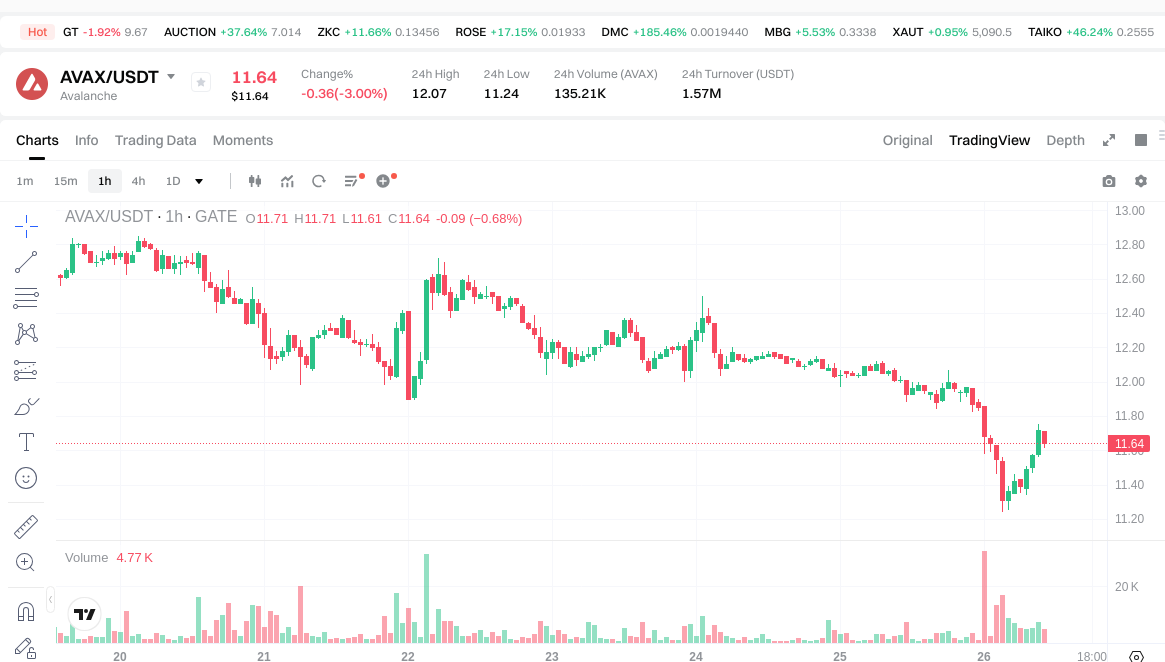
Click to view AVAX USDT Price
From the supply structure, the current circulation represents about 93% of the total supply and around 60% of the maximum supply. Both price and market cap fluctuate with market conditions—always refer to live data for up-to-date information.
Who Created Avalanche (AVAX) and When?
Avalanche was initiated by Emin Gün Sirer, Kevin Sekniqi, and Ted Yin, based on the Avalanche consensus algorithm. According to available information, it launched on July 13, 2020. The project aims to provide fast confirmation speeds and high scalability without compromising security, targeting financial services and a wide range of on-chain applications.
How Does Avalanche (AVAX) Work?
In summary, Avalanche operates via fast consensus, a multi-chain structure, and scalable Subnets:
- Consensus Mechanism: Avalanche uses a sampling-based Byzantine Fault Tolerant protocol where validators reach agreement quickly through multiple rounds of small random sampling and message propagation. This results in low latency and high throughput. Validators—nodes that package and confirm transactions—must stake (lock up) AVAX to participate.
- Three-Chain Architecture: The mainnet is composed of three interoperable chains:
- C-Chain (Contract Chain): EVM-compatible (supports the Ethereum Virtual Machine), used for running smart contracts—account addresses typically start with "0x".
- P-Chain (Platform Chain): Handles staking, Subnet management, and coordination.
- X-Chain (Exchange Chain): Facilitates asset creation and transfer.
- Subnets: Subnets are independent chains or networks maintained by groups of validators. They can be customized for virtual machine type, token economics, permissions, or compliance rules—ideal for enterprise or specialized use cases.
- Fees & Incentives: AVAX is required to pay transaction fees; validators earn rewards for securing the network by staking AVAX. Staking periods, minimum amounts, and reward rates are subject to network parameters.
What Can Avalanche (AVAX) Be Used For?
- Paying Fees & Staking: Users need AVAX to pay gas fees when interacting with DApps on the C-Chain; holders can stake AVAX to support network security.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Lending, decentralized exchanges, yield aggregators, and more operate on the C-Chain—users can access them via EVM-compatible wallets.
- Asset Issuance & Settlement: The X-Chain enables on-chain asset issuance and transfers; institutions can deploy custom settlement and compliance logic within Subnets.
- Gaming & Consumer Applications: Subnets offer dedicated resources and fee models for games or high-frequency applications, avoiding mainnet congestion.
- Enterprise & Government Use Cases: Permissioned Subnets allow for access controls and audit requirements—ideal for compliant enterprise deployments.
Wallets and Expansion Solutions in the Avalanche (AVAX) Ecosystem
Common ways users interact include:
- Official Wallets & Tools: The official wallet and explorer for the C-Chain provide account management, asset viewing, and signing capabilities.
- EVM-Compatible Wallets: Since C-Chain is EVM-compatible, it supports mainstream Ethereum wallets for managing AVAX and interacting with smart contracts.
- Development & Infrastructure: The EVM toolchain (e.g., Solidity and common debugging/deployment tools) is fully supported; Subnets allow customization of virtual machines and parameters for specific business needs.
Always back up your mnemonic phrase (the recovery words for your account) securely. For long-term holders, consider layered storage of large assets to reduce hot wallet exposure risks.
Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Avalanche (AVAX)
- Market Volatility: AVAX’s price is influenced by overall market sentiment and liquidity; expect significant short-term fluctuations.
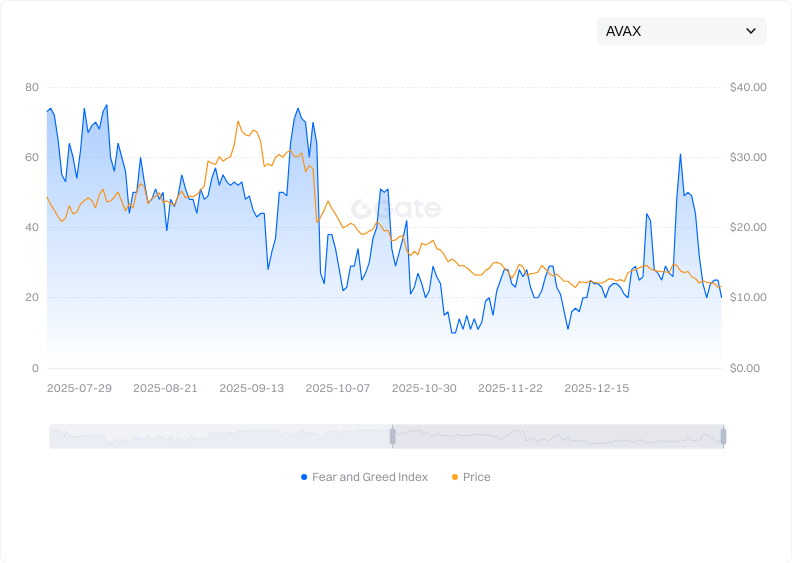
Click to view AVAX Fear & Greed Index
- Smart Contract Risks: Vulnerabilities in contracts, oracle failures, or misuse of admin privileges can lead to asset loss—stick with audited and community-vetted applications.
- Subnet & Governance Risks: While Subnets are flexible, their security and reliability may vary; governance changes can impact fees, rewards, or inflation parameters.
- Regulatory Compliance: Token trading, custody, and taxation are subject to local regulations—always understand your jurisdiction’s requirements before participating.
- Custody & Private Key Management: Keeping assets on exchanges exposes you to platform risk; self-custody wallets require you to manage your own private keys—loss of these keys can make recovery nearly impossible. Enable two-factor authentication, diversify storage locations, and set withdrawal whitelists as security measures.
How to Buy and Securely Store Avalanche (AVAX) on Gate
Step 1: Register and Complete KYC
Create an account on Gate and complete identity verification to enhance account security and increase withdrawal limits.
Step 2: Fund Your Account
Deposit fiat currency or stablecoins into your account and confirm your balance is ready for trading. Note that different deposit channels may have varying processing times and fees.
Step 3: Search for Trading Pairs
On the trading page, search for pairs like “AVAX/USDT” to view order book depth and price trends.
Step 4: Choose Order Type
- Market Order: Executes instantly at current market price—best for immediate trades.
- Limit Order: Set your desired buy price and wait for execution—useful for cost control. After setting amount and price, submit your order and check status in the order panel.
Step 5: Withdraw to Self-Custody Wallet (Optional)
If you prefer self-custody, withdraw using the Avalanche C-Chain network (C Chain). Enter a wallet address starting with “0x” and test with a small amount before transferring larger sums. Different networks have distinct address formats and fees—always match your withdrawal network with your receiving wallet.
Step 6: Security & Backup
Enable two-factor authentication, anti-phishing codes, and withdrawal whitelists. For self-custody wallets, back up your mnemonic phrase offline in multiple secure locations away from internet-connected devices.
How Does Avalanche (AVAX) Compare to Ethereum?
- Scaling Pathways: Avalanche leverages Subnets for custom resources and rules per application; Ethereum relies more on Layer 2 networks (Rollups) for scaling throughput. Both pursue multi-chain or layered scaling but use different approaches.
- Performance & Finality: Avalanche is known for rapid confirmations—often achieving transaction finality in about one second. Ethereum has improved efficiency through Proof of Stake consensus and Layer 2 solutions that further boost speed and reduce fees.
- Compatibility: Avalanche’s C-Chain is EVM-compatible, making contract deployment and tool migration seamless; Ethereum is the origin of EVM with a larger ecosystem and developer base.
- Fees & User Experience: Transaction costs fluctuate on both chains based on congestion. Under light load, Avalanche typically offers smoother experiences; during high congestion, Layer 2 solutions greatly improve Ethereum’s user experience.
- Decentralization & Maturity: Ethereum has a longer history with diverse nodes and client implementations. Avalanche’s validator requirements and flexible Subnet architecture result in a unique decentralization profile. Chain selection depends on application needs and ecosystem preferences.
Summary of Avalanche (AVAX)
Avalanche (AVAX) centers on rapid consensus and Subnet architecture while maintaining Ethereum toolchain compatibility for easy adoption by developers and enterprises needing custom performance solutions. As of the latest data (2026-01-26), AVAX’s supply structure is clear, but short-term price volatility remains a concern. Beginners should start small—use the correct C-Chain address, secure their accounts, and back up private keys properly. Developers and institutions can leverage Subnets for differentiated compliance and performance combinations. Whether investing or building, stay informed about network parameters, ecosystem developments, regulatory updates—and always act within your risk tolerance.
FAQ
What Is the Relationship Between AVAX and the Avalanche Network?
AVAX is the native token of the Avalanche network—they are inseparable. AVAX is used for transaction fees, staking by validators, and governance voting; Avalanche is a high-performance public blockchain whose consensus mechanism is secured by AVAX holders. Think of Avalanche as infrastructure—and AVAX as the fuel powering it.
What Yields Can I Earn by Holding AVAX?
The main way AVAX holders earn returns is through staking. You can delegate AVAX to validator nodes to participate in network consensus and receive proportional rewards—annual yields typically range from 10%–15%. Some DeFi protocols also distribute governance tokens as incentives to AVAX holders.
How Can Beginners Quickly Experience Real AVAX Use Cases?
The most direct way is to try applications in the Avalanche ecosystem yourself. You can buy a small amount of AVAX on Gate, then interact with DeFi protocols (like lending or swapping), NFT platforms, or gaming DApps—this lets you see firsthand how AVAX powers real-world use cases. Stay updated via official Avalanche community channels for ecosystem news.
What Secures AVAX?
The security of AVAX—and the entire Avalanche network—is underpinned by the amount of AVAX staked by validators. Only those who stake AVAX can validate transactions; malicious actors risk their staked assets being slashed (Slashing). The more AVAX staked, the higher the network’s security—creating a self-reinforcing security model.
Why Buy AVAX on Gate?
Gate is an established crypto exchange offering deep liquidity for AVAX trades, transparent price discovery, and robust security measures. You can easily purchase AVAX on Gate then withdraw to a self-custody wallet for staking or DeFi participation—the entire process is secure, reliable, and cost-transparent.
Glossary of Key Avalanche (AVAX) Terms
- Subnet: An independent blockchain on Avalanche with customizable validator sets and rules—enables tailored application deployments.
- Validator: A node that stakes AVAX to participate in network consensus—responsible for validating transactions and blocks.
- Staking: The mechanism where users lock up AVAX tokens to gain validation rights and earn rewards.
- Gas Fee: The fee paid in AVAX for executing transactions or smart contracts on Avalanche.
- Smart Contract: Self-executing programs running on Avalanche virtual machines—powering DeFi applications.
- Consensus Mechanism: Avalanche uses Proof of Stake, where validators vote to achieve network consensus.
Further Reading & References on Avalanche (AVAX)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Trusted Media / Research:
Related Articles

The Future of Cross-Chain Bridges: Full-Chain Interoperability Becomes Inevitable, Liquidity Bridges Will Decline

Solana Need L2s And Appchains?
