What is Fartcoin?

What Is FartCoin (FART)?
Critical disambiguation: This page describes a Base-network ERC-20 token using the ticker FART. Multiple unrelated tokens use the name “FartCoin” (and sometimes the same ticker) across different blockchains. Before trading or interacting, users must confirm the network (Base) and the exact contract address. Failure to do so is one of the most common causes of user loss.
This FartCoin is marketed as a community-oriented token intended for cultural and social interaction scenarios, such as tipping, participation rewards, or symbolic transfers within online communities. It is a token issued on an existing blockchain, not a standalone cryptocurrency with its own independent consensus layer.
At a glance (verify each field):
| Attribute | Reported detail | How to verify |
|---|---|---|
| Network | Base (Ethereum Layer 2) | Check the token’s contract page on a Base block explorer |
| Token standard | ERC-20 | Confirm standard functions on the contract page |
| Ticker | FART | Match ticker + contract address together |
| Max supply | 69,420,000,000 (reported) | Review totalSupply behavior and mint permissions |
| Primary risks | Identity confusion, liquidity, volatility | Compare venues, spreads, and on-chain data |
For beginners: Base is an Ethereum Layer 2 network designed to reduce transaction fees and increase throughput. Layer 2 security depends on the network’s design (bridge architecture, sequencer operation, and verification or proof mechanisms) and its operational assumptions. ERC-20 is the most widely used token standard in the Ethereum ecosystem. Gas fees are transaction costs paid in ETH when interacting on Base.
Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of FartCoin (FART)
Based on publicly visible market data and project statements as of 2025-03-10, this Base-network FART token appeared to be in an early market phase with limited liquidity and variable pricing conditions. These figures are historical and may no longer reflect current conditions.
Metric definitions:
- Price: The most recent traded value of one token on a given venue.
- Market Cap: Price multiplied by circulating supply.
- Fully Diluted Market Cap (FDV): Price multiplied by the reported maximum or total supply.
- Circulating Supply: Tokens currently available for trading, excluding locked or unreleased balances.
The project reports a maximum supply of 69,420,000,000 tokens. Users should confirm this by checking the token’s contract page on a Base block explorer and verifying both (1) whether the source code is verified and (2) whether minting or administrative functions exist that could alter supply.
Data source and date: Based on publicly visible market data and project statements as of 2025-03-10. All values are subject to change and should be verified using current exchange pages and on-chain explorers.
Who Created FartCoin (FART) and When?
Community disclosures suggest the token began circulating in late 2024. This timing should be independently verified by reviewing the contract deployment date and earliest observable on-chain activity (such as first transfers or initial liquidity events) on Base.
The project presents itself as community-driven. Public communications and resource links are aggregated through community channels. As with all similarly named tokens, users should confirm that any referenced materials correspond to the same Base-network contract address.
Why timing matters: Early circulation periods often involve concentrated ownership, thin liquidity, and elevated volatility. These factors materially increase execution and custody risk.
How Does FartCoin (FART) Work?
FartCoin follows the ERC-20 standard and uses smart contracts to manage balances and transfers. Transactions occur on Base, with gas fees paid in ETH. Trading may occur on centralized spot markets (where listed) or via decentralized exchanges on Base.
Any claims about fixed supply or non-mintability should be treated as reported until validated by examining the contract’s functions and permissions on a block explorer.
Key concepts:
- Contract address: The definitive identifier of the token on-chain.
- Slippage: The difference between expected and executed price, often higher in low-liquidity conditions.
- Total transaction cost: Exchange fees plus on-chain gas fees.
What Are the Use Cases for FartCoin (FART)?
FartCoin is marketed for community-oriented social use. Any practical utility depends entirely on voluntary adoption, integrations, and ongoing community participation, all of which can change over time.
Commonly cited examples:
- Distribution as participation rewards during community events.
- Peer-to-peer tipping between users.
- Symbolic or commemorative use within Base-ecosystem applications.
Wallets and Extensions in the FartCoin (FART) Ecosystem
FART can be managed using Base-compatible wallets for sending, receiving, and signing transactions. Base block explorers allow users to review balances, transfers, and contract details.
- Wallets & signing tools: Used to custody tokens and approve transactions.
- Cross-chain transfer tools: Used to move assets from Ethereum mainnet or other networks onto Base.
- Data query tools: Block explorers for verifying addresses, transfers, and token supply behavior.
Security note: Always verify URLs, contract addresses, and wallet prompts. Phishing and fake token contracts are common in meme-token ecosystems.
Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for FartCoin (FART)
- Price and liquidity risk: Early-stage community tokens can experience extreme volatility, wide spreads, and high slippage.
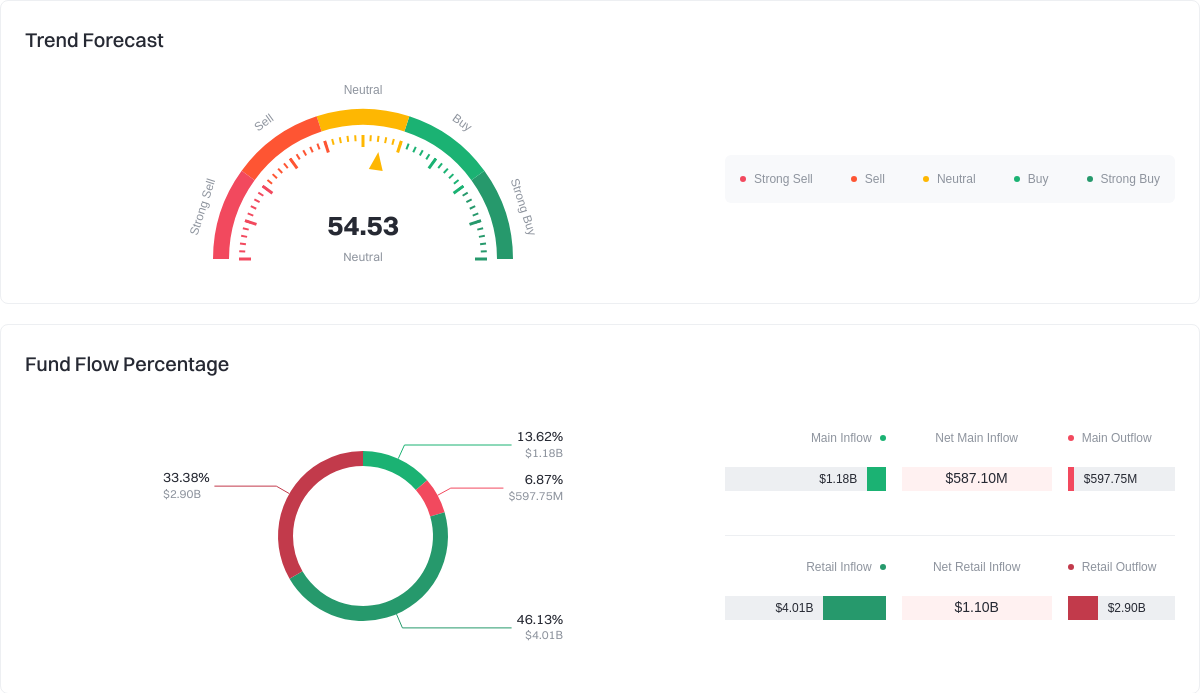
Click to view FART fund flow breakdown
- Contract and counterfeit risk: Name and ticker collisions increase the likelihood of interacting with the wrong token.
- Wallet and private key security: Losses resulting from compromised keys or approvals are often irreversible.
- Account and compliance considerations: Trading on centralized platforms may require identity verification and compliance with local regulations.
- Project execution risk: Community engagement, transparency, and liquidity management directly affect usability and market behavior.
What Is the Long-Term Value Proposition of FartCoin (FART)?
Long-term outcomes depend on sustained community participation, cultural relevance, and transparent operations. A reported fixed supply does not guarantee appreciation. Users should evaluate adoption signals, on-chain activity, and governance practices rather than relying on narratives alone.
How Can I Buy and Securely Store FartCoin (FART) on Gate?
Step 1: Account setup.
Register a Gate account and complete identity verification if required for your jurisdiction and intended features (such as trading or withdrawals).
Step 2: Fund your account.
Deposit or purchase USDT. A small amount of ETH may be required for gas fees if transferring assets on Base.
Step 3: Locate FART.
Search for FART in Spot Trading. If listed, confirm the network and contract identifiers before placing orders.
Step 4: Choose an order type.
- Market order: Immediate execution, potentially higher slippage.
- Limit order: Price control, but execution is not guaranteed.
Step 5: On-chain alternatives.
If not listed, users may trade via decentralized exchanges on Base after confirming the correct contract address and setting conservative slippage limits.
Step 6: Secure storage.
- Self-custody: Back up seed phrases offline; consider hardware wallets.
- Account security: Enable two-factor authentication and anti-phishing protections.
How Is FartCoin (FART) Different from Dogecoin?
| Category | Dogecoin (DOGE) | FartCoin (FART) on Base |
|---|---|---|
| Asset type | Standalone blockchain coin | ERC-20 token on Base |
| Consensus / settlement | Proof-of-Work | Layer 2 settlement with design-dependent security assumptions |
| Supply model | Inflationary | Reported fixed cap (verify on-chain) |
| Market maturity | Longer history, deeper liquidity | Earlier-stage, higher volatility risk |
Summary of FartCoin (FART)
This article covers a Base-network ERC-20 token using the ticker FART. Because similarly named tokens exist, correct identification is the highest-priority safety step. Users should independently verify the contract address, supply behavior, and liquidity conditions before trading or custody. Participation carries elevated volatility and execution risk typical of early-stage community tokens.
FAQ
Is FartCoin suitable for beginners?
Due to high volatility and identity-confusion risk, it is generally unsuitable for beginners with low risk tolerance. Only discretionary funds should be used.
How liquid is FartCoin trading?
Liquidity varies significantly by venue and time. Thin order books can result in substantial slippage, especially for large orders.
How do I verify the authenticity of a FartCoin contract?
Confirm the network (Base), obtain the contract address from project channels, and cross-check it on a Base block explorer. Verify whether source code is published and whether the address matches what exchanges list.
How influential is the FartCoin community?
Community activity can influence visibility and short-term demand, but users should prioritize on-chain data and transparency over social momentum.
What are the technical features of FartCoin?
FartCoin uses standard ERC-20 mechanics. Innovation, if any, is typically social rather than protocol-level.
Glossary of Terms Related to FartCoin (FART)
- Meme Coin: A cryptocurrency driven primarily by community and cultural narratives.
- Total Supply: The total number of tokens defined by the contract.
- Liquidity: The ease of buying or selling without significant price impact.
- Trading Pair: Two assets quoted together, such as FART/USDT.
- Market Cap: Price multiplied by circulating supply.
Further Reading & References for FartCoin (FART)
External references (may include similarly named tokens): Confirm that each link corresponds to the same Base-network contract address before relying on it.
Related Articles

What Are Altcoins?

What is Blum? All You Need to Know About BLUM in 2025
