What is GST Crypto?

What Is STEPN Green Satoshi Token on BSC?
STEPN Green Satoshi Token (GST) is a utility token used within the STEPN application. In this context, the article refers specifically to the token’s deployment on BNB Smart Chain (BSC), where GST exists as a BEP-20 token.
GST is generated through activity sessions recorded and validated by the STEPN application according to its anti-cheat mechanisms and session rules, which are subject to change over time. The token is primarily used for in-app actions such as upgrading, repairing, and minting NFT sneakers.
STEPN operates a dual-token structure. GST is intended for operational and activity-related usage, while GMT (Green Metaverse Token) is used for governance-level participation, including voting and access to certain advanced features. The platform also includes an integrated wallet, marketplace, and sneaker rental functionality to support user onboarding.
Quick Definition
Green Satoshi Token (GST) is a BEP-20 utility token used within the STEPN move-to-earn application on BNB Smart Chain. It is earned through activity sessions recorded by the app and is primarily consumed through predefined in-app actions such as upgrades, repairs, and minting.
What Are the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of STEPN Green Satoshi Token on BSC (GST)?
Market data is time-sensitive. The following table reflects a snapshot as of January 27, 2026, based on the provided dataset, and figures may differ across venues and over time.
| Metric | Value | Context |
|---|---|---|
| Latest Price | $0.001228 | Reported spot price at snapshot time |
| Circulating Supply (reported) | 1,147,161,857 GST | Estimated circulating amount reported by the data source |
| Total Supply (reported) | 1,157,161,857 GST | Total amount reported by the data source |
| Maximum Supply (reported) | 1,157,161,858 GST | A cap may be shown for this token version by the data source; contract details should be verified before treating this as a hard limit |
| Market Capitalization | $1,420,994.76 | Derived from reported circulating supply and price |
| 24h Trading Volume | $8,069.85 | Aggregate reported exchange activity |
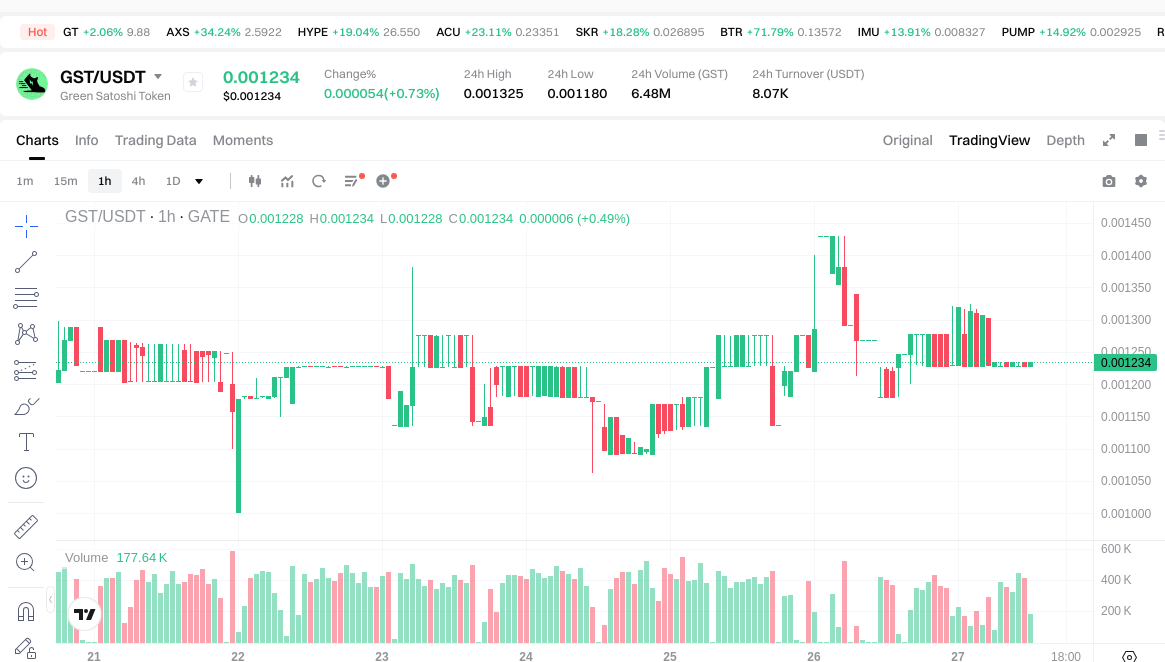
View GST USDT Price
The reported circulating supply in this snapshot is close to the reported total supply. This comparison reflects the data source at a specific point in time and should not be interpreted as a protocol-level guarantee.
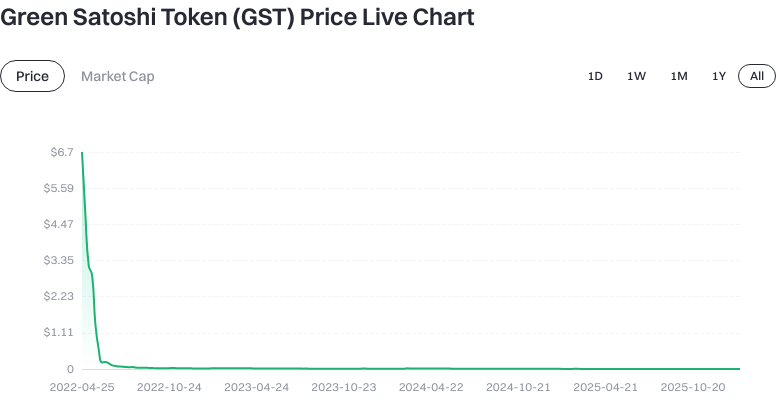
Who Created STEPN Green Satoshi Token on BSC (GST), and When?
GST was introduced by Find Satoshi Lab as part of the STEPN project, which combines mobile fitness tracking with blockchain-based incentives. The application initially launched on the Solana network and later expanded to BNB Smart Chain as part of a multi-network deployment strategy.
Public documentation and third-party reporting indicate that STEPN’s broader user adoption occurred primarily between 2021 and 2022, following its availability through mainstream mobile app stores. Earlier dates referenced in some datasets are typically associated with technical or registry records rather than public ecosystem activity.
The separation of GST (utility) and GMT (governance) was implemented to distinguish operational usage from governance participation. Features such as sneaker rentals and activity validation mechanisms were introduced progressively.
How Does STEPN Green Satoshi Token on BSC (GST) Work?
GST is generated when users complete eligible activity sessions recorded by the STEPN application. Earnings depend on sneaker attributes and system parameters defined by the platform.
GST may be used in the following in-app actions:
- Sneaker upgrades: Modifying attributes that affect in-app performance.
- Minting new sneakers: Combining GST with other NFTs to create additional assets.
- Repairs and enhancements: Actions that restore durability or adjust sneaker characteristics.
These actions follow STEPN’s in-app rules and token-sink mechanics. Depending on the specific function, GST may be burned or otherwise allocated according to predefined logic. On BSC, GST conforms to the BEP-20 standard, enabling compatibility with common wallets and exchanges.
What Can STEPN Green Satoshi Token on BSC (GST) Be Used For?
GST is primarily used within the STEPN application environment. Its functions include enabling sneaker upgrades, repairs, minting, and interaction with enhancement systems.
Although GST can be transferred and traded as a blockchain asset, its designed utility is closely tied to application-level usage rather than general-purpose payment activity.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations of STEPN Green Satoshi Token on BSC (GST)?
- Market data variability: Reported prices and volumes may differ across venues and timeframes.
- Protocol changes: Adjustments to reward formulas or consumption rules can alter usage patterns.
- Technical dependencies: Smart contracts and cross-chain infrastructure introduce operational considerations.
- Regulatory treatment: Legal classification of tokens and NFTs varies by jurisdiction.
- Custody responsibility: Users are responsible for account and key security when using non-custodial wallets.
What Drives the Long-Term Value of STEPN Green Satoshi Token on BSC (GST)?
GST demand is influenced by participation levels within the STEPN application and the frequency of in-app actions that require token usage.

Relevant indicators include user activity, retention trends, and the balance between reported issuance and consumption. Multi-chain deployment reduces reliance on a single network, but demand remains application-dependent.
Key Takeaways
- GST is a BEP-20 utility token used within the STEPN application on BNB Smart Chain.
- It is earned through activity sessions recorded by the app and used for predefined in-app actions.
- GST and GMT serve distinct roles, separating operational usage from governance participation.
- Reported supply and market data are snapshot-based and may vary across sources.
FAQ
How Is GST Token Different from Regular Goods & Services Tax (GST)?
GST in this context refers to Green Satoshi Token, a blockchain-based digital asset. It is unrelated to government Goods & Services Tax systems.
What Are the Main Uses of GST Token?
GST is used for in-app actions such as sneaker upgrades, repairs, minting, and enhancements within the STEPN ecosystem.
What Risks Should I Watch for When Holding GST Token?
Potential risks include changes to application mechanics, regulatory developments, variable market data, and digital asset custody responsibilities.
Where Should Beginners Buy GST Tokens?
GST is available on platforms that list the BSC version of the token, subject to platform-specific requirements.
What Factors Most Affect GST Token Price Volatility?
Reported price movements are influenced by application usage levels, exchange liquidity conditions, and broader digital asset market activity.
Key Terms Related to GST (GST)
- Move-to-Earn: A blockchain application model where users receive digital tokens based on recorded physical activity.
- NFT Sneakers: Non-fungible tokens representing in-app footwear assets that determine eligibility and parameters for earning GST.
- Token Consumption: The use of tokens within predefined application functions, such as upgrades or repairs, according to platform rules.
- Activity Validation: The process by which the application records and evaluates activity sessions using its internal rules and anti-cheat mechanisms.
- Liquidity Mining : A DeFi mechanism where users provide trading liquidity to earn transaction fees or token incentives.
- Smart Contract : Self-executing blockchain programs that enforce rules and process token actions automatically.
References & Further Reading on GST (GST)
- Official site: https://www.stepn.com/
- Whitepaper: https://stepn.gitbook.io/whitepaper/
- Developer repository: https://github.com/stepn-dev
- Documentation: https://docs.stepn.com/
- Media coverage: https://www.coindesk.com/business/2022/05/13/stepn-raises-25m-in-series-b-funding/
- Market analysis: https://www.theblock.co/post/148373/stepn-gst-token-drops-90-percent-from-ath
Related Articles

In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium

Sui: How are users leveraging its speed, security, & scalability?
