What is MDT coin?
What Is Measurable Data Token (MDT)?
Measurable Data Token (MDT) is a blockchain-based token designed to enable the anonymous exchange of big data value. MDT incentivizes data contributors and acts as a payment and settlement tool for data purchasers. Its core aim is to quantify and fairly trade user data, connecting users, data providers, and buyers to build a transparent data marketplace.
The blockchain functions as a distributed ledger, where transactions are recorded by multiple nodes. Decentralization means that no single entity can arbitrarily alter records or block accounts. MDT circulates as a token within this network, serving roles in pricing, payment, and rewards.
What Are the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of MDT?
As of January 23, 2026, MDT is priced at approximately $0.012957 per token, with a circulating market cap around $12,957,000 and a circulating supply of roughly 606,319,736 tokens out of a total supply of 1,000,000,000. In the last hour, MDT saw a price increase of about 0.02%; over 24 hours, up 2.45%; over 7 days, down 1.77%; and over 30 days, down 2.56%. The 24-hour trading volume stands at approximately $21,245.
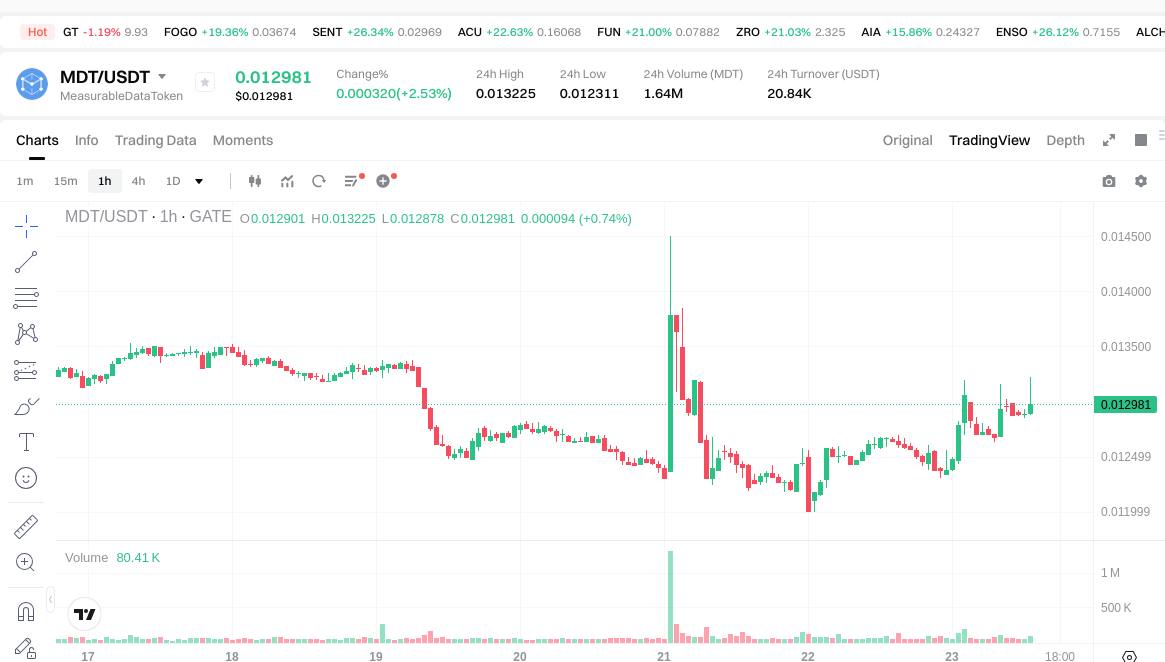
Click to view MDT USDT Price
Circulating market cap is calculated as “current price × circulating supply”; fully diluted market cap uses “current price × total theoretical supply”. Trading volume reflects the total value exchanged within a set period. Currently, MDT is marked as “inactive,” indicating low trading activity and possible risks such as limited order book depth and slippage. Slippage refers to the difference between expected and executed prices, common in markets with low liquidity.
Who Created Measurable Data Token (MDT) and When?
MDT was launched in 2018 by the MeasurableData project team, with MDT serving as the unified unit for data contribution incentives and transaction settlement. Its vision is to allow everyday users to receive fair value distribution from their anonymous data under compliance requirements, addressing transparency and fairness issues in traditional data trading.
Public information (as of October 2024) shows MDT initially focused on data consumption insights, rewarding contributors for anonymized data and settling purchases, gradually expanding its ecosystem partnerships and integration interfaces.
How Does Measurable Data Token (MDT) Work?
MDT leverages smart contracts to handle token issuance and transfers, recording data transactions and reward distributions. A smart contract is an on-chain program that automatically executes payments or settlements when preset conditions are met—eliminating manual approval.
The ecosystem operates as follows: Data contributors submit anonymized data through compliant channels; platforms or purchasers price the data and settle payments using MDT; rewards are distributed to users' wallets based on their contributions; all settlement records are traceable and immutable, enhancing transparency and auditability.
The total supply of MDT is capped at one billion tokens, with about 606 million currently circulating. Project rules balance incentive efficiency and long-term supply constraints to mitigate the impact of over-inflation on price stability and rewards.
What Can You Do With Measurable Data Token (MDT)?
MDT serves three main use cases:
- Rewards & Incentives: Users share anonymized data and receive MDT rewards according to contribution rules.
- Settlement & Access: Data purchasers pay with MDT to access efficient consumer insights or data services.
- Governance & Ecosystem Collaboration: In select applications, MDT functions as a governance or rights token, enabling partners to participate in data trading and settlement processes.
For example, a brand seeking regional consumer trends can compliantly purchase aggregated anonymous data and pay with MDT; contributors receive proportional rewards, promoting fair value distribution.
What Wallets and Expansion Solutions Exist in the MDT Ecosystem?
Wallets manage token assets and sign transactions. Common options include browser extension wallets and mobile wallets for convenience; hardware wallets offer enhanced offline security. Private keys control asset ownership; mnemonic phrases serve as readable backups of private keys—both must be securely stored to prevent irreversible loss.
Ecosystem extensions include:
- Data interfaces & partner applications: Standardized tools for data suppliers and buyers to connect and settle.
- Compliance tools & privacy technologies: Support for data anonymization, access control, and compliance auditing to reduce privacy risks.
- Developer support: Documentation and SDKs facilitate third-party integration of MDT settlements into their products.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for MDT?
Market volatility: Crypto asset prices are highly sensitive to supply-demand dynamics and market sentiment, with short-term fluctuations common.
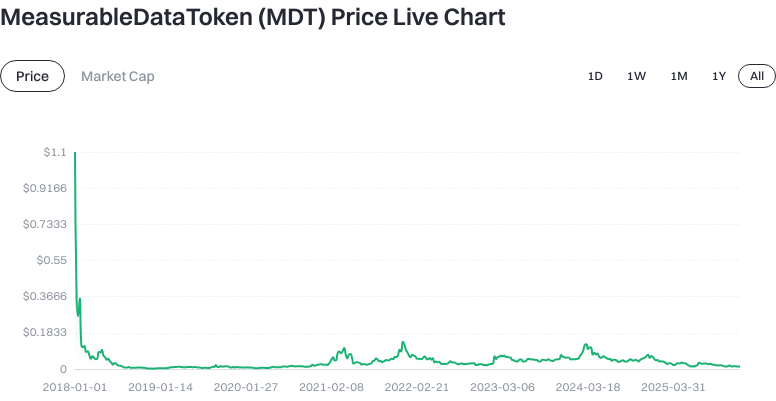
Click to view Latest MDT Price
Liquidity risk: Low current activity may result in slippage and wide bid-ask spreads; pay attention to order book depth before trading.
Smart contract & technical risk: Vulnerabilities in contracts or integrated apps could lead to settlement errors or asset losses.
Privacy & compliance risk: All data contributions and purchases must adhere to local privacy and data protection laws—illegal collection or use must be avoided.
Exchange custody risk: Holding assets on exchanges poses platform and account security risks; enable two-factor authentication and consider self-custody wallets for long-term storage.
Personal operation risk: If your private key or mnemonic phrase is lost or leaked, assets cannot be recovered. Always keep encrypted offline backups and restrict access.
How Can I Buy and Securely Store MDT on Gate?
Step 1: Register an account on Gate (gate.com) and complete identity verification (KYC). KYC stands for “Know Your Customer”—submit identification documents and face verification as required for compliance and account security.
Step 2: Fund your account. Use Gate's fiat deposit channels or transfer USDT or other stablecoins from your personal wallet. USDT is a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar, commonly used as a base asset for trading pairs.
Step 3: Search for the MDT trading pair and place an order. On Gate's spot market, find MDT/USDT and choose between limit or market orders. Spot trading means buying or selling actual tokens at current market prices.
Step 4: Withdraw tokens to your personal wallet. After purchase, withdraw MDT to a self-managed wallet to reduce centralized custody risks. Confirm the withdrawal network, minimum amount, and fees—test first with a small transfer.
Step 5: Configure security settings. Enable account two-factor authentication and address whitelisting; use hardware wallets or trusted software wallets for storage; keep mnemonic phrases and private keys encrypted offline—never store them online or via screenshots.
How Does MDT Differ From Ocean Protocol?
Positioning: MDT focuses on incentivizing and settling anonymous consumer and behavioral data contributions—making both contributions and purchases transparent. Ocean Protocol is more oriented toward foundational data marketplace infrastructure and data asset tokenization, offering tools like data NFTs and access controls.
Technology & features: MDT centers on token-based incentives and settlements around anonymized data contributions; Ocean Protocol enables packaging datasets into tradable assets with broader development frameworks for governance.
Ecosystem pathways: MDT forms a closed trading loop between suppliers, buyers, and integrated applications; Ocean Protocol promotes a toolchain-driven marketplace for developers and institutions to build diverse data services on its protocol.
Risk structure: MDT’s risks center on adoption rates and liquidity; Ocean Protocol faces challenges in regulatory compliance and technical implementation due to its complex features. Both projects must prioritize privacy regulations and manage market volatility.
Summary of Measurable Data Token (MDT)
Measurable Data Token aims to standardize and bring transparency to the contribution, pricing, and settlement of anonymous big data using blockchain technology—enabling collaboration between users, suppliers, and buyers within a single value network. Currently, MDT's price and market cap reflect its status as a mid-to-small scale token with low trading activity; traders should monitor liquidity and slippage closely. Understanding how MDT works and its practical use cases can help determine its role in the evolving data economy. If considering participation, follow step-by-step purchasing procedures on Gate while prioritizing wallet and private key security. Diversify your portfolio according to your own risk tolerance, stay updated on compliance developments, ecosystem progress, and real-world adoption of data consumption solutions.
FAQ
What Is MDT Token?
MDT Token is a blockchain-based digital asset representing specific project utility or rights. It is typically traded on decentralized exchanges or platforms like Gate. Holders may participate in project governance or earn ecosystem rewards. Understanding MDT’s use cases and issuer background can help assess its investment value.
Where Can I Buy MDT Token?
MDT tokens are available on major crypto exchanges such as Gate and Binance. Register an account, complete identity verification, fund with stablecoins or other mainstream assets, then search for MDT trading pairs to buy or sell. For best prices, choose trading pairs with high liquidity.
What Are the Real-World Use Cases for MDT Token?
MDT’s use cases depend on its project positioning. Common applications include: serving as an in-ecosystem payment medium, participating in governance votes, or redeeming specific services. Refer to the official MDT whitepaper or community resources for details on ecosystem plans.
What Risks Should I Consider When Investing in MDT?
Crypto investments involve high price volatility as well as project-specific and technical risks. As a smaller-cap token, MDT may have limited liquidity—slippage is possible when trading; always monitor project updates and community reputation. Invest only what you can afford to lose—practice sound risk management.
What Is the Supply And Inflation Mechanism for MDT?
MDT’s total supply, circulating supply, and inflation mechanism are determined by the project team—this information is usually publicly available on the official website or blockchain explorer. Lower supply with stable circulation tends to offer stronger inflation resistance; review these metrics before trading to assess long-term value.
Quick Reference Glossary for Measurable Data Token (MDT)
- Liquidity mining: A mechanism where users provide token liquidity to trading pairs in exchange for transaction fee rewards and platform incentives.
- Tokenomics: Rules governing token issuance, distribution, destruction, etc., designed to incentivize ecosystem participation.
- Circulating-to-diluted market cap ratio: The ratio between circulating market cap and fully diluted market cap—reflects dilution risk.
- Order book depth: The quantity and value of buy/sell orders for a given trading pair on an exchange—affects slippage magnitude.
- Token release schedule: The planned timeline for token unlocks/distribution—impacts supply changes and price trends.
Measurable Data Token (MDT) References & Further Reading
-
Official Website/Whitepaper:
-
Developer Docs:
-
Trusted Media/Research:
Related Articles

The Future of Cross-Chain Bridges: Full-Chain Interoperability Becomes Inevitable, Liquidity Bridges Will Decline

Solana Need L2s And Appchains?
