What is VET coin?

What Is VeChain?
VeChain is an enterprise-focused blockchain network, with VET serving as its native token on the mainnet. VET is used for value transfer, network incentives, and participation in ecosystem activities. VeChain adopts a dual-token model: VET functions as the store of value, and by holding VET, users generate VTHO according to protocol rules. VTHO is a utility token used to pay on-chain “gas fees” for executing transactions and smart contracts. VeChain prioritizes efficiency, stability, and regulatory compliance, aiming for real-world adoption in areas such as supply chain management, anti-counterfeiting traceability, and sustainability.
What Are the Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply of VeChain (VET)?
As of 2026-01-23 (data provided in the prompt), key VeChain (VET) metrics are as follows: Latest price: $0.010430; Circulating market cap: $896,823,979.476110; Fully diluted market cap: $896,823,979.476110; Circulating supply: 85,985,041,177 VET; Total supply: 85,985,041,177 VET; Max supply: 86,712,634,466 VET; Market dominance: 0.028%; 24-hour trading volume: $259,493.162502. Recent volatility: 1 hour +1.25%, 24 hours -1.25%, 7 days -8.21%, 30 days +0.85%.
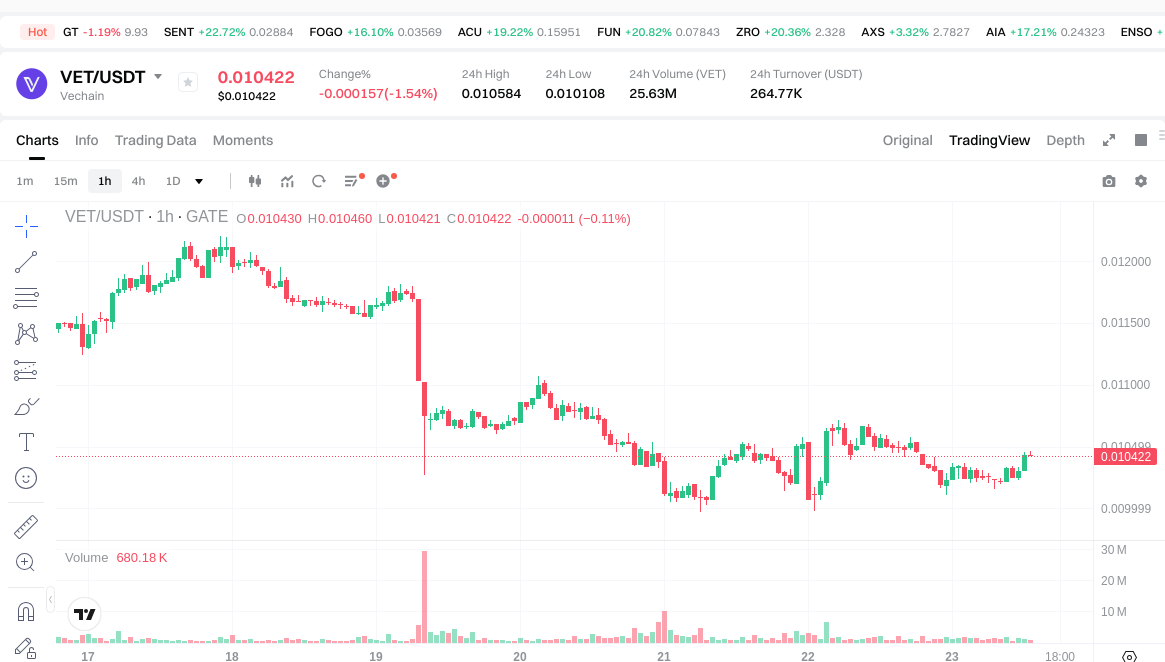
Click to view VET/USDT price
Market data updates in real time—always refer to the trading page for the latest price.
Who Founded VeChain (VET) and When?
VeChain was founded by Sunny Lu in 2015, initially focusing on enhancing transparency in supply chains and anti-counterfeiting traceability. The 2017 token launch and early enterprise applications laid the groundwork for the VeChainThor mainnet. VeChain has partnered with institutions such as DNV, Walmart, and Boston Consulting Group to drive pilot projects and scalable commercial adoption. Recent strategic directions include building Ethereum-compatible infrastructure, advancing a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) consensus mechanism, implementing a dynamic VTHO tokenomics model, and developing the StarGate NFT staking system. The project also emphasizes a token architecture compliant with EU MiCA regulations and cross-chain interoperability.
How Does VeChain (VET) Work?
VeChain operates as an enterprise-grade Layer-1 blockchain, meaning it functions independently at the protocol layer without relying on other blockchains. It aims for stability, high throughput, and low transaction costs. On the consensus layer, VeChain employs Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS), where token holders vote to delegate validators for block production, boosting efficiency. Its economic layer uses a dual-token model: VET serves for value storage and incentives, while VTHO pays gas fees. Gas costs are dynamically adjusted based on network demand to ensure predictable expenses for businesses. The smart contract layer supports Ethereum compatibility (EVM compatibility), making it easy to migrate contracts and tools from the Ethereum ecosystem. Cross-chain solutions enable seamless data and asset transfers across multiple blockchains.
What Can VeChain (VET) Be Used For?
In supply chain and anti-counterfeiting applications, brands can assign each product a unique on-chain identity. Users can scan codes to access critical data on raw materials, quality inspections, logistics, and temperature control—reducing counterfeiting and information asymmetry. For sustainability and carbon management, enterprises can record emissions data on-chain for verification and disclosure purposes. In compliance and certification scenarios, third-party organizations can upload audit records and certificates to increase trust and traceability. Developers and businesses can deploy smart contracts for loyalty programs, ticketing systems, or IoT device data management; VTHO covers transaction fees for predictable budgeting.
What Wallets and Expansion Solutions Exist in the VeChain (VET) Ecosystem?
Wallet options include official wallets (browser extensions and mobile apps) for managing VET and VTHO—enabling transaction signing and DApp interactions. Hardware wallets can also be used for offline private key storage to enhance security. Block explorers allow users to query transactions, contracts, and addresses—facilitating auditability and traceability. For enterprises, SaaS tools enable low-barrier onboarding of supply chain or certification data onto the blockchain while integrating with existing IT workflows. Cross-chain functionality and Ethereum compatibility make it easier for developers to migrate existing contracts and front-end tools—accelerating the journey from prototype to production.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for VeChain (VET)?
Technical and roadmap risks: Upgrades to consensus mechanisms or tokenomics require long-term stability testing—unexpected bugs or delays may impact network usability. Commercial adoption risk: Enterprise projects often involve long cycles and complex integrations; slower-than-expected partnerships may affect real-world demand for the network. Regulatory risk: Evolving local policies could impact token trading, accounting treatment, or cross-border data flows; while VeChain emphasizes MiCA compliance, ongoing monitoring of regulatory implementation is needed. Market and liquidity risk: VET’s price is influenced by market sentiment—shifts in trading depth or volume can impact execution costs. Operational security risk: Exchange accounts should use two-factor authentication; self-custody wallets require secure backup of seed phrases/private keys—loss is usually irreversible. Beware of phishing links and counterfeit wallets.
How Can I Buy and Securely Store VeChain (VET) on Gate?
Step 1: Register and complete identity verification. Visit gate.com to open an account and follow KYC procedures to increase your account limits and withdrawal rights.
Step 2: Deposit funds or transfer assets in. You can buy crypto with fiat or deposit stablecoins like USDT—then swap for VET in the spot market. Ensure your funding method matches your account name to avoid delays.
Step 3: Search for trading pairs and place an order. On the spot trading page, search “VET” and select pairs such as VET/USDT. Choose between limit (set your own price) or market orders (execute at current price), enter your desired amount, and submit.
Step 4: Review holdings and manage risk. After purchase, check your VET balance under assets. Consider averaging into positions or setting take-profit/stop-loss orders (where available) to mitigate volatility risk.
Step 5: Withdraw to a self-custody wallet (optional). For long-term holding or full control over your assets, transfer VET to your personal wallet. Select the correct “VeChainThor” network when withdrawing; test with a small amount first before transferring larger sums.
Step 6: Secure storage and backup. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA), anti-phishing codes, and login alerts on your account. For self-custody wallets, securely store your seed phrase/private key offline—never screenshot or upload it to cloud storage; write it down and keep copies in separate safe places.
What Is the Difference Between VeChain (VET) and VeThor (VTHO)?
Use cases: VET is a store of value and incentive token—reflecting economic interest in the network; VTHO is a utility token used solely for paying gas fees on-chain. Generation: Holding VET automatically generates VTHO according to protocol rules—for use in transactions or contract execution. Price drivers: VET’s value is mainly influenced by network growth and market sentiment; VTHO’s price is driven by on-chain usage demand and dynamic fee adjustments.
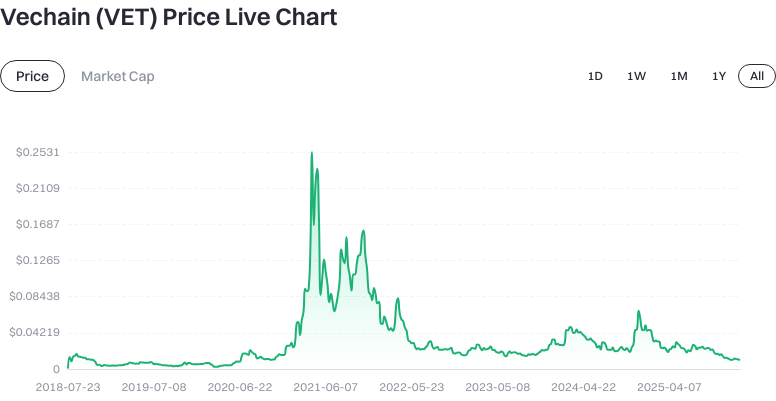
Click to view latest VET price
Target users: Those interested in ecosystem participation or long-term holding typically focus on VET; users who need frequent on-chain operations or development will hold some VTHO to cover costs. The two tokens work together to support network operations.
Summary of VeChain (VET)
VeChain (VET) positions itself as an enterprise-grade Layer-1 blockchain that separates value storage from usage costs via a dual-token model: VET handles value/incentives while VTHO covers transaction fees. With Ethereum compatibility, cross-chain interoperability, and a compliance-focused architecture, VeChain prioritizes real-world applications in supply chain management, anti-counterfeiting, and sustainability sectors. Short-term price volatility is expected; long-term performance depends on enterprise adoption, ecosystem activity, and regulatory developments. If you’re considering participation, first understand the differences between VET and VTHO as well as fee structures—follow the outlined steps to purchase and securely store your tokens on Gate, while keeping up with technical upgrades, partnership progress, and regulatory updates. This information is for reference only—it does not constitute investment advice.
FAQ
What Is the Relationship Between VET and VTHO?
VET is the native token of the VeChain mainnet; VTHO is generated from holding VET as an “energy” token. Users holding VET automatically receive daily VTHO rewards that can be used to pay network transaction fees. In short: VET is your asset; VTHO is like “interest” earned from holding VET—they work together to lower on-chain costs.
Where Should Beginners Buy VET?
Major cryptocurrency exchanges such as Gate offer trading pairs for VET. The process is straightforward: register → complete identity verification → deposit fiat or other cryptocurrencies → search for VET in the trading section → place an order at your preferred price → withdraw your VET to your own wallet for safekeeping. Always choose reputable exchanges; after purchase, promptly transfer your tokens into a hardware or secure software wallet for safety.
Are There Ways to Earn Yield by Holding VET?
The main benefit is automatic generation of VTHO tokens—simply keep your VET in a supported wallet to receive about 0.000432 VTHO per VET daily. Some exchanges and DeFi platforms also offer staking programs for additional rewards—always assess platform risks and prefer established providers for safety.
Is VET Suitable for Long-Term Holding?
The investment potential of VET depends on VeChain’s ecosystem development and enterprise adoption progress. As an infrastructure chain focused on supply chain traceability, it offers real-world use cases—but crypto markets are highly volatile with prices affected by multiple factors. Long-term holders should carefully assess risk tolerance—invest only what you can afford to lose—and keep updated with project developments through regular research.
What Are the Real-World Applications of VET?
VET primarily enables transaction settlement and proof-of-stake within the VeChain ecosystem. Enterprises use it to record supply chain data—such as product traceability, authentication, logistics tracking—on-chain. Individual holders can participate in governance voting or stake their tokens for yield opportunities. The core value of VET lies in expanding its application ecosystem and driving enterprise adoption.
VeChain (VET) Key Terms
- PoA Consensus Mechanism: Proof-of-Authority mechanism where authorized nodes validate transactions; more energy-efficient than Proof-of-Work.
- VTHO: The fuel token in the VeChain ecosystem—used to pay transaction fees and smart contract execution costs.
- Dual-token model: Separates value storage (VET) from fuel consumption (VTHO), stabilizing operational costs.
- Supply Chain Traceability: A primary use case for VeChain—blockchain records end-to-end production and circulation information.
- Smart Contract: Self-executing code that supports deployment of enterprise-grade applications on VeChain.
- Node Economy: Holding VET allows participation as a node operator to earn VTHO rewards—creating an incentive mechanism within the ecosystem.
Further Reading on VeChain (VET)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Developer Resources / Documentation:
-
Media / Research:
Related Articles

The Future of Cross-Chain Bridges: Full-Chain Interoperability Becomes Inevitable, Liquidity Bridges Will Decline

Solana Need L2s And Appchains?
