ETHS vs LRC: A Comprehensive Comparison of Ethereum Staking and Loopring Layer-2 Solutions in the DeFi Ecosystem

Introduction: Investment Comparison Between ETHS and LRC
In the cryptocurrency market, the comparison between ETHS vs LRC has become a topic that investors cannot ignore. The two differ significantly in market cap ranking, application scenarios, and price performance, representing distinct positioning within the crypto asset landscape.
ETHS: Since its launch in 2023, it has gained market recognition as the core asset of Facet, a decentralized Ethereum L1 scaling protocol funded by the Ethereum Foundation. ETHS serves as a pioneering asset driving the next generation of data and value layers.
LRC: Launched in 2017, Loopring has been positioned as a decentralized token exchange protocol based on ERC20 and smart contracts, enabling off-chain order matching and on-chain settlement without asset custody.
This article will comprehensively analyze the investment value comparison between ETHS vs LRC, focusing on historical price trends, supply mechanisms, institutional adoption, technological ecosystems, and future predictions, attempting to answer the question investors care about most:
"Which is the better buy right now?"
I. Historical Price Comparison and Current Market Status
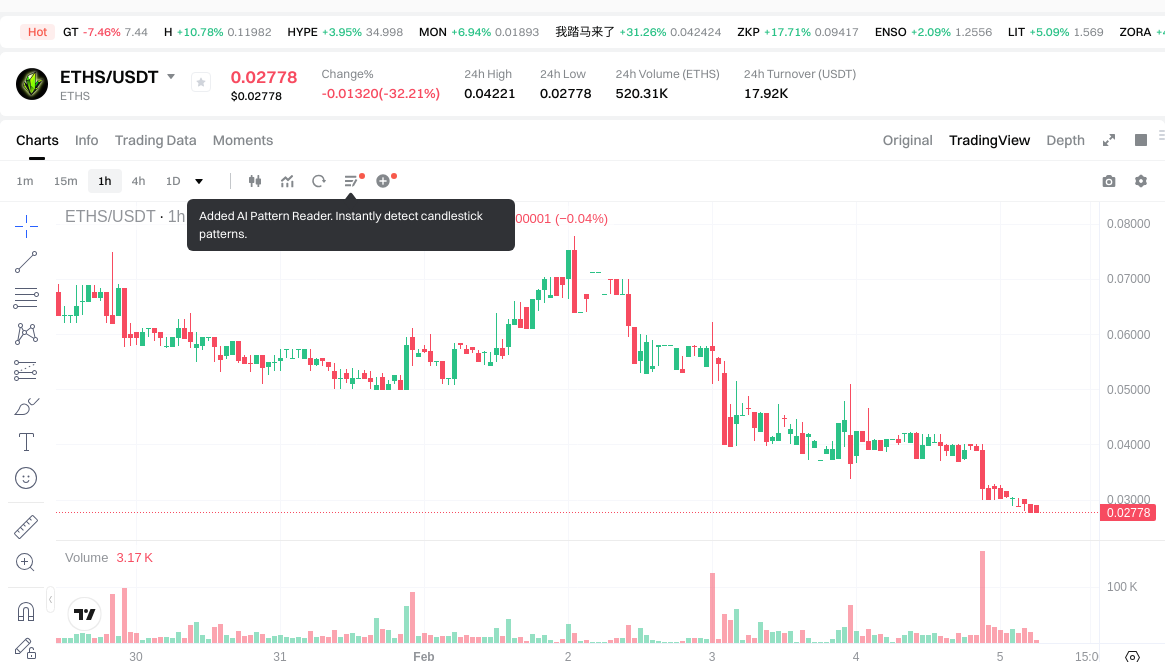
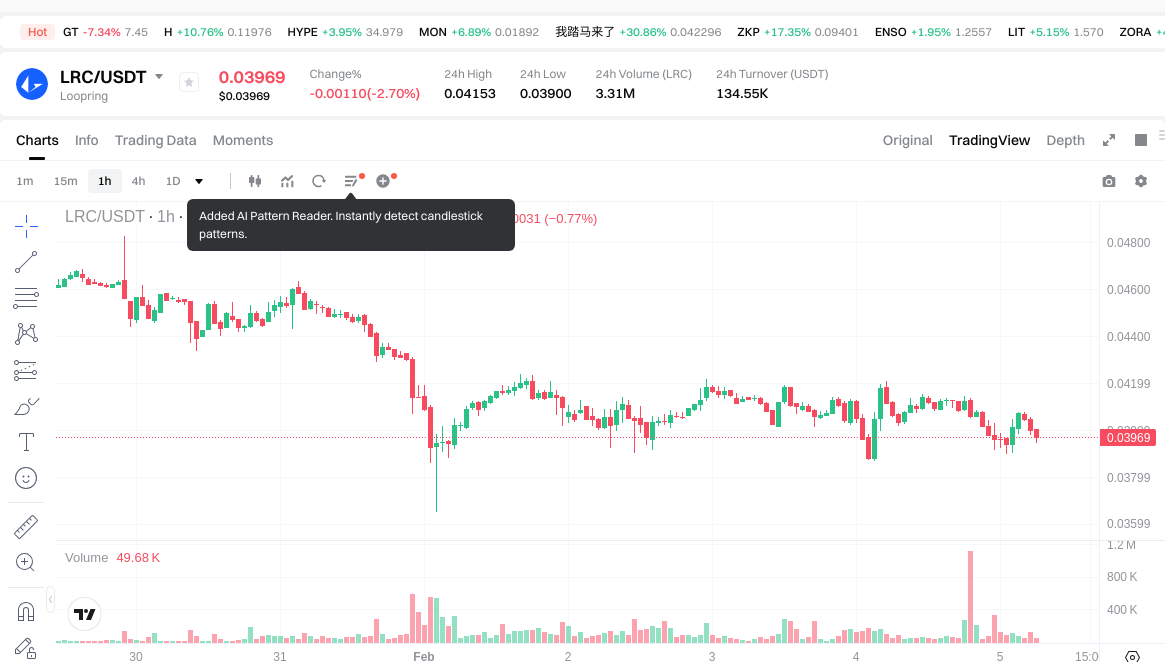
ETHS and LRC Historical Price Trends
- 2024: ETHS experienced significant volatility, reaching a historical high of $13.9 in January 2024, driven by its launch as the core asset of the Facet protocol, a decentralized Ethereum L1 scaling solution funded by the Ethereum Foundation.
- 2021: LRC saw substantial growth, achieving a historical high of $3.75 in November 2021, supported by increased adoption of Loopring's Layer 2 zkRollup technology and growing interest in decentralized exchange solutions.
- Comparative Analysis: During the subsequent market downturn, ETHS declined from its peak of $13.9 to $0.02778, representing a decrease of approximately 99.8%, while LRC decreased from its high of $3.75 to $0.01963893, reflecting a decline of approximately 99.5%.
Current Market Situation (February 5, 2026)
- ETHS Current Price: $0.02884
- LRC Current Price: $0.03952
- 24-Hour Trading Volume: ETHS $17,835.30 vs LRC $132,928.67
- Market Sentiment Index (Fear & Greed Index): 14 (Extreme Fear)
View real-time prices:
- View ETHS current price Market Price
- View LRC current price Market Price
II. Core Factors Influencing ETHS vs LRC Investment Value
Supply Mechanism Comparison (Tokenomics)
-
ETHS: Current supply mechanism details are not explicitly documented in available materials. As an inscription-based token protocol, ETHS follows the ethscriptions standard on Ethereum, which may involve fixed supply characteristics determined at deployment.
-
LRC: Loopring operates as a Layer 2 scaling solution with its native token supporting protocol operations. The token economics involve staking mechanisms and fee distribution models that align with network usage and transaction volume.
-
📌 Historical Pattern: Supply mechanisms in Layer 2 solutions typically influence price cycles through reduced circulating supply during high staking periods and network adoption phases.
Institutional Adoption and Market Application
-
Institutional Holdings: Layer 2 solutions like LRC have attracted attention from institutional investors seeking scalability solutions. ETHS, as an inscription protocol, represents a newer experimental approach with limited institutional presence to date.
-
Enterprise Adoption: LRC has established partnerships within decentralized exchange ecosystems, focusing on high-throughput trading infrastructure. ETHS remains primarily within the inscription and collectibles space, with applications centered on data storage on Ethereum.
-
Regulatory Environment: Both protocols operate within the broader Ethereum regulatory framework. Layer 2 solutions face evolving compliance requirements around transaction reporting, while inscription protocols navigate digital asset classification questions across different jurisdictions.
Technology Development and Ecosystem Building
-
ETHS Technical Evolution: Built on the ethscriptions protocol, ETHS utilizes Ethereum's data availability for inscribing content. The protocol's development focuses on storage optimization and calldata utilization efficiency.
-
LRC Technical Advancement: Loopring continues developing zero-knowledge proof technology for enhanced scalability and reduced transaction costs. The protocol emphasizes zkRollup improvements and cross-layer interoperability.
-
Ecosystem Comparison: LRC maintains established presence in DeFi through decentralized exchange infrastructure and trading protocols. ETHS operates within the emerging inscription ecosystem, with applications primarily in digital collectibles and data permanence. Neither protocol demonstrates extensive NFT marketplace integration or widespread smart contract deployment outside their core use cases based on current documentation.
Macroeconomic Environment and Market Cycles
-
Performance During Inflationary Periods: Layer 2 solutions typically benefit from increased network activity during market expansion phases. Inscription protocols exhibit correlation with broader crypto market sentiment and experimental asset interest.
-
Monetary Policy Impact: Interest rate environments affect risk appetite for speculative crypto assets. Both ETHS and LRC demonstrate sensitivity to liquidity conditions, though established infrastructure projects like LRC may show more stable institutional interest during tightening cycles.
-
Geopolitical Factors: Cross-border transaction demand influences Layer 2 adoption, particularly for protocols focused on payment and exchange infrastructure. Inscription protocols remain less directly impacted by international transaction flows, with value primarily driven by collector and community interest within specific blockchain ecosystems.
III. 2026-2031 Price Forecast: ETHS vs LRC
Short-term Forecast (2026)
- ETHS: Conservative $0.0228 - $0.0278 | Optimistic $0.0278 - $0.0319
- LRC: Conservative $0.0301 - $0.0396 | Optimistic $0.0396 - $0.0582
Mid-term Forecast (2028-2029)
- ETHS may enter a consolidation phase, with projected prices ranging from $0.0237 to $0.0392
- LRC may enter a growth phase, with projected prices ranging from $0.0526 to $0.0705
- Key drivers: institutional capital inflows, ETF developments, ecosystem expansion
Long-term Forecast (2030-2031)
- ETHS: Baseline scenario $0.0281 - $0.0365 | Optimistic scenario $0.0365 - $0.0586
- LRC: Baseline scenario $0.0655 - $0.0676 | Optimistic scenario $0.0676 - $0.0986
Disclaimer
ETHS:
| Year | Predicted High Price | Predicted Average Price | Predicted Low Price | Price Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2026 | 0.031947 | 0.02778 | 0.0227796 | -3 |
| 2027 | 0.0358362 | 0.0298635 | 0.018814005 | 3 |
| 2028 | 0.034820841 | 0.03284985 | 0.023651892 | 13 |
| 2029 | 0.03924900078 | 0.0338353455 | 0.022669681485 | 17 |
| 2030 | 0.0522553075902 | 0.03654217314 | 0.0281374733178 | 26 |
| 2031 | 0.058606337281932 | 0.0443987403651 | 0.034187030081127 | 53 |
LRC:
| Year | Predicted High Price | Predicted Average Price | Predicted Low Price | Price Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2026 | 0.058212 | 0.0396 | 0.030096 | 0 |
| 2027 | 0.06553404 | 0.048906 | 0.04254822 | 23 |
| 2028 | 0.0720972252 | 0.05722002 | 0.0526424184 | 44 |
| 2029 | 0.070477898634 | 0.0646586226 | 0.053020070532 | 63 |
| 2030 | 0.09864966050082 | 0.067568260617 | 0.06554121279849 | 70 |
| 2031 | 0.093913125431568 | 0.08310896055891 | 0.075629154108608 | 110 |
IV. Investment Strategy Comparison: ETHS vs LRC
Long-term vs Short-term Investment Strategies
-
ETHS: May appeal to investors interested in experimental inscription protocols and data storage innovations on Ethereum. The asset demonstrates characteristics associated with early-stage protocol development, with potential tied to broader adoption of inscription-based applications and collectibles ecosystems.
-
LRC: May suit investors seeking exposure to established Layer 2 scaling infrastructure with focus on decentralized exchange technology. The protocol's maturity since 2017 and integration within DeFi trading systems represent a different risk-reward profile compared to emerging inscription assets.
Risk Management and Asset Allocation
-
Conservative Investors: A balanced approach might consider LRC allocation given its longer operational history and established use cases within decentralized exchange infrastructure. Allocation consideration: ETHS 20-30% vs LRC 70-80% within crypto portfolios focused on Ethereum-based protocols.
-
Aggressive Investors: Higher risk tolerance may accommodate increased ETHS exposure for potential gains from inscription protocol adoption, while maintaining LRC positions for Layer 2 growth. Allocation consideration: ETHS 50-60% vs LRC 40-50% for speculative Ethereum ecosystem plays.
-
Hedging Tools: Stablecoin reserves for volatility management, diversification across multiple Layer 2 and infrastructure protocols, consideration of options strategies where available for downside protection.
V. Potential Risk Comparison
Market Risks
-
ETHS: Exposure to inscription protocol market cycles, with value significantly influenced by collector interest and experimental asset sentiment. Limited trading volume ($17,835.30 as of February 5, 2026) may result in liquidity challenges and price volatility during market stress periods.
-
LRC: Subject to Layer 2 competition dynamics and broader DeFi market conditions. While trading volume is higher ($132,928.67), the protocol faces ongoing competitive pressure from alternative scaling solutions and evolving Ethereum roadmap developments that may impact Layer 2 value propositions.
Technical Risks
-
ETHS: Protocol development focuses on calldata optimization and storage efficiency within the ethscriptions standard. Scaling limitations may emerge as inscription activity increases, and the experimental nature of the protocol presents uncertainties around long-term technical viability and ecosystem support.
-
LRC: zkRollup technology requires continuous development to maintain competitive transaction throughput and cost efficiency. Security considerations around zero-knowledge proof implementations and bridge infrastructure represent ongoing technical dependencies requiring sustained development resources.
Regulatory Risks
- Global regulatory frameworks continue evolving around digital asset classification, with potential differential treatment between Layer 2 infrastructure protocols and inscription-based assets. Exchange listing requirements, reporting obligations for decentralized protocols, and cross-border transaction compliance may impact both assets differently based on their respective use cases and operational characteristics.
VI. Conclusion: Which Is the Better Buy?
📌 Investment Value Summary:
-
ETHS Characteristics: Represents early-stage inscription protocol exposure with experimental positioning within Ethereum's data storage landscape. The asset has experienced significant price volatility, declining approximately 99.8% from its January 2024 peak, and currently trades at $0.02884 with limited trading volume.
-
LRC Characteristics: Established Layer 2 scaling protocol with operational history since 2017 and integration within decentralized exchange infrastructure. The asset has declined approximately 99.5% from its November 2021 peak and currently trades at $0.03952 with comparatively higher liquidity than ETHS.
✅ Investment Considerations:
-
Novice Investors: Consider focusing on understanding fundamental differences between inscription protocols and Layer 2 infrastructure before allocation. Both assets demonstrate high volatility characteristics, suggesting careful position sizing and risk management practices regardless of choice.
-
Experienced Investors: Evaluate allocation based on thesis regarding inscription protocol adoption versus Layer 2 scaling demand. LRC offers exposure to established DeFi infrastructure, while ETHS provides positioning in experimental data storage applications. Neither asset demonstrates clear superiority without consideration of individual risk tolerance and market view.
-
Institutional Participants: May find LRC's longer operational track record and established ecosystem presence more aligned with due diligence requirements, though both assets remain speculative relative to broader market capitalization cryptocurrencies. Infrastructure exposure through Layer 2 protocols may offer clearer use case documentation compared to inscription-based experimental assets.
⚠️ Risk Disclosure: Cryptocurrency markets exhibit extreme volatility. This analysis does not constitute investment advice. Both ETHS and LRC have experienced significant price declines exceeding 99% from historical peaks. Market conditions as of February 5, 2026 indicate "Extreme Fear" sentiment (Fear & Greed Index: 14). Investors should conduct independent research and consider personal financial circumstances before making allocation decisions.
VII. FAQ
Q1: What are the main differences between ETHS and LRC in terms of their core technology and use cases?
ETHS is an inscription-based protocol focused on data storage on Ethereum Layer 1, while LRC is a Layer 2 zkRollup scaling solution for decentralized exchanges. ETHS operates through the ethscriptions standard, utilizing Ethereum's calldata for inscribing content and prioritizing data permanence and storage optimization. Launched in 2023 as part of the Facet protocol, it primarily serves the digital collectibles and experimental asset space. In contrast, LRC, operational since 2017, leverages zero-knowledge proof technology to enable high-throughput trading infrastructure with off-chain order matching and on-chain settlement, positioning itself within the DeFi ecosystem as an exchange protocol solution.
Q2: Which asset has better liquidity and trading volume?
LRC demonstrates significantly better liquidity with a 24-hour trading volume of $132,928.67 compared to ETHS's $17,835.30 as of February 5, 2026. This approximately 7.5x difference in trading volume indicates that LRC offers more liquid markets for entry and exit positions. The higher liquidity of LRC stems from its longer operational history since 2017, broader exchange listings, and established presence within the DeFi trading ecosystem. ETHS, as a newer inscription protocol launched in 2023, faces liquidity constraints that may result in wider bid-ask spreads and increased slippage during transactions, particularly during periods of market volatility.
Q3: How have ETHS and LRC performed during market downturns?
Both assets have experienced severe drawdowns from their historical peaks, with ETHS declining approximately 99.8% from $13.9 to $0.02778, and LRC falling approximately 99.5% from $3.75 to current levels around $0.03952. These comparable decline percentages indicate that both assets exhibit high correlation with broader cryptocurrency market cycles and demonstrate similar vulnerability during bear market conditions. The extreme fear market sentiment (Fear & Greed Index: 14) as of February 2026 continues to pressure both assets, suggesting that neither has shown significant defensive characteristics during market stress periods.
Q4: What are the price predictions for ETHS and LRC through 2031?
Conservative 2026 forecasts suggest ETHS may trade between $0.0228-$0.0278, while LRC may range from $0.0301-$0.0396. By 2031, baseline scenarios project ETHS reaching $0.0281-$0.0365 and LRC achieving $0.0655-$0.0676. Optimistic 2031 scenarios suggest ETHS could reach $0.0365-$0.0586 and LRC could attain $0.0676-$0.0986. These predictions indicate that LRC maintains a higher absolute price forecast across all timeframes, though both assets show potential for recovery from current depressed levels. The projections assume continued ecosystem development, institutional adoption growth, and favorable macroeconomic conditions for cryptocurrency markets.
Q5: Which asset is more suitable for conservative versus aggressive investors?
Conservative investors may find LRC more appropriate due to its longer operational track record since 2017, established use cases within DeFi infrastructure, and higher trading liquidity. A conservative allocation might consider 70-80% LRC versus 20-30% ETHS within Ethereum-focused portfolios. Aggressive investors seeking higher risk-reward exposure to experimental protocols might allocate 50-60% to ETHS and 40-50% to LRC, capitalizing on potential inscription protocol adoption while maintaining Layer 2 infrastructure exposure. Both allocation strategies require consideration of individual risk tolerance, portfolio diversification needs, and understanding that both assets remain highly speculative with significant downside risk.
Q6: What regulatory risks differentiate ETHS and LRC?
Both assets face evolving regulatory frameworks, but potential differential treatment exists based on their classification and use cases. LRC, as a Layer 2 infrastructure protocol supporting decentralized exchange activity, may face scrutiny around securities classification, exchange reporting requirements, and DeFi regulatory developments. ETHS, as an inscription-based protocol focused on data storage, may encounter different regulatory considerations related to digital collectibles classification and experimental asset categorization. Cross-border compliance requirements, exchange listing standards, and reporting obligations continue evolving across jurisdictions, with neither asset demonstrating clear regulatory clarity advantages. Investors should monitor regulatory developments in their specific jurisdictions before making allocation decisions.
Q7: How do market conditions and the Fear & Greed Index affect investment timing for these assets?
The current Extreme Fear reading (Fear & Greed Index: 14) indicates depressed market sentiment that historically precedes potential accumulation opportunities, though timing market bottoms remains challenging. Both ETHS and LRC have experienced over 99% drawdowns from peaks, suggesting prices reflect significant pessimism. However, extreme fear conditions can persist for extended periods, and further downside remains possible. Dollar-cost averaging strategies may be more appropriate than lump-sum investments during extreme fear periods. Investors should avoid attempting to perfectly time market bottoms and instead focus on accumulation strategies aligned with their risk tolerance, recognizing that both assets carry substantial volatility risk regardless of sentiment indicators.
Q8: What ecosystem developments could drive future value for ETHS versus LRC?
LRC's value proposition depends on continued adoption of Layer 2 scaling solutions, growth in decentralized exchange volumes, and successful competition against alternative zkRollup protocols. Ethereum's roadmap developments, particularly around data availability and Layer 2 interoperability, could significantly impact LRC's positioning. ETHS value drivers center on broader adoption of inscription protocols, expansion of use cases beyond digital collectibles, and sustained interest in Ethereum-based data storage applications. Neither asset demonstrates extensive NFT marketplace integration or widespread smart contract deployment outside core use cases. Ecosystem growth for both protocols remains speculative and dependent on broader cryptocurrency market recovery and sustained developer activity within their respective technological niches.

How to Mine Ethereum in 2025: A Complete Guide for Beginners

Ethereum 2.0 in 2025: Staking, Scalability, and Environmental Impact

What is Ethereum: A 2025 Guide for Crypto Enthusiasts and Investors

How does Ethereum's blockchain technology work?

What are smart contracts and how do they work on Ethereum?

Ethereum Price Analysis: 2025 Market Trends and Web3 Impact

Top 5 Tokens to Consider for DeFi Investment

Tax Planning for Bitcoin Investors Who Have Achieved Millionaire Status
FUD and FOMO in Crypto: Key Concepts Explained with Practical Examples

OpenSea NFT Exchange: Reviews, Advantages and Disadvantages

Top 10 Metaverse Platforms: An In-Depth Overview







