ETHS vs QNT: A Comprehensive Comparison of Two Leading Enterprise Blockchain Solutions


Introduction: Investment Comparison Between ETHS and QNT
In the cryptocurrency market, the comparison between ETHS vs QNT has been a recurring topic among investors. The two differ significantly in market cap ranking, application scenarios, and price performance, representing distinct positioning within crypto assets.
ETHS (ETHS): Launched in December 2023, it serves as the core asset of the Facet protocol, a decentralized Ethereum L1 scaling solution that has received funding from the Ethereum Foundation as an Unstoppable Rollup. It aims to empower the secure expansion of the Ethereum mainnet while serving as a pioneering asset driving the next generation of data and value layers.
QNT (QNT): Introduced in August 2018, Quant Network is recognized as a technology provider enabling trusted digital interactions through its global blockchain operating system, Overledger. Headquartered in London, UK, it addresses blockchain interoperability challenges and facilitates innovation and blockchain adoption across enterprises.
This article will comprehensively analyze the investment value comparison between ETHS vs QNT through historical price trends, supply mechanisms, institutional adoption, technological ecosystems, and future predictions, attempting to answer investors' most pressing question:
"Which is the better buy right now?"
I. Historical Price Comparison and Current Market Status
ETHS and QNT Historical Price Trends
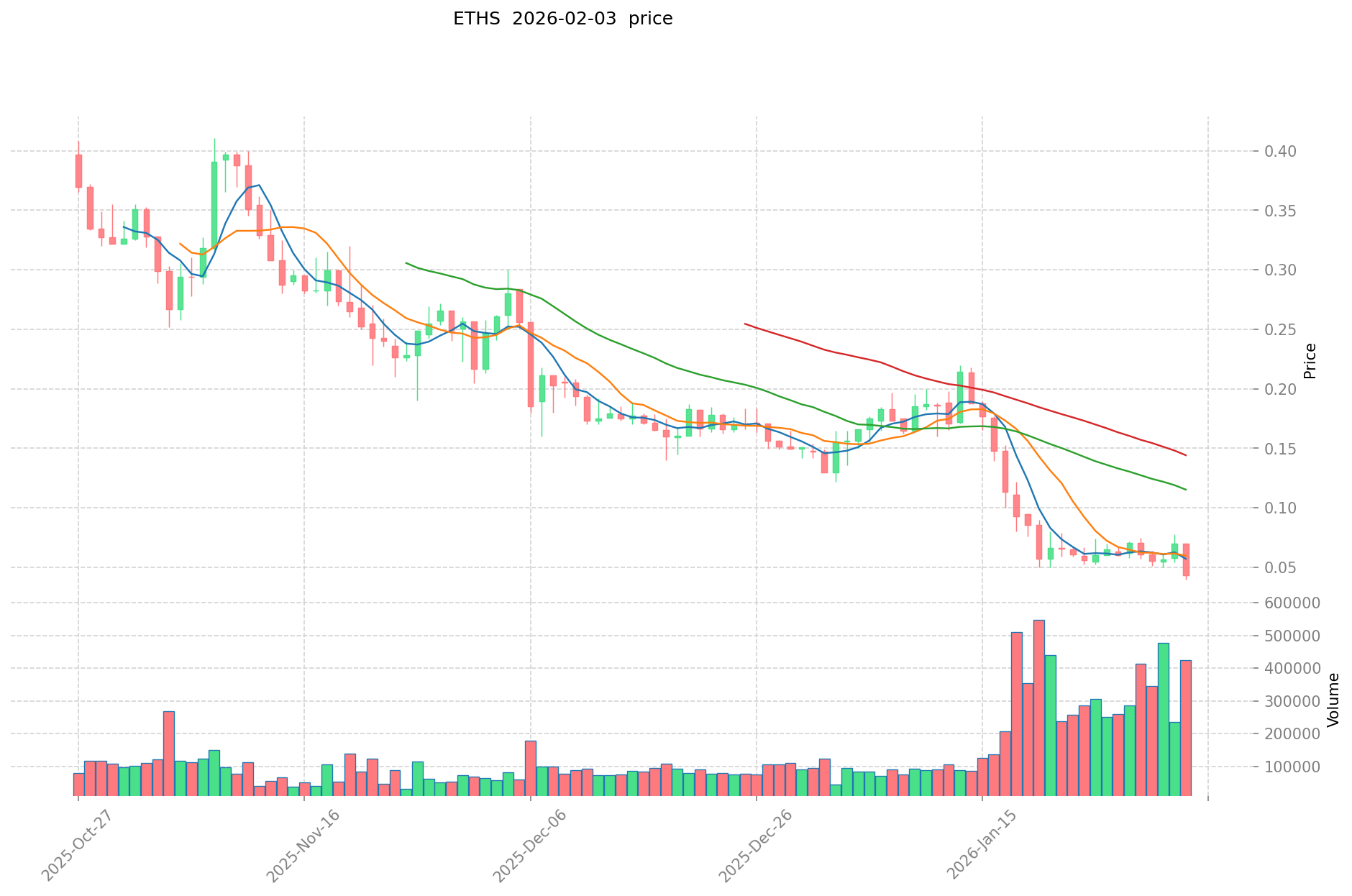
- 2024: ETHS experienced price volatility following its launch in December 2023, reaching a peak of $13.9 in January 2024.
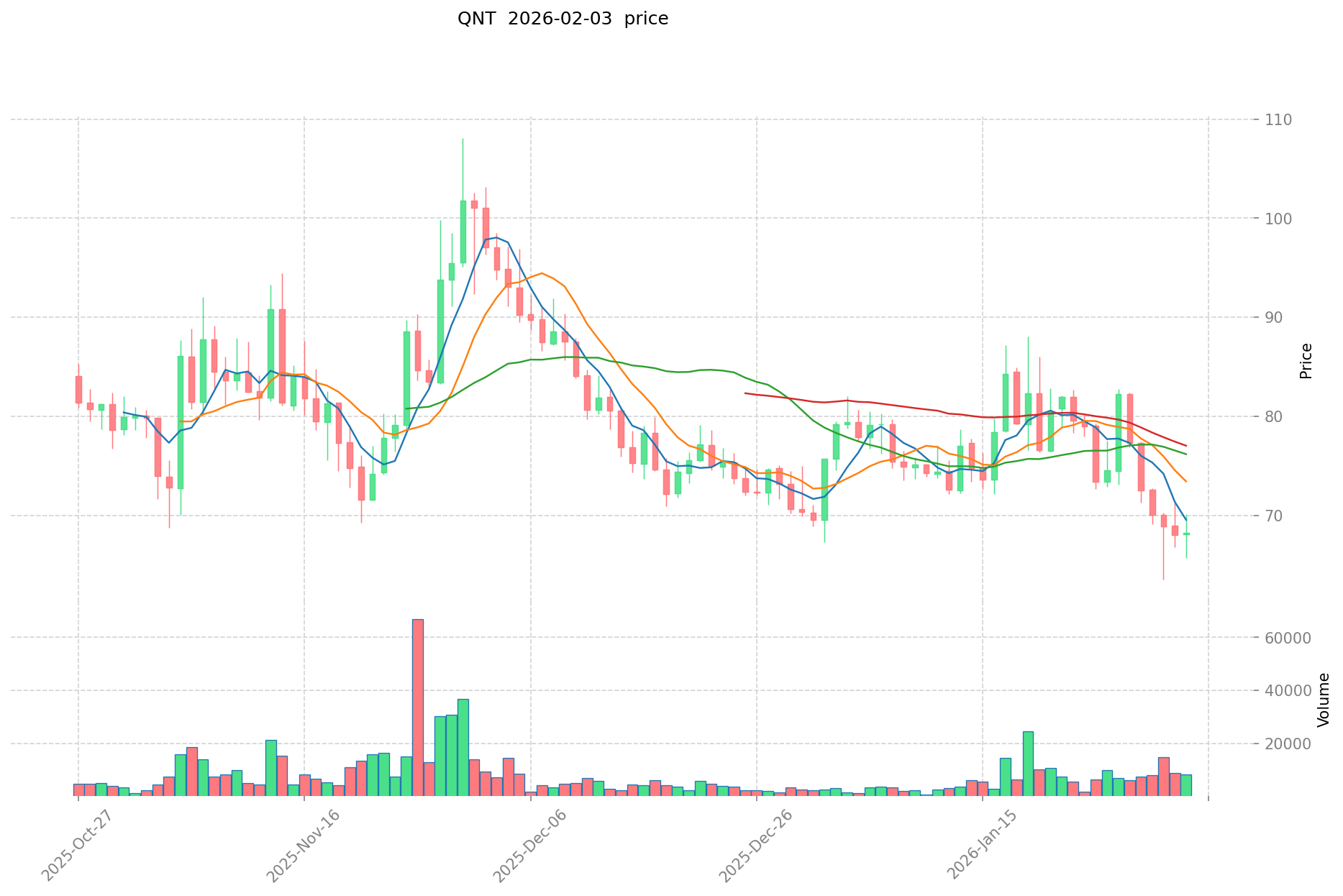
- 2021: QNT benefited from increased adoption of blockchain interoperability solutions, with its price reaching $427.42 in September 2021.
- Comparative Analysis: During the recent market cycle, ETHS declined from its peak of $13.9 to a low of $0.03377, representing a decline of over 99%. Meanwhile, QNT fell from its peak of $427.42 to $65.95, showing a decline of approximately 84%.
Current Market Status (2026-02-04)
- ETHS Current Price: $0.04084
- QNT Current Price: $65.95
- 24-Hour Trading Volume: ETHS $18,178.01 vs QNT $564,349.61
- Market Sentiment Index (Fear & Greed Index): 17 (Extreme Fear)
View real-time prices:
- View ETHS Current Price Market Price
- View QNT Current Price Market Price
II. Core Factors Affecting the Investment Value of ETHS vs QNT
Supply Mechanism Comparison (Tokenomics)
- ETHS: Features a fixed total supply of 21 million tokens, all of which are currently in circulation. This supply model incorporates Bitcoin-style scarcity characteristics with deflationary properties. The fully diluted market cap aligns with the current market cap, indicating no future token releases.
- QNT: Supply mechanism details depend on the protocol's tokenomics structure, with investment value tied to technical applications and market demand dynamics.
- 📌 Historical Pattern: Supply variations have historically influenced price movements for ETHS, with scarcity factors playing a role in value determination.
Institutional Adoption and Market Application
- Institutional Holdings: The level of institutional interest varies between the two assets based on their respective use cases and market positioning.
- Enterprise Adoption: Both tokens serve different roles in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, with demand, scarcity, and utility factors contributing to their relative market values.
- National Policies: Regulatory approaches toward these assets differ across jurisdictions, affecting their adoption trajectories.
Technical Development and Ecosystem Building
- ETHS Technical Features: The token operates within its designated ecosystem with specific technical characteristics related to its implementation.
- QNT Technical Development: Development depends on blockchain technology evolution and network efficiency improvements.
- Ecosystem Comparison: Both projects participate in various aspects of the digital asset space, with distinct positioning in their respective market segments.
Macroeconomic Factors and Market Cycles
- Inflation Environment Performance: The assets' responses to inflationary pressures reflect their distinct economic properties and market positioning.
- Macroeconomic Monetary Policy: Interest rates and broader financial market conditions influence both assets, though the degree of impact may vary.
- Geopolitical Factors: Cross-border transaction demands and international developments affect the utility and adoption of both tokens in different ways.
III. 2026-2031 Price Prediction: ETHS vs QNT
Short-term Prediction (2026)
- ETHS: Conservative $0.0322-$0.0393 | Optimistic $0.0393-$0.0585
- QNT: Conservative $49.16-$65.55 | Optimistic $65.55-$95.05
Mid-term Prediction (2028-2029)
- ETHS may enter a consolidation phase, with projected price range of $0.0299-$0.0760
- QNT may enter an expansion phase, with projected price range of $68.82-$124.31
- Key drivers: institutional capital inflows, ETF developments, ecosystem growth
Long-term Prediction (2031)
- ETHS: Base scenario $0.0505-$0.0721 | Optimistic scenario $0.0721-$0.0750
- QNT: Base scenario $72.37-$126.97 | Optimistic scenario $126.97-$162.52
Disclaimer
ETHS:
| Year | Predicted High Price | Predicted Average Price | Predicted Low Price | Price Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2026 | 0.0585123 | 0.03927 | 0.0322014 | -3 |
| 2027 | 0.0562248225 | 0.04889115 | 0.0278679555 | 19 |
| 2028 | 0.0625440036375 | 0.05255798625 | 0.0336371112 | 28 |
| 2029 | 0.07596731332575 | 0.05755099494375 | 0.02992651737075 | 40 |
| 2030 | 0.07744061879631 | 0.06675915413475 | 0.036717534774112 | 63 |
| 2031 | 0.074983881924151 | 0.07209988646553 | 0.050469920525871 | 76 |
QNT:
| Year | Predicted High Price | Predicted Average Price | Predicted Low Price | Price Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2026 | 95.0475 | 65.55 | 49.1625 | 0 |
| 2027 | 101.176425 | 80.29875 | 57.8151 | 21 |
| 2028 | 124.310494875 | 90.7375875 | 84.385956375 | 37 |
| 2029 | 117.201204894375 | 107.5240411875 | 68.81538636 | 63 |
| 2030 | 141.57690503158125 | 112.3626230409375 | 101.12636073684375 | 70 |
| 2031 | 162.521297966412 | 126.969764036259375 | 72.372765500667843 | 92 |
IV. Investment Strategy Comparison: ETHS vs QNT
Long-term vs Short-term Investment Strategies
-
ETHS: May appeal to investors seeking exposure to Ethereum L1 scaling solutions and blockchain infrastructure innovation. The token's fixed supply mechanism and positioning within the Facet protocol ecosystem represent characteristics relevant to those exploring emerging blockchain technologies.
-
QNT: May suit investors interested in blockchain interoperability infrastructure and enterprise-focused solutions. The token's role within the Overledger operating system positions it within cross-chain connectivity developments.
Risk Management and Asset Allocation
-
Conservative Investors: Consider diversified exposure across multiple asset classes, potentially including a smaller allocation to digital assets (ETHS: 5-10% | QNT: 10-15% of crypto portfolio)
-
Aggressive Investors: May explore higher concentration in growth-oriented positions (ETHS: 15-25% | QNT: 20-30% of crypto portfolio)
-
Hedging Tools: Portfolio risk management may incorporate stablecoin allocations, derivatives instruments, and cross-asset diversification strategies
V. Potential Risk Comparison
Market Risks
-
ETHS: Price volatility patterns since launch have demonstrated substantial fluctuations, with the token experiencing significant drawdowns from peak levels. Trading volume metrics indicate relatively lower liquidity compared to established assets.
-
QNT: Market dynamics reflect the evolving landscape of blockchain interoperability solutions, with price movements influenced by enterprise adoption trends and competitive developments in the cross-chain infrastructure sector.
Technical Risks
-
ETHS: Considerations include the ongoing development of scaling solutions, network adoption rates, and the evolution of the Facet protocol ecosystem. Technical implementation challenges may affect utility and adoption trajectories.
-
QNT: Infrastructure dependencies relate to the continued advancement of Overledger technology, enterprise integration requirements, and the competitive landscape of blockchain interoperability platforms.
Regulatory Risks
- Global regulatory frameworks continue to evolve, with varying approaches across jurisdictions affecting both assets. Compliance requirements for blockchain infrastructure projects and digital assets may influence adoption patterns and market accessibility.
VI. Conclusion: Which Is the Better Buy?
📌 Investment Value Summary:
-
ETHS Characteristics: Fixed supply model with deflationary properties, positioning within Ethereum scaling infrastructure, early-stage development with corresponding growth potential and volatility risk
-
QNT Characteristics: Established presence in blockchain interoperability sector, enterprise-focused positioning, longer operational history with demonstrated market cycles
✅ Investment Considerations:
-
Novice Investors: Prioritize education and understanding of both assets' underlying technologies and use cases. Consider starting with smaller position sizes and established assets before exploring higher-risk opportunities.
-
Experienced Investors: Evaluate portfolio fit based on existing allocations, risk tolerance, and investment thesis. Consider diversification across different blockchain infrastructure segments and maintain appropriate risk management protocols.
-
Institutional Investors: Conduct comprehensive due diligence on technical architectures, regulatory compliance frameworks, and long-term viability of both ecosystems. Assess alignment with institutional investment mandates and risk parameters.
⚠️ Risk Disclaimer: Cryptocurrency markets exhibit substantial volatility. This analysis does not constitute investment advice. Conduct independent research and consult qualified financial advisors before making investment decisions.
VII. FAQ
Q1: What is the main difference between ETHS and QNT in terms of their core function?
ETHS serves as the core asset of a decentralized Ethereum L1 scaling solution (Facet protocol), while QNT functions as the utility token for blockchain interoperability infrastructure (Overledger). ETHS focuses on enabling secure expansion of the Ethereum mainnet as an Unstoppable Rollup, having received funding from the Ethereum Foundation. In contrast, QNT addresses cross-chain connectivity challenges, facilitating trusted digital interactions and blockchain adoption across enterprises through its global blockchain operating system. The fundamental distinction lies in ETHS targeting Ethereum-specific scaling needs versus QNT's broader multi-chain interoperability mission.
Q2: How do the supply mechanisms of ETHS and QNT differ, and what impact does this have on their investment characteristics?
ETHS features a fixed total supply of 21 million tokens with all currently in circulation, incorporating Bitcoin-style scarcity characteristics with deflationary properties. This fully diluted supply means no future token releases, creating clear supply constraints. QNT's supply mechanism follows a different structure tied to its protocol's tokenomics and market demand dynamics. ETHS's fixed supply model theoretically provides scarcity-driven value appreciation potential, while QNT's investment value depends more on technical applications and enterprise adoption rates rather than supply mechanics alone.
Q3: Which asset has shown better price stability during market downturns?
QNT has demonstrated relatively better price resilience during market corrections. While ETHS declined over 99% from its peak of $13.9 to a low of $0.03377, QNT fell approximately 84% from its peak of $427.42 to $65.95. The substantial difference in drawdown magnitude suggests QNT maintained better price stability, likely attributable to its longer operational history (launched August 2018 vs December 2023), established enterprise relationships, and more mature market positioning. However, both assets experienced significant volatility characteristic of cryptocurrency markets.
Q4: What are the projected price ranges for ETHS and QNT in 2026 and 2031?
For 2026, ETHS conservative projection ranges from $0.0322-$0.0393, with optimistic scenarios reaching $0.0393-$0.0585. QNT's 2026 conservative estimate spans $49.16-$65.55, with optimistic projections of $65.55-$95.05. Looking toward 2031, ETHS base scenario forecasts $0.0505-$0.0721 (optimistic $0.0721-$0.0750), while QNT's base scenario projects $72.37-$126.97 (optimistic $126.97-$162.52). These predictions reflect QNT's higher absolute price levels and ETHS's potential for percentage-based growth from current low valuations.
Q5: What risk factors should investors consider when choosing between ETHS and QNT?
Investors should evaluate multiple risk dimensions. Market risks include ETHS's significantly lower trading volume ($18,178.01 vs QNT's $564,349.61) indicating limited liquidity, and its extreme price volatility since launch. Technical risks for ETHS involve early-stage protocol development and network adoption uncertainties, while QNT faces competitive pressures in the crowded blockchain interoperability sector. Regulatory risks affect both assets differently—ETHS as an emerging Ethereum infrastructure component and QNT as an enterprise-focused solution with compliance considerations across jurisdictions. Additionally, ETHS's 99%+ drawdown history presents heightened volatility risk compared to QNT's more established but still volatile profile.
Q6: Which asset is more suitable for conservative versus aggressive investors?
Conservative investors may find QNT more aligned with their risk tolerance due to its longer operational track record, established enterprise positioning, and relatively better price stability during market corrections. Suggested allocation ranges from 10-15% of a crypto portfolio. Aggressive investors seeking higher growth potential might consider ETHS's early-stage positioning and fixed supply mechanics, though this comes with substantially higher volatility risk. Recommended aggressive allocation spans 15-25% for ETHS versus 20-30% for QNT within crypto portfolios. Both strategies should maintain diversification across asset classes and implement appropriate hedging mechanisms including stablecoin allocations and derivatives instruments.
Q7: How does institutional adoption differ between ETHS and QNT?
QNT demonstrates more established institutional traction through its enterprise-focused blockchain interoperability solutions and London headquarters positioning within traditional financial infrastructure. The Overledger platform targets cross-enterprise blockchain adoption, facilitating institutional digital transformation initiatives. ETHS, while backed by Ethereum Foundation funding as an Unstoppable Rollup, represents a newer infrastructure layer with emerging institutional interest primarily from Ethereum ecosystem participants. QNT's longer operational history (since 2018) and enterprise client relationships provide clearer institutional adoption indicators compared to ETHS's early-stage (December 2023 launch) institutional engagement trajectory.
Q8: What macroeconomic factors most significantly impact ETHS versus QNT price performance?
Both assets respond to broader cryptocurrency market conditions, though with differing sensitivities. ETHS, as an Ethereum infrastructure token, shows stronger correlation with Ethereum ecosystem developments, Layer 1 scaling narratives, and overall crypto market sentiment (currently at Fear & Greed Index of 17 - Extreme Fear). QNT's performance ties more closely to enterprise blockchain adoption rates, cross-chain transaction volumes, and traditional financial institution digitalization trends. Macroeconomic monetary policy—particularly interest rates affecting technology valuations—influences both assets, though QNT's enterprise positioning may provide partial insulation from retail-driven crypto market volatility. Geopolitical factors affecting cross-border transactions benefit QNT's interoperability use case more directly than ETHS's Ethereum-specific scaling function.

XZXX: A Comprehensive Guide to the BRC-20 Meme Token in 2025

Survey Note: Detailed Analysis of the Best AI in 2025

Detailed Analysis of the Best 10 GameFi Projects to Play and Earn in 2025

Kaspa’s Journey: From BlockDAG Innovation to Market Buzz

Best Crypto Wallets 2025: How to Choose and Secure Your Digital Assets

Popular GameFi Games in 2025

Ultimate Guide to Free NFT Minting

Investigating the True Identity of Bitcoin Founder Satoshi Nakamoto

How to Participate in Cryptocurrency Airdrops and Essential Security Measures

Top 7 Hardware Picks for Cryptocurrency Mining
What Does DYOR Mean in Crypto?