How Does Monad Achieve High Performance? A Deep Dive into Its Core Technical Architecture
Across today’s blockchain ecosystem, performance bottlenecks have become one of the primary obstacles to large scale adoption. As DeFi, on chain gaming, SocialFi, and high frequency trading applications continue to grow, network congestion, volatile gas fees, and transaction delays have become increasingly common. Without an underlying architecture capable of handling high concurrency and low latency, Web3 applications struggle to offer an experience comparable to Web2. In that sense, high performance public blockchains are not merely technical upgrades, they are foundational infrastructure for mainstream adoption.
This article provides a structured analysis of Monad’s core technical architecture. It explains how the network achieves 10,000+ TPS through parallel transaction execution, the MonadBFT consensus mechanism, an asynchronous execution model, and state database optimization. It also compares Monad with Ethereum and other high performance Layer1 networks, and explores potential future upgrade paths. The goal is to offer a clear understanding of the engineering logic behind Monad’s performance gains.
Why Blockchain Performance Has Become the Primary Bottleneck
In blockchain systems, performance is typically measured across three dimensions, TPS, confirmation time, and transaction cost. Most mainstream EVM compatible chains, including Ethereum, use a serial execution model in which transactions are processed strictly one after another. While this guarantees determinism and consistency, it also severely limits throughput.
As ecosystems such as DeFi, NFTs, and Web3 gaming expand, user interactions have multiplied. The result has been frequent congestion, elevated gas fees, and longer transaction delays. These issues directly impact user experience and reduce overall ecosystem vitality.
Traditional consensus mechanisms, whether Proof of Work or serial BFT models, also face inherent trade offs between security and performance. Improving throughput and reducing finality time without compromising decentralization and security has therefore become one of the most important research directions in blockchain engineering.
Overview of Monad’s Technical Architecture
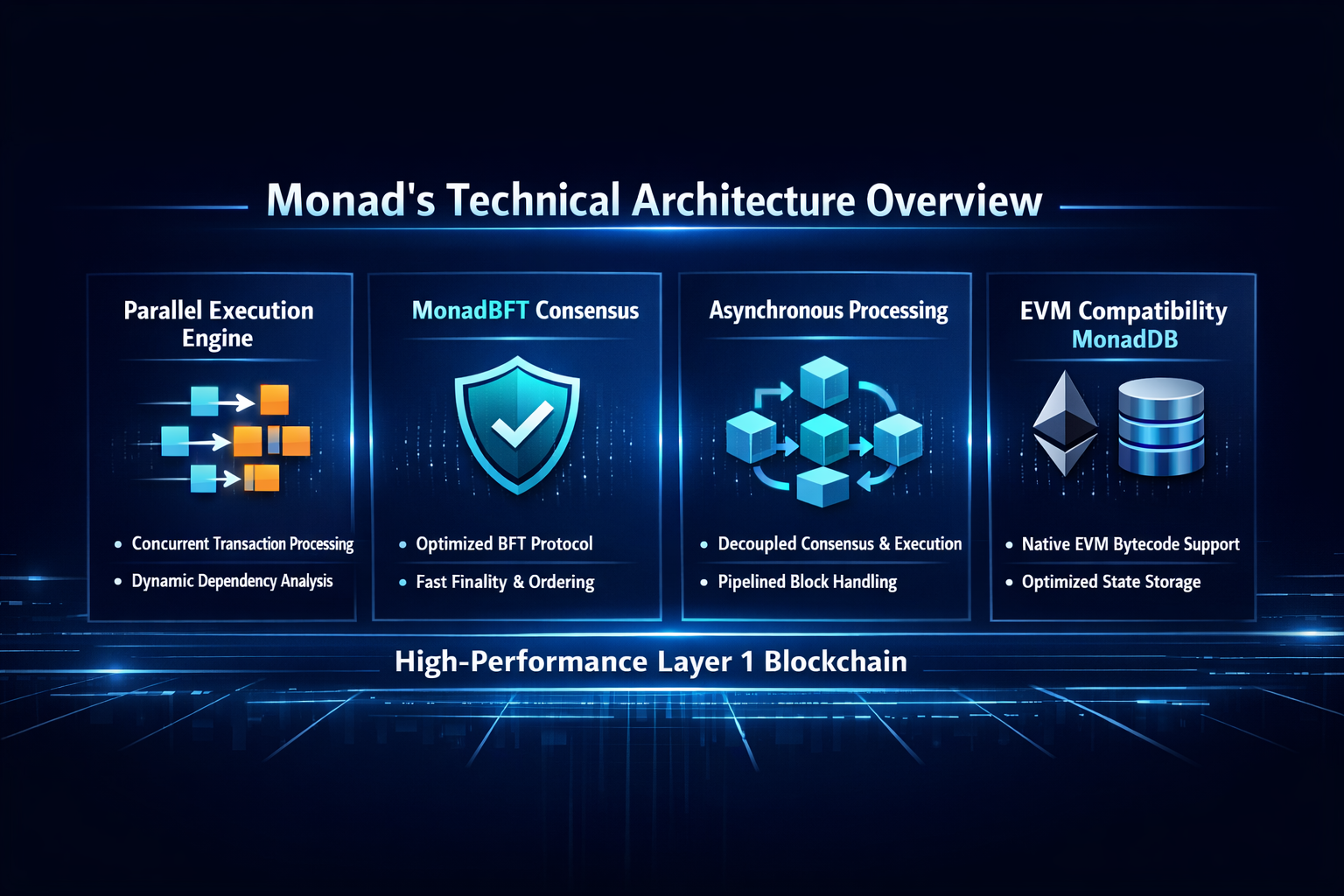
As a newly designed high performance, EVM compatible Layer1 blockchain, Monad’s architecture can be understood as a combination of several key layers:
- Parallel transaction execution: Identifies non conflicting transactions and processes them simultaneously.
- MonadBFT consensus mechanism: An optimized BFT protocol that rapidly determines transaction ordering and block proposals.
- Asynchronous and deferred execution design: Decouples consensus from execution to accelerate block processing.
- EVM compatibility layer and MonadDB state database: Supports native EVM bytecode while reducing hardware requirements.
By coordinating these components, Monad can achieve 10,000+ TPS and reduce single block finality time to approximately 0.8 to 1 second, significantly outperforming many existing chains.
How Parallel Transaction Execution Improves Throughput
Traditional EVM chains execute transactions serially, meaning every transaction must wait for the previous one to finish, even if they do not interact with the same state. One of Monad’s core innovations is its parallel execution model.
This efficiency gain is achieved through several mechanisms:
- Dynamic dependency analysis: Before execution, the system analyzes how transactions interact with state to determine which ones do not conflict.
- Parallel execution threads: Non conflicting transactions are distributed across multiple threads and processed concurrently.
- Conflict retry mechanism: If two transactions access the same state and conflict, only the conflicting portion is retried rather than re executing the entire block.
In effect, this transforms transaction processing from a single lane road into a multi lane highway, dramatically increasing throughput. Theoretical capacity can exceed 10,000 TPS.
How MonadBFT Optimizes Network Performance
In distributed systems, consensus ensures that all nodes agree on transaction ordering. Monad uses a protocol called MonadBFT, a lightweight and efficient Byzantine Fault Tolerant consensus mechanism inspired by HotStuff and further optimized to reduce communication rounds and validation latency.
Key optimizations include:
- Linear message complexity: While many traditional BFT protocols require multiple rounds of communication, MonadBFT reduces overhead in the optimistic path.
- Predictable finality: Transactions can reach finality quickly within a single slot, making them irreversible in a very short time.
- Decoupling from execution: Consensus is responsible only for ordering transactions, while execution is handled by the parallel execution engine, preventing execution delays from blocking block confirmation.
These improvements allow Monad to significantly increase performance while maintaining decentralized security guarantees.
Asynchronous Execution and Block Processing Mechanism
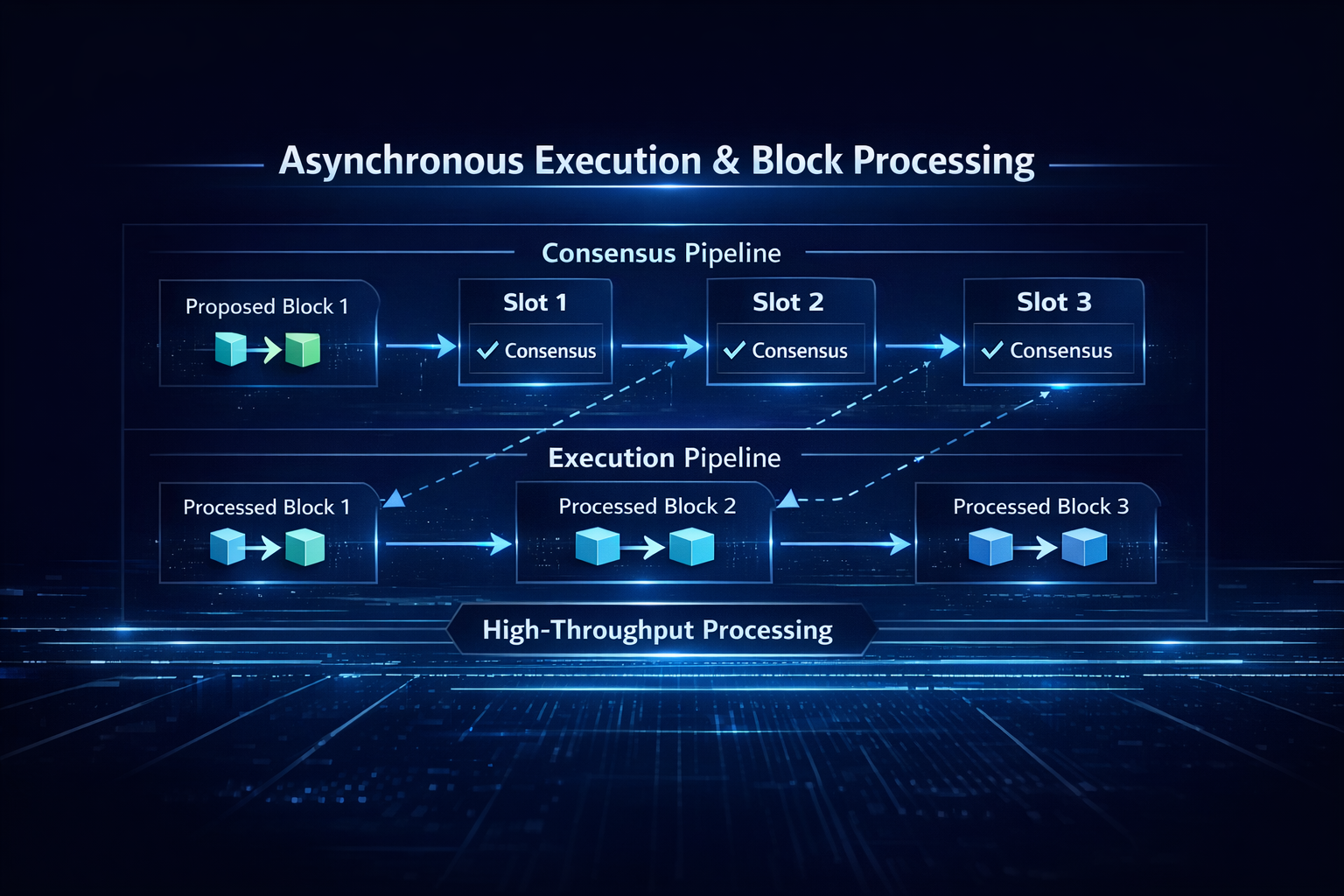
Monad’s architecture goes beyond execution level optimization by introducing asynchronous and deferred execution mechanisms.
Its core principles include:
- Consensus first, execution later: During the consensus phase, only transaction ordering is determined, and execution does not occur immediately.
- Asynchronous execution pipeline: Execution and consensus proceed in parallel, so the next round of consensus does not need to wait for all transactions from the previous round to finish executing.
This design accelerates overall system throughput because execution is no longer a bottleneck for consensus. Combined with parallel processing capabilities, it enables exceptionally high performance.
How Monad Preserves EVM Compatibility While Increasing Speed
EVM compatibility is essential for ecosystem adoption, as most smart contracts and developer tools are built around this standard. Monad maintains compatibility through several approaches:
- Native execution of EVM bytecode: Existing Solidity contracts can be deployed without modification.
- Support for standard Ethereum RPC APIs: Developers can continue using familiar tools such as MetaMask and Hardhat.
- State database optimization with MonadDB: The underlying storage system is redesigned to support more efficient parallel reads and writes.
This balance between compatibility and performance lowers migration costs for developers while delivering substantial speed improvements.
Technical Differences Compared With Ethereum and Other High Performance Layer1 Networks
Compared with Ethereum’s serial execution model and longer confirmation times, Monad’s parallel execution and fast consensus design are better suited for high throughput environments. When compared to other high performance Layer1 networks such as Solana, Monad maintains full EVM compatibility, addressing many of the ecosystem migration and tooling challenges faced by non EVM chains.
Unlike Ethereum Layer2 solutions, Monad does not require cross chain bridges or external validators. As an independent Layer1 network, it can provide high throughput and low latency directly, while remaining interoperable with the broader EVM ecosystem.
Potential Future Upgrade Directions for Monad
Looking ahead, Monad’s technical evolution may focus on several areas:
- More advanced dependency analysis algorithms: further reduce transaction conflicts and retry overhead.
- Support for heterogeneous execution environment: potentially expanding parallel processing across different virtual machines or languages.
- Enhanced cross chain interoperability: enable more seamless data and asset transfers with major ecosystems.
- Improve the security toolchain: Enhance protection and static analysis capabilities against MEV-type attacks.
These developments could further enhance performance, security, and ecosystem diversity.
Conclusion
Monad’s high performance is not the result of a single breakthrough, but rather the combined effect of parallel execution, optimized consensus, asynchronous architecture, and full EVM compatibility. By overcoming the limitations of serial execution, Monad achieves industry leading throughput of 10,000+ TPS and sub second finality. For applications that demand high performance and low latency without sacrificing compatibility, Monad represents a compelling architectural model and may help shape the next generation of blockchain infrastructure.
Related Articles

The Future of Cross-Chain Bridges: Full-Chain Interoperability Becomes Inevitable, Liquidity Bridges Will Decline

Solana Need L2s And Appchains?

Sui: How are users leveraging its speed, security, & scalability?

Navigating the Zero Knowledge Landscape

What is Tronscan and How Can You Use it in 2025?


