What is TIA Coin?
What Is Celestia?
Celestia is a modular blockchain that specializes in data availability (DA). Data availability refers to the ability of on-chain data to be fully published and accessible for validation. Unlike traditional blockchains that handle smart contract execution, settlement, and data management all on one chain, Celestia focuses solely on providing the foundational layer for publishing and verifying data for rollups and Layer 2 networks. Its goal is to reduce transaction costs and improve overall scalability.
By separating responsibilities, Celestia allows developers to execute and settle transactions on their own chains, while publishing the relevant data to Celestia. Light nodes can utilize Data Availability Sampling (DAS) to verify the accessibility of this data without downloading the entire dataset, enabling broader participation in network validation at lower costs.
Celestia (TIA): Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply
As of 2026-01-27, based on the provided data:
- Latest price: $0.444600
- Circulating supply: 872,245,559.591463 TIA
- Total supply: 1,160,280,813.530685 TIA
- Max supply: ∞ (no fixed upper limit; issuance follows a defined emission schedule.)
- Circulating market cap: $515,860,849.695743
- Fully diluted market cap: $515,860,849.695743
- Market dominance: 0.016%
- Price change: 1h: -0.52%; 24h: +1.06%; 7d: -9.83%; 30d: -6.85%
- 24h trading volume: $2,193,933.457537
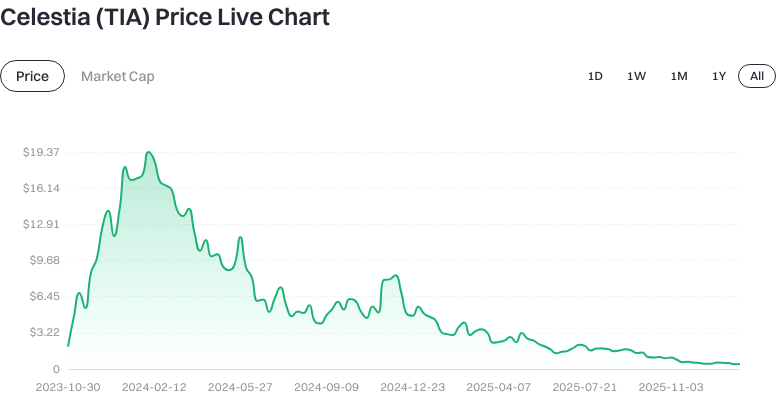
Click to view latest TIA price action
Please note that these figures fluctuate with market conditions and may vary across different sources. Always refer to the actual trading page for the most accurate information.
Who Created Celestia (TIA) and When?
Celestia was launched by a team dedicated to the modular blockchain vision. Early research was driven by contributors from both the community and academia. The mainnet went live in 2023, attracting integrations from various rollup ecosystems. Between 2024 and 2026, Celestia has focused on connecting its DA layer with toolchains and rollup frameworks, emphasizing compatibility with major Layer 2 stacks and real-world adoption (Sources: Celestia docs and official blog, as of Jan 2026).
The project timeline includes a testnet phase validating key mechanisms such as DAS and Namespaced Merkle Trees (NMT), followed by mainnet launch that opened up data publishing for developers. Modular adoption has advanced through ecosystem integrations.
How Does Celestia (TIA) Work?
Celestia’s architecture is modular, with two main innovations:
-
Data Availability Sampling (DAS): This allows light nodes to randomly sample fragments of a block’s data for verification. Without needing to download entire blocks, light nodes can confidently determine whether data has been published and is accessible. This lowers hardware requirements for validators.
-
Namespaced Merkle Trees (NMT): NMTs are hash trees with built-in namespaces that organize transaction data by category or rollup. Nodes only need to download branches relevant to their namespace for validation, increasing efficiency and supporting the separation of execution and settlement layers.
With this design, developers can handle execution (running contracts, processing state) and settlement (finalizing state changes) on their own chains or other layers, while publishing data to Celestia. Users can participate as light nodes, creating a more decentralized validation network.
What Are the Main Use Cases for Celestia (TIA)?
-
Data publishing for rollups and appchains: Projects using frameworks like Polygon CDK, Arbitrum Orbit, OP Stack, or Starkware can publish data on Celestia to lower per-transaction data costs.
-
Supporting high-frequency, cost-sensitive applications: For use cases like gaming, social platforms, or micropayments that demand high throughput and low fees, executing transactions on their own chain while leveraging Celestia for data availability strikes a balance between performance and decentralized validation.
-
Enabling broader validator participation: DAS lowers the validation threshold so ordinary devices can help secure data availability—improving network robustness and resistance to censorship.
What Are the Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for Celestia (TIA)?
-
Technical risks: Flaws in DAS or NMT could lead to unavailable or unverifiable data. As these mechanisms are new, they require ongoing audits and real-world testing.
-
Tokenomics and emission risks: With no fixed maximum supply, inflation or new issuance schedules are possible. Unlocking periods, staking rewards, and fee distribution all impact long-term TIA supply-demand dynamics.
-
Ecosystem competition: Competing DA layers or enhancements by major blockchains may divert demand. Adoption rates, compatibility with mainstream stacks, and developer retention are key mid- to long-term factors.
-
Regulatory uncertainty: Legal classification, compliance requirements, and disclosure standards for tokens differ across jurisdictions, potentially affecting trading and custody services.
-
User security risks: Operational risks such as exchange security breaches, private key leaks, phishing attacks, or incorrect addresses can result in asset losses.
What Is the Long-Term Value Proposition of Celestia (TIA)?
If modular blockchain adoption grows, demand for efficient data availability will increase across chains and rollups. Key value drivers for TIA include:
-
Fee and security asset for the DA layer: If publishing data requires TIA payments, protocol usage may influence fee demand, subject to network design and adoption outcomes.
-
Staking and governance utility: If the network uses a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) security model, staking TIA helps secure the network and earns rewards; holders can also participate in governance over parameters and fee models.
-
Network effects from ecosystem integration: More rollups integrating with Celestia amplifies positive feedback loops. However, it’s important to monitor whether fee revenue accrues to TIA holders and how inflation affects net dilution.
Ultimately, value realization depends on adoption growth rate, fee capture mechanisms, competitive landscape, and regulatory developments.
How Can I Buy and Securely Store Celestia (TIA) on Gate?
Step 1: Register and set up security features on Gate. Create an account on the official website, enable Google Authenticator and withdrawal whitelist settings, and set up anti-phishing codes. Complete KYC as needed for increased limits.
Step 2: Deposit funds. Use “Wallet” to deposit fiat or crypto. For crypto deposits, confirm that your network selection matches your deposit address; test with a small amount first.
Step 3: Search for trading pairs. On the spot trading page, search “TIA” to find pairs like TIA/USDT.
Step 4: Place a buy order. Beginners may use “market orders” for instant execution at current prices; use “limit orders” to set your preferred price. Double-check quantity and fee information before submitting.
Step 5: Withdraw to a self-custody wallet (optional but recommended). On the withdrawal page select TIA and the correct network, paste your Celestia address, confirm format/Memo/Tag requirements if any, then test with a small amount. Use self-custody wallets compatible with Celestia’s ecosystem; back up seed phrases offline—hardware wallets add extra security.
Step 6: Monitor security and compliance. Regularly review account safety settings and be cautious of phishing links; know your local compliance obligations regarding reporting and taxation.
How Does Celestia (TIA) Compare With Ethereum (ETH)?
-
Positioning & Architecture: Ethereum operates as a monolithic smart contract platform gradually becoming more modular—execution, settlement, and data are mainly secured within one domain. Celestia focuses on modularity for data availability only; execution and settlement are handled by upper-layer chains or rollups.
-
Fees & Resources: Ethereum users pay ETH as gas fees to compete for resources on-chain; Celestia charges mainly for data publishing so upper-layer chains can access verifiable data at lower costs.
-
Security & Finality: Ethereum relies on its consensus mechanism and extensive validator/node network; Celestia increases light node participation through its validator set plus DAS—security assumptions differ.
-
Ecosystem Focus: Ethereum boasts extensive DeFi and NFT ecosystems; Celestia’s strength is supporting rollups/appchains—its core proposition is enabling more chains to publish data affordably.
These networks are not direct substitutes—they are complementary in many ways. Some Ethereum-based rollups may choose external DA layers like Celestia for cost optimization.
Summary of Celestia (TIA)
Celestia defines itself as a modular blockchain focused on data availability. Through DAS and NMT technologies, light nodes can verify data efficiently—providing rollups and appchains with low-cost publishing capabilities. As of January 27th 2026, market metrics such as price and supply are in flux; investment decisions should prioritize real adoption rates, fee capture mechanisms, and tokenomics design. Beginners can follow a stepwise approach on Gate for purchases while prioritizing self-custody solutions. Long-term participation should involve ongoing risk assessment regarding technical stability, ecosystem integration progress, and regulatory environment—consider dollar-cost averaging and strong asset security measures.
FAQ
Is TIA Suitable for Beginners?
As the native token of an innovative modular blockchain project, TIA presents significant technical novelty along with higher risks. Beginners should first understand its fundamentals and market volatility before investing—start with small amounts rather than treating it as a stable asset. Set risk tolerance plans with stop-losses to avoid overexposure.
What Security Precautions Should I Take When Holding TIA?
The most critical step is safeguarding your private key and seed phrase—use hardware wallets or reputable custody solutions when possible. On exchanges, enable two-factor authentication and withdrawal whitelists to reduce theft risk. Never use wallets on public networks or disclose your private key information to anyone.
How Liquid Is TIA? Where Can I Trade It?
TIA is listed on multiple leading exchanges—with Gate offering pairs like TIA/USDT—providing good liquidity. Always choose exchanges with strong security credentials and high trading volumes for best execution quality. Check order book depth before trading to minimize slippage.
What Unique Advantages Does TIA Have Over Other L1 Blockchains?
TIA adopts a modular blockchain design—unlike traditional monolithic chains—by separating execution and settlement layers for enhanced scalability. This architecture theoretically lowers node operation barriers while increasing throughput. However, its ecosystem is still developing; thus risk levels remain higher compared to mature platforms like Ethereum.
What Is TIA’s Tokenomics and Supply Structure?
TIA’s supply is governed by protocol-defined issuance parameters rather than a fixed hard cap.; initial allocations are distributed via public sale and ecosystem incentives. Over time, tokenomics will influence inflation rates and price trends—beginners should review the official whitepaper for release schedules before buying. Study token allocation plans and unlock timelines carefully prior to investing.
Glossary of Key Celestia (TIA) Terms
- Modular blockchain: A blockchain architecture that separates functions like execution, settlement, consensus—enabling independent appchains.
- Data availability: Mechanisms ensuring blockchain data remains accessible to validators/light clients so no information is hidden.
- Appchain: An independent blockchain built on modular frameworks optimized for specific applications.
- Blob: Data blocks used by Celestia to store transaction information—allowing appchains to publish their data on-chain.
- Light client: A client that verifies transactions without downloading full blockchain data—lowering participation barriers.
- Staking: The mechanism where holders lock up TIA tokens to participate in network validation/consensus for rewards.
References & Further Reading
-
Official Site / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Docs:
-
Media / Research:
Related Articles

AltLayer Explanation: Aggregation as a Service

What is Nautilus Chain: All you need to know about Nautilus Chain
