Merkle Tree Explained: A Simple Overview

What Is a Merkle Tree
A Merkle tree is a method of organizing and structuring data that enables efficient storage of large amounts of information and rapid verification of its integrity. This technology is also known as a hash tree, reflecting its fundamental operating principle.
The core of this concept is hashing—the process of converting any data set into a unique, fixed-length string. Each piece of information has a unique hash, serving as its digital fingerprint. A hash function is a one-way transformation: it's straightforward to generate a hash from original data, but nearly impossible to recover the original data from the hash.
To illustrate this principle, consider the SHA-256 algorithm used by Bitcoin. The number 256 refers to the output's bit length. No matter the size of the input—whether a single letter or an entire book—SHA-256 always generates a 64-character string. This makes information storage compact and greatly accelerates data operations.
The benefits of hashing are clear: rather than storing large volumes of information, the system operates with concise hash values. This conserves storage space and boosts processing speed. Any change in the original data, even a single character, completely changes the resulting hash, making the system highly sensitive to modifications.
Who Created the Concept
The Merkle tree was developed by American cryptographer Ralph Merkle in 1979. At that time, he was seeking efficient methods to verify data integrity and protect information from unauthorized changes. His approach—organizing data as a tree-like structure of hashes—was a groundbreaking innovation for its time.
Notably, Merkle's invention remained largely theoretical for decades, used only in niche areas of cryptography. The concept only gained widespread popularity with the emergence of blockchain technology and the growth of cryptocurrencies. Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin, made Merkle trees a core element of blockchain architecture, demonstrating their practical value.
Today, Merkle trees are used not only in cryptocurrencies, but also in version control systems (like Git), distributed databases, backup solutions, and other technologies where efficient verification of large data sets is required.
The Purpose of the Concept: A Simple Example
The Merkle tree concept enables efficient organization, storage, and integrity verification of information without processing the entire data set. To clarify, let's use a practical example involving a rare book library.
Imagine a collector with an extensive library of rare books, stored in a secure facility. The owner needs a control system to quickly detect any changes to the collection—whether theft, substitution, or book relocation.
The traditional approach would require regular, complete inventories: checking each book against a catalog, which is time-consuming and resource-intensive. The Merkle concept provides a more elegant solution:
Step one—comprehensive cataloging. Each book receives a unique tag (analogous to a hash) reflecting all its characteristics: title, author, year of publication, cover condition, page number with a specific misprint. All books are linked in a defined hierarchy—by shelf, rack, and room.
Step two—creating summary information. Tags from individual books are used to generate shelf tags (summarizing all books on a shelf), then rack tags, and finally a single tag for the entire library. This hierarchical tag structure mirrors a Merkle tree.
Step three—establishing a control system. The owner stores only the library's final tag and its formation structure. To check the collection's integrity, they need only compare the current final tag to the reference. If they match, the collection is unchanged. If not, the system quickly pinpoints which shelf has been altered, without having to check every book.
Results of using the Merkle concept:
- Comprehensive data control—any change is instantly reflected in the final hash
- High verification efficiency—no need to process the full data set
- Rapid localization of changes—the tree structure precisely identifies modifications
- Security without intermediaries—the system works automatically, with no reliance on third parties
- Resource efficiency—control data is stored compactly instead of duplicating all information
How the Concept Works and the Role of Trees
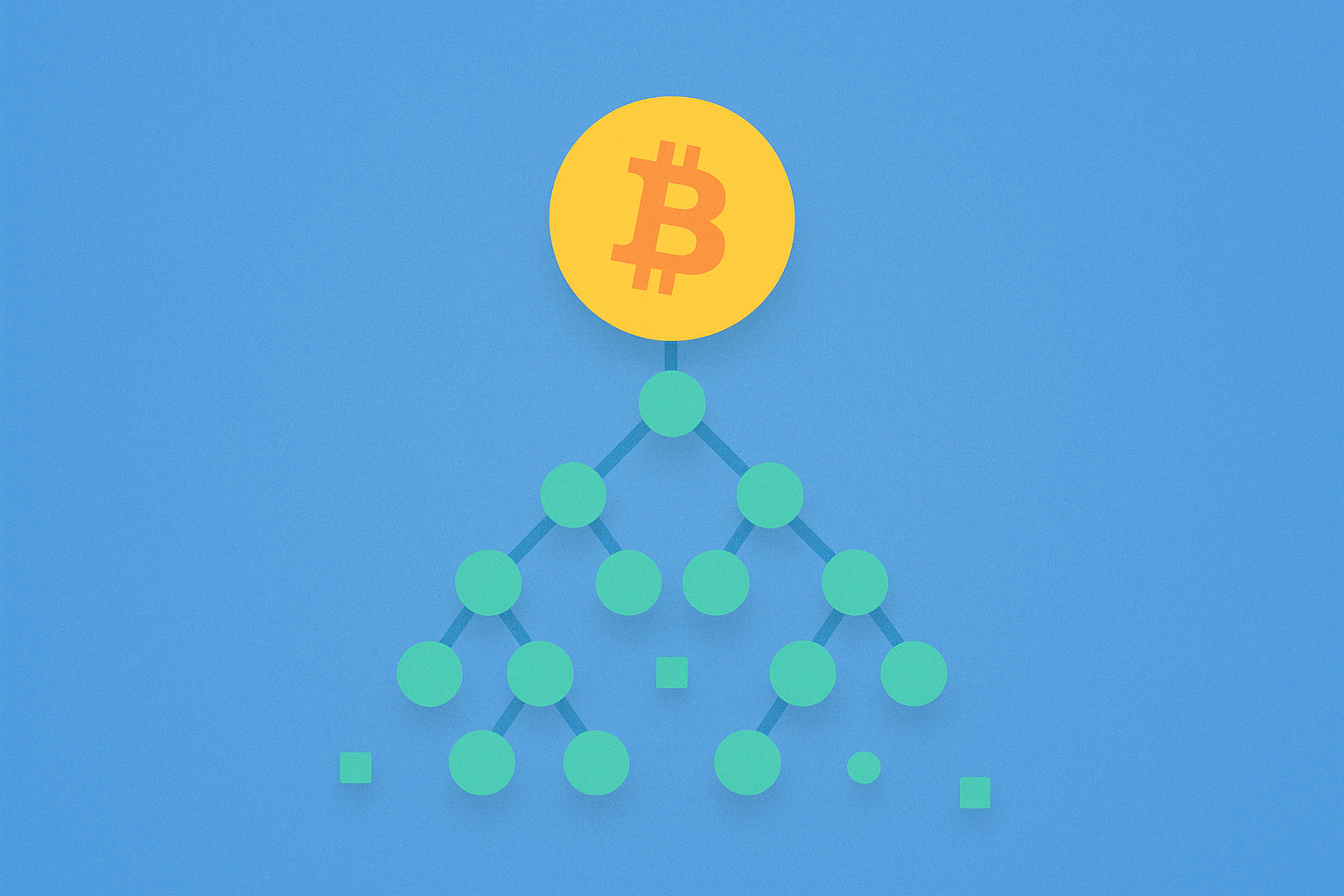
The name "Merkle tree" refers to its visual structure, which resembles an upside-down tree with branches. Let's examine how it works using an example with four blocks of original data.
Bottom level—tree leaves. Suppose we have four data blocks (data block 1, 2, 3, 4). These could be blockchain transactions, files in a storage system, or any other data. Each block is hashed to generate a unique hash. Let's call them hash 0-0, hash 0-1, hash 1-0, and hash 1-1.
Second level—first combination. Next, we group the hashes into pairs. Hash 0-0 and hash 0-1 are combined and hashed together to create hash 0. Similarly, hash 1-0 and hash 1-1 are combined to create hash 1. The key point: instead of simply concatenating the hashes, we generate a new hash based on their combination.
Third level—the tree root. Two hashes remain: hash 0 and hash 1. These are combined and hashed to produce a single hash, known as the root hash or top hash. This is the top of the tree, containing cryptographic information about all original data blocks.
Visually, the structure resembles a tree:
- Root (top hash)—at the top
- Branches (hash 0, hash 1)—intermediate level
- Leaves (hash 0-0, 0-1, 1-0, 1-1)—hashes of the original data blocks
- Base—the data blocks themselves
The critical feature of this structure is cascading hash changes. If even a single character in data block 1 is altered, it triggers a cascade of changes:
- Hash 0-0 changes
- Therefore, hash 0 changes (since it's calculated from hash 0-0)
- As a result, the top hash (root hash) changes
To check the integrity of all data, it’s sufficient to compare only the root hash. If it matches the reference, all data remains unchanged. If not, you can quickly identify which branch contains the change by checking the hashes at each level.
This approach is especially effective for large data sets. For example, instead of verifying a million transactions, you can simply compare a single 64-character root hash. This saves computational resources and time, making the system scalable and efficient.
How a Hash Tree Secures Data
The full power of Merkle trees is realized when combined with decentralized data storage, as used in blockchain technology. Let’s look at the protection mechanism using the Bitcoin network as an example.
A blockchain is a chain of blocks, each containing:
- A set of transactions organized as a Merkle tree
- The root hash of the tree (Merkle root)
- The previous block's hash
- Other metadata
The essential point is that copies of the entire blockchain are stored on thousands of independent nodes worldwide. This is decentralization: there is no single control center, and data is distributed among many participants.
Consider an attack scenario. An attacker wants to alter a transaction in one of the blocks to increase their transfer amount. Here’s what happens:
Step 1—Data modification. The attacker changes the transaction data in their copy of the blockchain.
Step 2—Cascading hash changes. Because of the Merkle tree structure, changing the transaction leads to changes in:
- The hash of that transaction
- All intermediate hashes up to the root
- The block’s Merkle root
- The block’s hash
- The hashes of all subsequent blocks (since each block contains the previous block’s hash)
Step 3—Detecting discrepancies. When this modified blockchain attempts to synchronize with the network, the system detects the inconsistency. Network nodes compare block hashes and find that the attacker’s version differs from the consensus version on thousands of other nodes.
Step 4—Rejecting changes. The network operates on a consensus basis: the version supported by the majority of nodes is valid. The modified version is rejected as invalid.
For a successful attack, an attacker would need to:
- Simultaneously change data on the majority of nodes (which is technically impossible with sufficient decentralization)
- Recalculate all hashes in the altered block and in every subsequent block
- Perform an enormous amount of computational work (proof-of-work) for each block
- Accomplish this faster than the rest of the network generates new blocks
The cost of such an attack on major blockchain networks far exceeds any possible gain, making the system economically secure.
Comparing to centralized systems highlights the advantages of Merkle trees:
Centralized system:
- Data is stored in a single location or managed by a single operator
- Compromising the central server grants full data control
- Changes can be made undetected
- Trust in the system operator is required
Decentralized system with Merkle trees:
- Data is distributed across thousands of independent nodes
- Attacks require compromising most nodes simultaneously
- Any change is immediately detected through hash mismatches
- No need to trust any party—the system is governed by mathematical principles
Additional advantages of hash tree protection:
Fast verification. To verify whether a specific transaction is in a block, there’s no need to download the entire block. Only the path from that transaction to the root hash (Merkle proof) is needed, which can be compared to the root hash in the block header.
Lightweight clients. Users can verify transactions without storing the entire blockchain. Storing only block headers with root hashes suffices, requiring minimal space.
Efficient damage detection. If a node’s data is corrupted (for example, due to hardware failure), hash mismatches quickly reveal the problem, and the node can restore a correct version from other network participants.
In this way, Merkle trees combined with decentralization create a robust data protection system, where security is ensured by the mathematical properties of cryptographic functions and distributed storage—not by trust in authority.
FAQ
What Is a Merkle Tree? What Is Its Main Definition?
A Merkle tree is a binary tree of hash values, where each leaf node represents data or its hash. It is used for efficient integrity verification of large data sets by sequentially hashing nodes from the bottom up to the root hash, protecting against data tampering.
How Does a Merkle Tree Work? What Is Its Structure and Principle?
A Merkle tree arranges data in a hierarchical hash structure. Each node contains the hash of its two child nodes, and the root node is the hash of the entire data set. This allows for rapid data integrity checks and detection of any modifications.
What Are the Applications of Merkle Trees in Blockchain? Why Does Bitcoin Use Them?
Merkle trees organize transaction data in Bitcoin blocks. The Merkle root in the block header aggregates all transaction hashes, enabling fast verification and increasing blockchain security.
What Are the Advantages of a Merkle Tree? What Problems Does It Solve?
A Merkle tree allows rapid verification of large data sets by minimizing comparisons. Any change to the data—however small—modifies the root hash. This ensures information integrity and security within the blockchain.
How Is a Merkle Tree Different from Standard Data Structures?
A Merkle tree uses hash pointers instead of typical pointers and builds a hierarchical structure via hashing. This provides cryptographic data verification and improves the efficiency of integrity checks in the blockchain.
How Do You Verify Data Integrity in a Merkle Tree?
Obtain the Merkle root hash and the hash of the leaf node. Calculate the hash of your data and compare it to the provided leaf hash. If they match, the data is verified and unaltered.
How Is Merkle Tree Security Achieved in Cryptography?
Merkle tree security relies on cryptographic hash functions. Each node contains the hash of its child nodes, so any change to the data alters the hash and is immediately detected. This ensures data integrity and immutability in the blockchain.

XZXX: A Comprehensive Guide to the BRC-20 Meme Token in 2025

What Is a Phantom Wallet: A Guide for Solana Users in 2025

Ethereum 2.0 in 2025: Staking, Scalability, and Environmental Impact

2025 Layer-2 Solution: Ethereum Scalability and Web3 Performance Optimization Guide

What is BOOP: Understanding the Web3 Token in 2025

Altcoin Season Index 2025: How to Use and Invest in Web3

What Is SocialFi? Is This Emerging as a New Trend in the Crypto Market?

Best Crypto Wallets for 2025: A Review of Leading Options
Everything About Automated Market Makers

Are NFTs Dead? A Guide to NFT Applications

Six Cryptocurrencies That Achieved Over 1,000x Total Growth