GAI vs ARB: Comparing Two Leading Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers for Hypertension Management


Introduction: Investment Comparison Between GAI and ARB
In the cryptocurrency market, the comparison between GraphAI (GAI) and Arbitrum (ARB) represents a discussion about two distinct blockchain infrastructure approaches. These projects differ significantly in market capitalization ranking, application scenarios, and price performance, representing different positioning within the crypto asset landscape.
GraphAI (GAI): Launched in March 2025, it positions itself as an AI-native data layer for Web3, transforming blockchain events into structured knowledge graphs. The project focuses on bridging decentralized infrastructure with AI reasoning through its flagship product GraphEngine.
Arbitrum (ARB): Introduced in March 2023, it serves as a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum, offering faster and more cost-effective transactions while maintaining Ethereum-level security through its Optimistic Rollup protocol.
This article will analyze the investment value comparison between GAI and ARB through historical price trends, supply mechanisms, ecosystem development, and market positioning. Key questions addressed include:
"What are the fundamental differences in their technological approaches and market adoption?"
I. Historical Price Comparison and Current Market Status
Historical Price Trends of GAI (Coin A) and ARB (Coin B)
- 2025: GAI experienced significant price movements following its launch in January, reaching a peak of $0.5078 in September 2025 before entering a correction phase.
- 2023-2024: ARB, launched in March 2023, reached its historical high of $2.39 in January 2024, followed by an extended downward trend through 2025-2026.
- Comparative Analysis: During the recent market cycle, GAI declined from its high of $0.5078 to a low of $0.0164, representing a substantial correction. Meanwhile, ARB experienced a more prolonged decline from $2.39 to $0.12965, reflecting broader market challenges for Layer 2 scaling solutions.
Current Market Conditions (February 3, 2026)
- GAI Current Price: $0.01826
- ARB Current Price: $0.139
- 24-Hour Trading Volume: GAI recorded $15,362.37 compared to ARB's $4,603,026.02
- Market Sentiment Index (Fear & Greed Index): 14 (Extreme Fear)
View real-time prices:
- Check GAI current price Market Price
- Check ARB current price Market Price
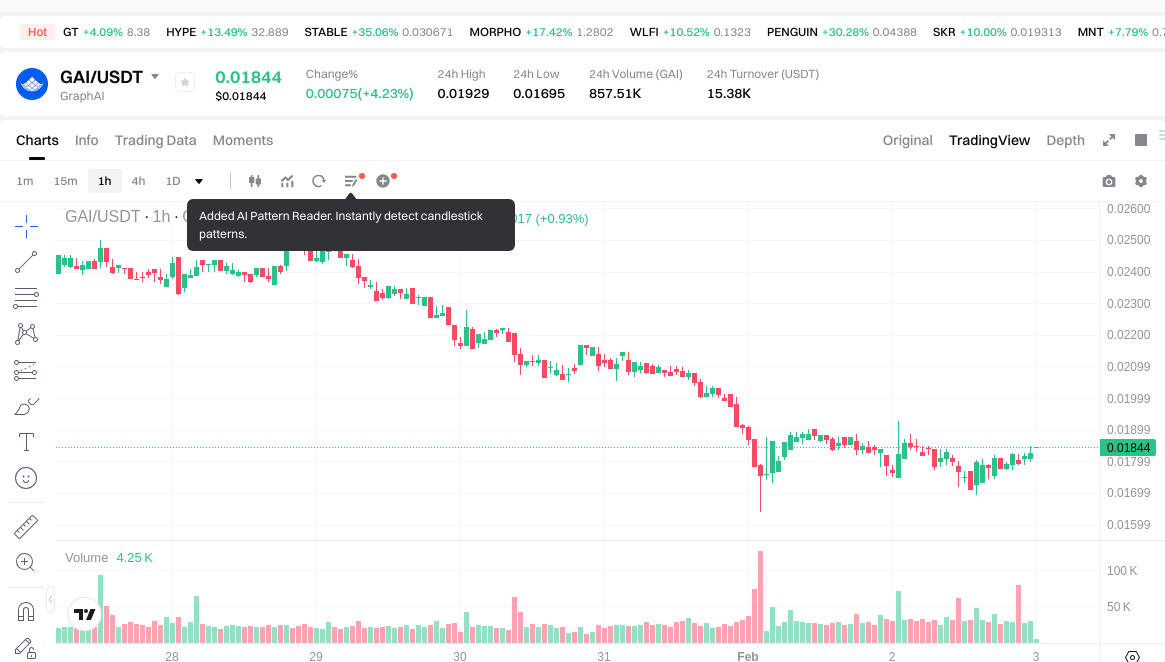
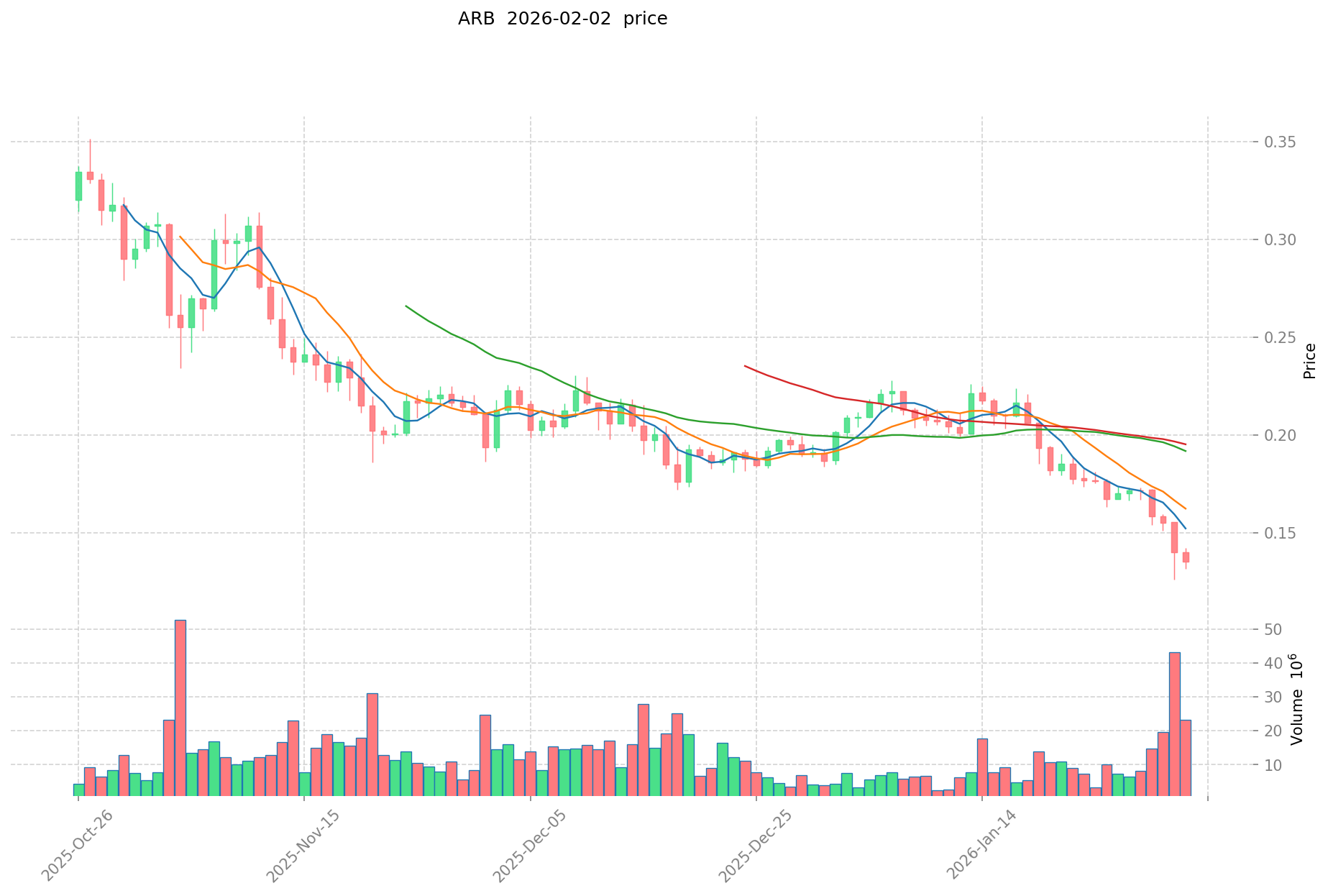
II. Core Factors Influencing GAI vs ARB Investment Value
Supply Mechanism Comparison (Tokenomics)
The supply dynamics of crypto assets fundamentally shape their long-term value proposition. Understanding tokenomics requires examining emission schedules, distribution models, and inflationary or deflationary mechanisms that govern token availability.
-
GAI: Specific supply mechanism details were not available in the provided materials. Investors should independently verify GAI's token distribution model, emission schedule, and whether it operates under fixed supply, inflationary, or deflationary frameworks.
-
ARB: Detailed supply mechanism information was not available in the reference materials. Market participants should research ARB's tokenomics independently, including total supply caps, vesting schedules, and governance-related token allocation.
-
📌 Historical Pattern: Supply mechanisms have historically influenced price cycles through scarcity dynamics, emission rate changes, and market expectations around token unlocks. Assets with transparent, predictable supply schedules tend to exhibit different volatility patterns compared to those with complex or opaque distribution models.
Institutional Adoption and Market Applications
Institutional participation and real-world utility significantly impact asset valuation and market stability.
-
Institutional Holdings: The reference materials did not provide comparative data on institutional preference between GAI and ARB. Institutional allocation decisions typically reflect risk assessment frameworks, regulatory compliance considerations, and strategic portfolio diversification objectives.
-
Enterprise Adoption: Specific information regarding GAI or ARB utilization in cross-border payments, settlement systems, or corporate treasury management was not available in the provided sources. Enterprise adoption patterns generally correlate with transaction efficiency, cost reduction potential, and integration compatibility with existing financial infrastructure.
-
National Policy Landscape: The materials emphasized that modern investment frameworks rely on international treaties and contractual agreements with binding arbitration clauses. Regulatory attitudes toward crypto assets vary substantially across jurisdictions, influenced by factors including financial stability concerns, consumer protection mandates, and technology innovation policy objectives. Investors should monitor evolving regulatory frameworks in relevant jurisdictions.
Technological Development and Ecosystem Construction
Technological innovation and ecosystem maturity represent critical differentiators in long-term value creation.
-
GAI Technical Upgrades: Specific technical development roadmaps for GAI were not detailed in the reference materials. Technical advancement typically encompasses scalability improvements, security enhancements, and interoperability features.
-
ARB Technical Evolution: Detailed information about ARB's technical development trajectory was not available in the provided sources. Technological progress in blockchain projects generally involves layer-2 scaling solutions, consensus mechanism optimizations, and cross-chain communication protocols.
-
Ecosystem Comparison: The materials did not provide specific comparative analysis of DeFi integration, NFT marketplace activity, payment system adoption, or smart contract deployment between GAI and ARB. Ecosystem vitality indicators typically include developer activity metrics, transaction volume trends, total value locked in protocols, and user growth patterns.
Macroeconomic Factors and Market Cycles
Broader economic conditions and policy environments exert substantial influence on crypto asset performance.
-
Inflationary Environment Performance: The reference materials did not contain specific data comparing GAI and ARB performance during inflationary periods. Assets with limited supply characteristics have historically been discussed in the context of inflation hedging potential, though actual performance varies based on multiple factors including market sentiment and liquidity conditions.
-
Macro Monetary Policy Impact: Interest rate adjustments and dollar index movements affect capital flows across asset classes. The materials noted that investment frameworks depend on contractual agreements and international standards, which operate within broader monetary policy environments. Rising rates typically influence risk asset valuations through discount rate effects and opportunity cost considerations.
-
Geopolitical Considerations: The reference documents emphasized that investment success depends on governance effectiveness and sustainable practices within established legal frameworks. Geopolitical developments affecting cross-border transaction demand, international regulatory coordination, and regional adoption patterns can influence market dynamics. Investors should consider how geopolitical factors may impact network accessibility, regulatory treatment, and institutional participation in different jurisdictions.
III. 2026-2031 Price Forecast: GAI vs ARB
Short-term Forecast (2026)
- GAI: Conservative $0.0114 - $0.0184 | Optimistic $0.0184 - $0.0251
- ARB: Conservative $0.0847 - $0.1389 | Optimistic $0.1389 - $0.1500
Mid-term Forecast (2028-2029)
- GAI may enter a consolidation phase with projected price range of $0.0205 - $0.0358
- ARB may enter a growth phase with projected price range of $0.0897 - $0.2277
- Key drivers: institutional capital inflows, ETF developments, ecosystem expansion
Long-term Forecast (2030-2031)
- GAI: Baseline scenario $0.0214 - $0.0306 | Optimistic scenario $0.0300 - $0.0412
- ARB: Baseline scenario $0.1551 - $0.2041 | Optimistic scenario $0.2041 - $0.2388
Disclaimer
GAI:
| Year | Predicted High Price | Predicted Average Price | Predicted Low Price | Price Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2026 | 0.0250784 | 0.01844 | 0.0114328 | 0 |
| 2027 | 0.02393512 | 0.0217592 | 0.015449032 | 19 |
| 2028 | 0.0278735352 | 0.02284716 | 0.020562444 | 25 |
| 2029 | 0.035758090116 | 0.0253603476 | 0.022063502412 | 38 |
| 2030 | 0.03330954855522 | 0.030559218858 | 0.0213914532006 | 67 |
| 2031 | 0.041195354981526 | 0.03193438370661 | 0.030018320684213 | 74 |
ARB:
| Year | Predicted High Price | Predicted Average Price | Predicted Low Price | Price Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2026 | 0.150012 | 0.1389 | 0.084729 | 0 |
| 2027 | 0.19212648 | 0.144456 | 0.08522904 | 3 |
| 2028 | 0.176705802 | 0.16829124 | 0.1531450284 | 20 |
| 2029 | 0.22769804772 | 0.172498521 | 0.08969923092 | 24 |
| 2030 | 0.2081022157344 | 0.20009828436 | 0.1780874730804 | 43 |
| 2031 | 0.238797292555224 | 0.2041002500472 | 0.155116190035872 | 46 |
IV. Investment Strategy Comparison: GAI vs ARB
Long-term vs Short-term Investment Strategies
-
GAI: May appeal to investors interested in AI-infrastructure integration and early-stage Web3 data solutions. The asset's relatively recent launch in 2025 positions it as a higher-risk opportunity with potential for growth contingent upon ecosystem adoption and technical execution. Short-term strategies may focus on volatility patterns, while long-term approaches would require monitoring protocol development milestones and partnership announcements.
-
ARB: May suit investors seeking exposure to Ethereum layer-2 scaling solutions with established transaction volume and ecosystem integration. As a more mature protocol launched in 2023, ARB presents a different risk-return profile compared to newer entrants. Long-term strategies might consider institutional adoption trends and DeFi ecosystem expansion, while short-term approaches could focus on Ethereum network activity correlations.
Risk Management and Asset Allocation
Asset allocation decisions should reflect individual risk tolerance, investment horizons, and portfolio diversification objectives. The following frameworks represent illustrative approaches rather than prescriptive recommendations:
-
Conservative Investors: May consider allocating smaller portions to crypto assets within diversified portfolios, potentially favoring more established protocols with demonstrated network effects. A hypothetical allocation might include limited exposure to both GAI and ARB, with ARB receiving relatively higher weighting due to its longer operational history.
-
Aggressive Investors: May pursue higher allocations to emerging technologies and early-stage protocols, accepting increased volatility in exchange for potential growth opportunities. Such strategies might include comparative positions in both assets, with allocation decisions informed by technical development roadmaps and ecosystem traction metrics.
-
Hedging Tools: Portfolio risk management may incorporate stablecoin positions for liquidity preservation, derivatives instruments where available and appropriate, and cross-asset diversification strategies. Investors should evaluate correlation patterns between different crypto assets and traditional financial instruments when constructing hedged positions.
V. Potential Risk Comparison
Market Risks
-
GAI: As a relatively new protocol launched in 2025, GAI faces market adoption uncertainty and liquidity considerations. Price discovery mechanisms may exhibit higher volatility during early development phases. Trading volume data indicates substantially lower liquidity compared to more established assets, which may amplify price movements during periods of market stress.
-
ARB: Despite longer operational history, ARB experienced significant price declines from January 2024 highs, reflecting broader challenges in the layer-2 scaling sector. Market risks include competition from alternative scaling solutions, changes in Ethereum base layer dynamics, and shifts in DeFi protocol preferences. Transaction cost economics and network effect sustainability represent ongoing considerations.
Technical Risks
-
GAI: Technical risk assessment requires examination of protocol architecture, smart contract security audits, and infrastructure dependencies. Specific technical vulnerabilities were not detailed in available materials. Investors should independently research network stability records, upgrade implementation processes, and developer community engagement metrics.
-
ARB: Layer-2 scaling solutions face technical considerations including bridge security, fraud proof mechanisms, and state synchronization reliability. Optimistic Rollup architectures involve specific trust assumptions and challenge period mechanics. Network performance during high congestion periods and cross-chain interoperability represent ongoing technical development areas.
Regulatory Risks
Regulatory frameworks for crypto assets continue evolving across jurisdictions, with varying approaches to classification, taxation, and compliance requirements. Both GAI and ARB operate within this dynamic landscape:
-
Jurisdictional Variation: Regulatory treatment may differ based on protocol characteristics, token utility definitions, and jurisdictional policy objectives. Infrastructure protocols and application-layer tokens may face different regulatory considerations.
-
Compliance Evolution: Market participants should monitor developments in securities regulation, AML/KYC requirements, and cross-border transaction frameworks. Regulatory clarity in major markets may influence institutional participation and mainstream adoption trajectories.
-
Policy Impact: Changes in monetary policy, digital asset taxation, and international coordination efforts may affect market dynamics differently across asset categories and use cases.
VI. Conclusion: Which Is the Better Buy?
📌 Investment Value Summary
-
GAI Characteristics: Represents early-stage exposure to AI-native data infrastructure for Web3, with associated higher risk and potential for growth contingent upon ecosystem development. Limited operational history and lower liquidity levels characterize current market conditions. Price forecasts suggest consolidation patterns through 2026-2031, though actual outcomes depend on multiple factors including technical execution and market adoption.
-
ARB Characteristics: Provides exposure to established Ethereum layer-2 scaling infrastructure with demonstrated transaction volume and ecosystem integration. Longer operational track record and higher liquidity levels compared to newer protocols. Price projections indicate potential recovery patterns through 2026-2031, though performance depends on competitive dynamics and Ethereum ecosystem evolution.
✅ Investment Considerations
-
Newer Investors: Should prioritize education regarding blockchain technology fundamentals, risk management principles, and portfolio diversification strategies before allocating capital to crypto assets. Starting with smaller position sizes and more established protocols may provide learning opportunities while managing downside exposure.
-
Experienced Investors: May evaluate comparative positioning based on portfolio objectives, risk tolerance frameworks, and conviction regarding specific technology trajectories. Due diligence should encompass protocol documentation review, on-chain metrics analysis, and ecosystem development monitoring.
-
Institutional Participants: Investment decisions typically incorporate governance frameworks, regulatory compliance requirements, and risk management protocols. Institutional approaches may consider factors including custodial infrastructure availability, liquidity depth for position sizing, and alignment with strategic allocation mandates.
⚠️ Risk Disclosure: Cryptocurrency markets exhibit substantial volatility and involve significant risks including potential loss of capital. This analysis does not constitute investment advice, financial recommendations, or endorsements of specific assets. Market participants should conduct independent research, consult qualified advisors, and carefully evaluate their financial circumstances and risk tolerance before making investment decisions.
VII. FAQ
Q1: What are the fundamental differences between GAI and ARB's technological approaches?
GAI operates as an AI-native data layer for Web3, transforming blockchain events into structured knowledge graphs, while ARB functions as a layer-2 scaling solution for Ethereum using Optimistic Rollup technology. GAI focuses on bridging decentralized infrastructure with AI reasoning through its GraphEngine product, positioning itself in the emerging AI-infrastructure integration space. In contrast, ARB addresses Ethereum's scalability challenges by providing faster and more cost-effective transactions while maintaining Ethereum-level security. These represent fundamentally different value propositions: GAI targets data structuring and AI application development, whereas ARB solves transaction throughput and cost efficiency problems for Ethereum users.
Q2: How do the market maturity levels of GAI and ARB compare?
ARB demonstrates significantly greater market maturity compared to GAI. Launched in March 2023, ARB has accumulated nearly three years of operational history versus GAI's launch in March 2025. This maturity gap manifests in trading volume disparities, with ARB recording $4,603,026.02 in 24-hour volume compared to GAI's $15,362.37, indicating substantially higher liquidity. ARB's longer track record provides more historical data for analysis, established ecosystem integrations, and demonstrated network effects. However, GAI's recent entry potentially offers early-stage exposure opportunities, though with correspondingly higher uncertainty regarding adoption trajectories and technical execution outcomes.
Q3: Which asset experienced greater price volatility from its peak?
Both assets experienced substantial corrections from their respective peaks, though the magnitude differs. GAI declined from its September 2025 high of $0.5078 to a low of $0.0164, representing approximately a 96.8% decline. ARB fell from its January 2024 peak of $2.39 to $0.12965, reflecting roughly a 94.6% correction. While both experienced severe downward price movements, GAI's shorter operational period means its entire price history encompasses this volatility cycle, whereas ARB's decline occurred over a more extended timeframe following an initial growth phase. These patterns illustrate the high-risk nature of crypto assets during market correction phases, regardless of project maturity level.
Q4: What factors should investors prioritize when comparing these assets?
Investors should evaluate multiple dimensions including technological differentiation, ecosystem development stage, liquidity characteristics, and alignment with portfolio objectives. For GAI, critical factors include AI-data infrastructure adoption trends, GraphEngine development milestones, and partnership announcements that demonstrate real-world utility. For ARB, key considerations encompass Ethereum layer-2 competitive dynamics, DeFi ecosystem integration depth, transaction volume sustainability, and institutional adoption patterns. Risk tolerance plays a crucial role: conservative approaches may favor ARB's established infrastructure and higher liquidity, while risk-tolerant strategies might include GAI exposure for potential early-stage growth opportunities. Independent research into tokenomics, technical architecture, and regulatory treatment across relevant jurisdictions remains essential for informed decision-making.
Q5: How do price forecasts compare for 2026-2031?
Price projections suggest divergent trajectories for the two assets. GAI forecasts indicate consolidation patterns with conservative 2026 estimates of $0.0114-$0.0184 and long-term 2030-2031 baseline scenarios of $0.0214-$0.0306. ARB projections show potential recovery dynamics with conservative 2026 ranges of $0.0847-$0.1389 and long-term 2030-2031 baseline estimates of $0.1551-$0.2041. These forecasts suggest ARB may experience more substantial percentage appreciation from current levels, though actual outcomes depend on numerous variables including market cycles, technological execution, competitive positioning, and macroeconomic conditions. Investors should treat these projections as illustrative scenarios rather than definitive predictions, as cryptocurrency markets exhibit substantial uncertainty and volatility.
Q6: What are the primary risks differentiating these investments?
GAI faces early-stage protocol risks including unproven product-market fit, limited operational track record, and lower liquidity levels that may amplify price volatility. Technical risks encompass smart contract security considerations and infrastructure dependency uncertainties that require ongoing monitoring. ARB confronts maturity-stage challenges including intense competition from alternative layer-2 solutions, dependence on Ethereum base layer developments, and the need to maintain network effects amid evolving scaling technologies. Both assets share common cryptocurrency risks including regulatory uncertainty across jurisdictions, macroeconomic sensitivity, and market sentiment volatility. The risk differential primarily reflects GAI's earlier development stage versus ARB's established position with associated competitive pressures.
Q7: Which asset suits different investor profiles?
Conservative investors seeking crypto exposure within diversified portfolios may find ARB's longer operational history, higher liquidity, and established ecosystem integration more aligned with risk management frameworks. Such approaches might involve limited allocations emphasizing capital preservation over aggressive growth targeting. Aggressive investors comfortable with higher volatility and early-stage uncertainty might consider GAI for potential exposure to AI-infrastructure convergence trends, accepting lower liquidity and greater execution risk. Experienced crypto investors may evaluate comparative positioning based on conviction regarding specific technology trajectories, potentially maintaining diversified exposure across both layer-2 scaling solutions and AI-data infrastructure developments. Institutional participants typically prioritize governance frameworks, custodial infrastructure availability, and regulatory compliance considerations that may favor more established protocols with demonstrated network effects.
Q8: How should market conditions influence allocation decisions?
Current market sentiment indicators show Extreme Fear (14 on Fear & Greed Index), suggesting risk-off positioning across crypto markets. Such conditions historically present both elevated risk and potential opportunity, depending on individual circumstances and investment horizons. During extreme fear phases, conservative approaches emphasize capital preservation, potentially favoring assets with stronger liquidity profiles and established use cases like ARB. Risk-tolerant strategies might view depressed valuations as accumulation opportunities, though timing market bottoms involves substantial uncertainty. Regardless of market conditions, disciplined position sizing, diversification across uncorrelated assets, and alignment with predetermined risk tolerance frameworks remain fundamental principles. Investors should avoid emotional decision-making driven by short-term price movements, instead focusing on fundamental analysis, technological development trajectories, and long-term value propositions aligned with portfolio objectives.

Top Layer 2 projects worth following in 2025: From Arbitrum to zkSync

Pepe Unchained: Pepe Meme Coin evolves into a Layer-2 ecosystem

2025 Layer-2 Solution: Ethereum Scalability and Web3 Performance Optimization Guide

What is Layer 2 in crypto assets? Understand the scaling solution for Ethereum

How Layer 2 Changes the Crypto Assets Experience: Speed, Cost, and Mass Adoption

Pepe Unchained (PEPU): Building the New Era of Meme Coins on Layer 2

How to Buy Bitcoin Anonymously

Top 10 Play-to-Earn NFT Games

2026 NBLU Price Prediction: Expert Analysis and Market Forecast for NewBlue Interactive Stock Performance

2026 KYO Price Prediction: Expert Analysis and Market Forecast for the Upcoming Bull Run

2026 MTRG Price Prediction: Expert Analysis and Market Forecast for Matrixport Token







