Why did Bitcoin drop today? Non-farm payrolls at 130,000 lower interest rate cut expectations, US Treasury yields surge to 4.2%

The U.S. January employment report shows 130,000 new jobs, nearly double market expectations, with the unemployment rate dropping to 4.3%, indicating ongoing resilience in the labor market. Strong data pushed the 10-year U.S. Treasury yield up to 4.2%, reducing the likelihood of recent Fed rate cuts. The tightening financial environment puts pressure on risk assets. Analysts point out that Bitcoin is highly sensitive to liquidity; rising government bond yields lead funds to shift toward safer assets.
Non-Farm Payrolls Surpass Expectations: 130K Double Surprise
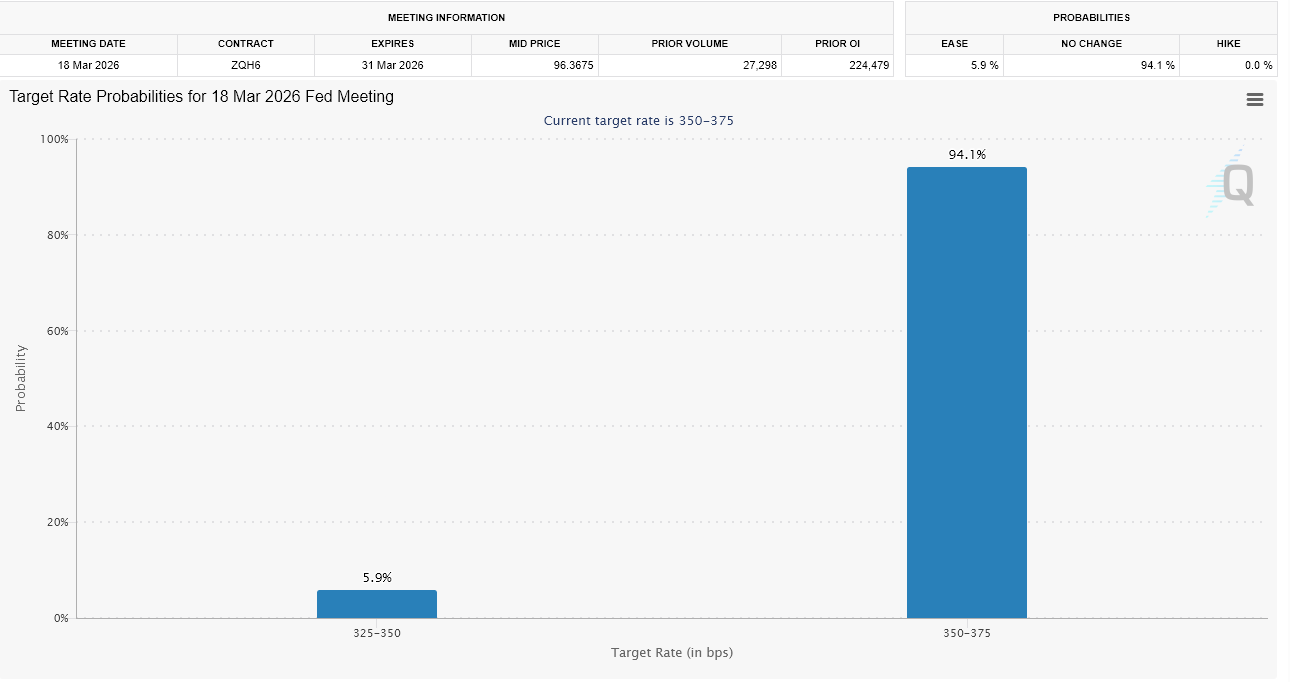
(Source: CME Fed Watch)
The latest U.S. January employment report shows a stronger-than-expected labor market, driving up U.S. Treasury yields and decreasing the likelihood of a Fed rate cut in the near term, creating new macroeconomic pressures for Bitcoin. The report shows 130,000 new jobs added in January, nearly twice the market forecast of 70,000. Meanwhile, the unemployment rate fell to 4.3%, below the expected 4.4%, indicating continued labor market strength.
This degree of surprise is extremely rare in economic data releases. Typically, market expectations and actual data differ by 10-20%, but this time, the gap of 130K vs. 70K reaches 85.7%. Such a large deviation can cause significant market shocks, as all asset prices have already priced in the 70K expectation. When actual data far exceeds expectations, rapid re-pricing occurs, leading to volatile price swings.
While strong employment figures are positive for the overall economy, they complicate the outlook for risk assets like Bitcoin. Due to concerns about economic slowdown, markets previously anticipated rate cuts in the coming months. However, the resilience of the labor market reduces the urgency for monetary easing. Consequently, investors are reassessing expectations for Federal Reserve policy.
CME FedWatch indicates that the probability of a 25 basis point rate cut at the March FOMC meeting has plummeted from 15% before the data release to 5% afterward. This sharp revision directly impacts all rate-sensitive assets, including Bitcoin, tech stocks, and real estate. When “cheap money” is no longer expected in the foreseeable future, investors naturally reduce allocations to high-risk assets.
From an economic logic perspective, the strong employment data signals that the U.S. economy is not in recession; consumers still have stable income, and companies are still hiring. In this context, the Fed has no reason to cut rates to “rescue the market.” The Fed’s dual mandate is full employment and price stability. When the labor market is healthy, the only concern is inflation. As long as inflation remains around 3%, the Fed will maintain a tightening stance.
Triple Impact of Non-Farm Payrolls on Bitcoin
Rate Cut Expectations Collapse: Probability of March rate cut drops from 15% to 5%, liquidity expectations worsen
U.S. Treasury Yields Surge: Risk-free returns rise, reducing attractiveness of high-risk assets
Dollar Strengthening Anticipated: Strong employment supports the dollar, global liquidity tightens
This macro environment deterioration explains why Bitcoin has fallen today. When markets realize that monetary policy will not shift to easing in the short term, risk appetite quickly declines. As the most extreme risk asset, Bitcoin bears the brunt of this shift.
U.S. Treasury Yield Soars to 4.2%: Capital Flows Out of Risk Assets
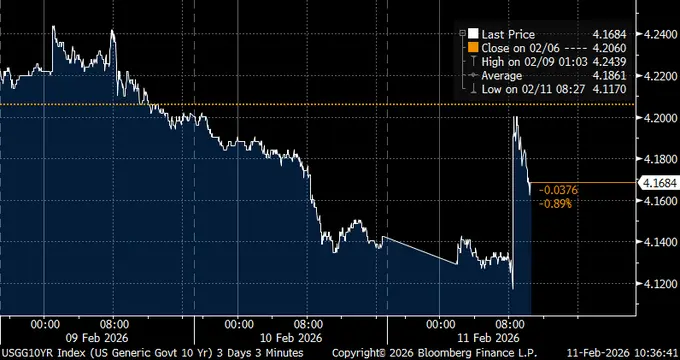
(Source: Bloomberg)
The bond market responded immediately. After the report, the 10-year U.S. Treasury yield surged to around 4.2%, rising several basis points. The 2-year Treasury yield also climbed, reflecting reduced expectations for rate cuts. Rising yields tighten financial conditions, increasing borrowing costs across the economy and raising discount rates used to evaluate risk assets.
How does this mechanism explain Bitcoin’s decline today? When the 10-year yield hits 4.2%, investors can earn 4.2% annualized by purchasing virtually risk-free U.S. government bonds. In comparison, Bitcoin offers no fixed income and carries high price volatility risks. In this environment, institutional investors reassess asset allocations, reducing holdings in zero-yield high-risk assets like Bitcoin and increasing allocations to fixed-income products such as government bonds.
Bitcoin is highly sensitive to liquidity conditions. When bond yields rise, funds tend to flow into safer, higher-yielding assets like government bonds. Simultaneously, a stronger dollar often accompanies rising yields. A stronger dollar reduces global liquidity, diminishing the appeal of speculative assets. This combination negatively impacts the crypto market.
Although Bitcoin briefly stabilized near $70,000 earlier this week, employment data has increased the risk of renewed volatility. With no clear dovish signals from the Fed, liquidity remains tight. Analyst Hernandez told BeInCrypto: “For Bitcoin, this report is a short-term negative factor. Such a large surprise significantly reduces the chance of a rate cut in March and reinforces the Fed’s strategy to keep rates in the 3.50%-3.75% range. The catalyst for a sustained recovery in risk assets is further delayed. Expect the dollar to strengthen and yields to reprice higher.”
From a capital flow perspective, the 4.2% risk-free rate creates a strong opportunity cost. Holding Bitcoin means sacrificing a guaranteed 4.2% return; investors will only hold if they expect Bitcoin to rise far above that. But in the current environment, Bitcoin’s short-term upside is suppressed by the non-farm payrolls data and the collapse of rate cut expectations. More investors now see the risk-adjusted return of holding government bonds as more attractive.
$65,000 Critical Support and $71,000 Breakout Level
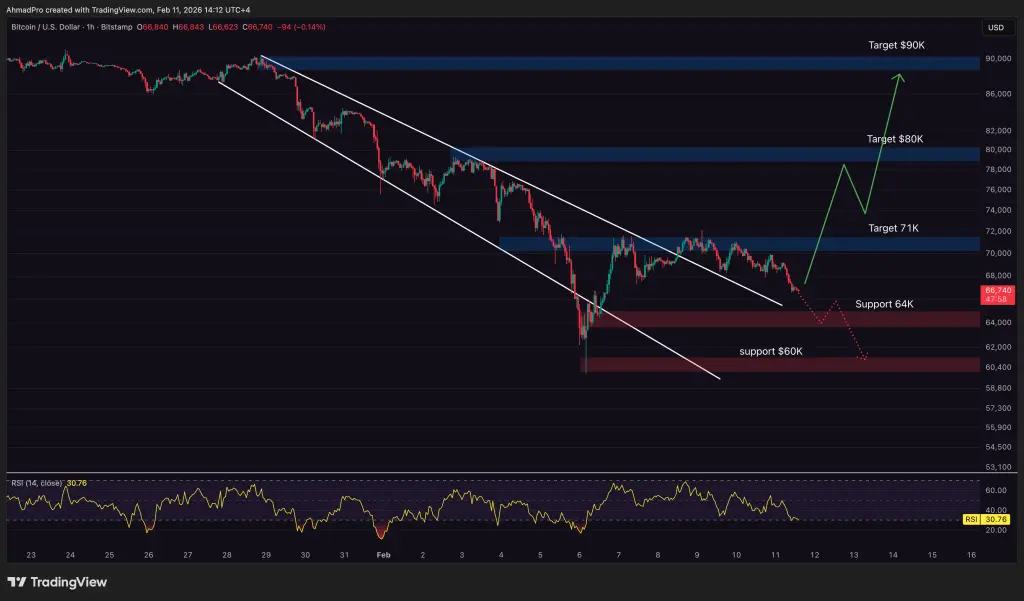
(Source: TradingView)
Market structure intensifies macro pressures. Recent sharp declines show Bitcoin’s extreme sensitivity to macroeconomic changes. When financial conditions tighten, large ETF inflows, institutional hedging, and leverage accelerate market volatility. A strong labor market does not necessarily mean Bitcoin will fall, but it weakens a key bullish catalyst: expectations of loose monetary policy.
Hernandez states: “In the short term, Bitcoin is defensive. The key level is $65,000. However, if this strong report is only temporary and not a sign of renewed economic heating, the Fed may still cut rates later this year. When that happens, Bitcoin’s limited supply will become crucial again. Today’s strong data may delay a rebound but won’t change the long-term trend.”
Bitcoin trades around $66,000, with RSI indicating oversold conditions. Technically, $64,000 is the first critical support; if broken, focus shifts immediately to $60,000. The $60,000 level is the previous low of this correction and an important psychological threshold. Falling below could trigger technical panic, leading to stop-losses and liquidations.
On the upside, $71,000 is the strongest resistance. If Bitcoin can break and hold above this level, the short-term trend could turn bullish quickly, with $80,000 as a target, and $90,000 no longer distant. However, in the current macro environment, breaking $71,000 requires strong catalysts, such as unexpected rate cuts, large ETF inflows, or easing geopolitical risks.
Until then, technically, the trend remains downward, but selling pressure appears to be waning. Oversold RSI suggests a potential short-term rebound, but whether it sustains depends on macroeconomic improvements.
The latest U.S. employment report further confirms the environment of “higher rates lasting longer.” For Bitcoin, this isn’t an immediate disaster but does increase the difficulty of sustained upward movement. Unless liquidity improves or yields decline, the current macro environment remains cautious rather than supportive.
Related Articles
Stablecoin license countdown begins: Hong Kong may issue the first licenses in March, with stablecoin concept stocks collectively gaining strength
ON (Orochi Network) increased by 20.08% in the last 24 hours
Overview of popular cryptocurrencies on February 12, 2026, with the top three being: Bitcoin, Ethereum, and BNB
BLESS (Bless) increased by 39.74% in the past 24 hours